Question
