Question
The diagram shows a fly.
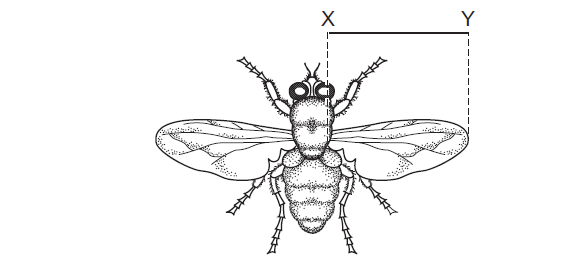
The line XY represents the length of the wing.
The length of line XY is 26 mm.
The actual size of the wing between XY is 4 mm.
What is the magnification of the image?
A ×0.15 B ×6.5 C ×22 D ×104
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
To determine the magnification of the image, we can use the formula:
Magnification = Image Size / Object Size
In this case, the image size is represented by the length of line XY, which is 26 mm, and the object size is the actual size of the wing, which is 4 mm.
Magnification = 26 mm / 4 mm = 6.5
Therefore, the magnification of the image is 6.5, or in other words, the image is magnified by a factor of 6.5.
Question
The diagram shows a drawing of part of a tulip flower. The actual width of the stigma, shown by the line PQ, is 5 mm. The length of line PQ is 15 mm.

What is the magnification of the diagram?
A x0.3 B x3 C x30 D x300
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Ans :B
To determine the magnification of the diagram, we can use the formula:
Magnification = Actual size / Apparent size
In this case, the actual size of the stigma (line PQ) is given as 5 mm, and the apparent size on the diagram is 15 mm. Plugging these values into the formula, we have:
Magnification = 5 mm / 15 mm
Simplifying the fraction, we get:
Magnification = 1/3
Therefore, the magnification of the diagram is 1/3 or x3.
Question
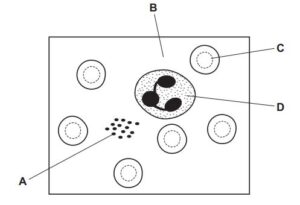
The diagram shows human blood as seen through a light microscope.
A person’s blood is unable to clot.
Which component of the blood is not functioning properly?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
If a person’s blood is unable to clot, it indicates a malfunction in the clotting mechanism of the blood. The component responsible for clotting is known as platelets or thrombocytes. Platelets are small, colorless cell fragments found in the blood, and they play a crucial role in the clotting process. They form clumps and adhere to damaged blood vessel walls, forming a plug to stop bleeding. Additionally, they release certain substances that initiate a cascade of reactions leading to the formation of fibrin, a protein that helps in the formation of a blood clot. If the platelets are not functioning properly, blood clotting can be impaired, resulting in a condition known as bleeding disorder or coagulopathy.
Question
The diagram shows some cells.
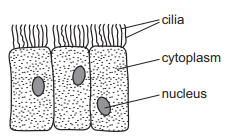
Where are these cells found?
A alimentary canal
B blood
C bronchus
D plant roots
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Cilia, cytoplasm, and nucleus can be found on the bronchus. The bronchus is a part of the respiratory system and is responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs. It is lined with a specialized epithelial tissue that has certain cellular components.
Cilia are hair-like structures that protrude from the surface of the bronchial epithelial cells. These cilia beat in a coordinated manner and help in moving mucus and trapped particles, such as dust or pathogens, out of the airways. The cilia play a crucial role in the respiratory system’s defense mechanism by helping to remove foreign substances and maintaining the health of the lungs.
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the interior of the bronchial epithelial cells. It contains various organelles, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum, which are responsible for the cell’s metabolic functions. The cytoplasm also houses other cellular components involved in protein synthesis, energy production, and other cellular processes.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and is present within the bronchial epithelial cells. It contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA, which carries the instructions for cell growth, development, and function. The nucleus regulates the activities of the cell by controlling gene expression and protein synthesis.
Together, these cellular components (cilia, cytoplasm, and nucleus) contribute to the normal functioning of the bronchus and the respiratory system as a whole.
Question
An egg measured 6.5 cm in diameter. A student made a drawing of this egg and the diameter was
measured as 19.5 cm.
What was the magnification of the drawing?
A ×0.3 B ×3.0 C ×6.5 D ×300
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The magnification of the drawing can be calculated by dividing the measured diameter of the drawing by the actual diameter of the egg.
Measured diameter of the drawing = 19.5 cm
Actual diameter of the egg = 6.5 cm
Magnification = Measured diameter / Actual diameter
Magnification = 19.5 cm / 6.5 cm
Magnification = 3.0
Therefore, the magnification of the drawing is 3.0. So, the correct answer is B.
Question
The diagram shows an insect as seen using the low power lens of a microscope.
The actual diameter of the circle is 0.3 cm.
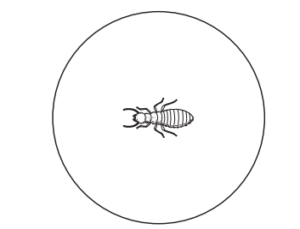
What is the approximate size of this insect in millimetres?
A 0.1 mm B 1.0 mm C 2.0 mm D 3.0 mm
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The approximate size of the insect in millimeters can be determined by comparing the diameter of the circle in the diagram to the actual diameter provided.
Given that the actual diameter of the circle is 0.3 cm, we can conclude that the diameter of the insect is also approximately 0.3 cm when viewed through the low power lens of the microscope.
Since 1 cm is equal to 10 mm, the size of the insect in millimeters is also 0.3 cm × 10 mm/cm = 3 mm.
Therefore, the approximate size of the insect in millimeters is 3.0 mm.
The correct answer is B.
Question
The diagram shows the human alimentary canal, with a string marked in meters beside it.
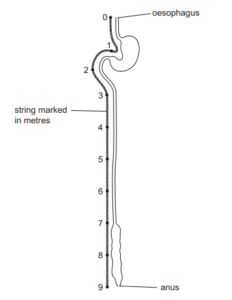
How long is the small intestine?
A 2 m B 6 m C 8 m D 9 m
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The correct length of the small intestine is option B, 6 meters. The small intestine is a long, coiled tube that connects the stomach to the large intestine. It consists of three sections: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. These sections work together to facilitate the digestion and absorption of nutrients from food. The length of the small intestine allows for a large surface area, which is essential for efficient nutrient absorption.
Question
The photograph shows a chloroplast magnified ×7000.

What is the actual size of the chloroplast?
A 0.0001 mm B 0.001 mm C 0.01 mm D 100 mm
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Given that the chloroplast is magnified ×7000 and the width in the photograph is 70 mm, we can calculate the actual width of the chloroplast by dividing the width in the photograph by the magnification:
Actual width = Width in the photograph / Magnification
Actual width = 70 mm / 7000
Actual width = 0.01 mm
Therefore, the actual size of the chloroplast is 0.01 mm.
So, the correct answer is option C) 0.01 mm.
Question
The diagram shows two shoots at the start of an experiment on transpiration.
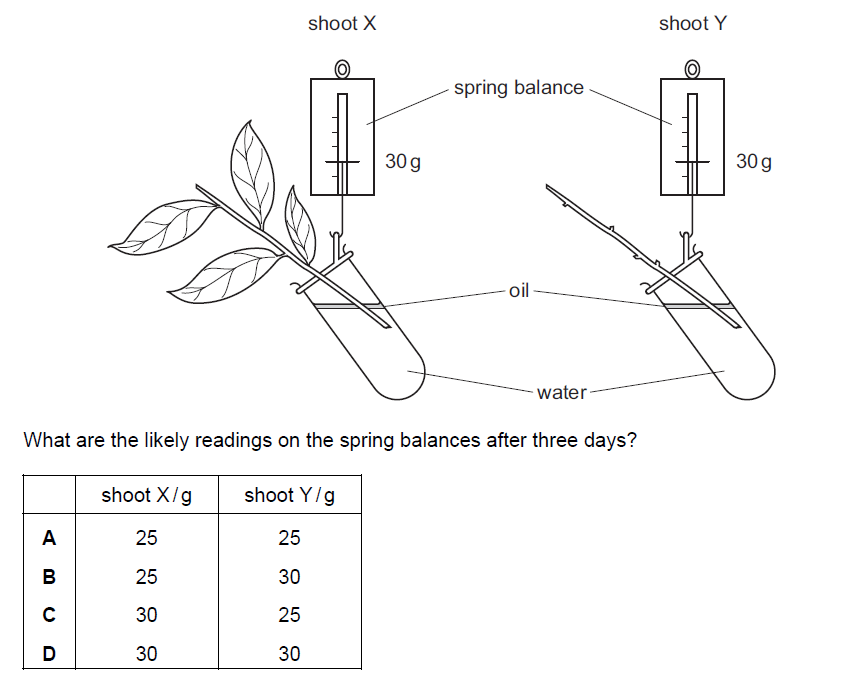
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The observed differences in weight between shoot X and shoot Y can be attributed to the process of transpiration. Transpiration is the loss of water vapor from plant tissues, primarily through the stomata present in the leaves. The readings suggest that shoot X, with leaves, experienced a decrease in weight over the course of three days, while shoot Y, without leaves, maintained a constant weight.
The weight measurements indicate that shoot X lost water during the three-day period, resulting in a decrease in weight from 30g to 25g. Meanwhile, shoot Y, which did not have leaves and thus did not undergo transpiration, remained at a constant weight of 30g. These observations highlight the significance of leaves in the process of transpiration and its impact on the water balance and weight of plant shoots.
Question
The diagram shows a drawing of part of a tulip flower. The actual width of the stigma, shown by the line PQ, is 5 mm. The length of line PQ is 15 mm.

What is the magnification of the diagram?
A x0.3 B x3 C x30 D x300
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
To determine the magnification of the diagram, we can use the formula:
Magnification = Actual size / Apparent size
In this case, the actual size of the stigma (line PQ) is given as 5 mm, and the apparent size on the diagram is 15 mm. Plugging these values into the formula, we have:
Magnification = 5 mm / 15 mm
Simplifying the fraction, we get:
Magnification = 1/3
Therefore, the magnification of the diagram is 1/3 or x3.
Question
The diagram shows a cell. The diameter of the cell in the diagram is 18 mm.
The actual diameter of the cell is 0.05 mm.
What is the magnification of the diagram?
A ×0.003 B ×0.9 C ×360 D ×36 000
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
To determine the magnification of the diagram, we can use the formula:
Magnification = Image size / Actual size
In this case, the image size is given as 18 mm, and the actual size of the cell is 0.05 mm. Plugging these values into the formula:
Magnification = 18 mm / 0.05 mm = 360
Therefore, the magnification of the diagram is 360. The correct answer is option C.
Question
A photograph shows a plant cell nucleus measuring 2 mm across.
If the magnification of the cell is 500, what is the actual size of the nucleus?
A 0.00002 mm
B 0.004 mm
C 0.04 mm
D 250 mm
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
To determine the actual size of the nucleus, we need to divide the measured size by the magnification factor.
Measured size of the nucleus = 2 mm
Magnification = 500x
Actual size = Measured size / Magnification
Actual size = 2 mm / 500
Actual size = 0.004 mm
Therefore, the actual size of the nucleus is 0.004 mm.
The correct answer is B) 0.004 mm.
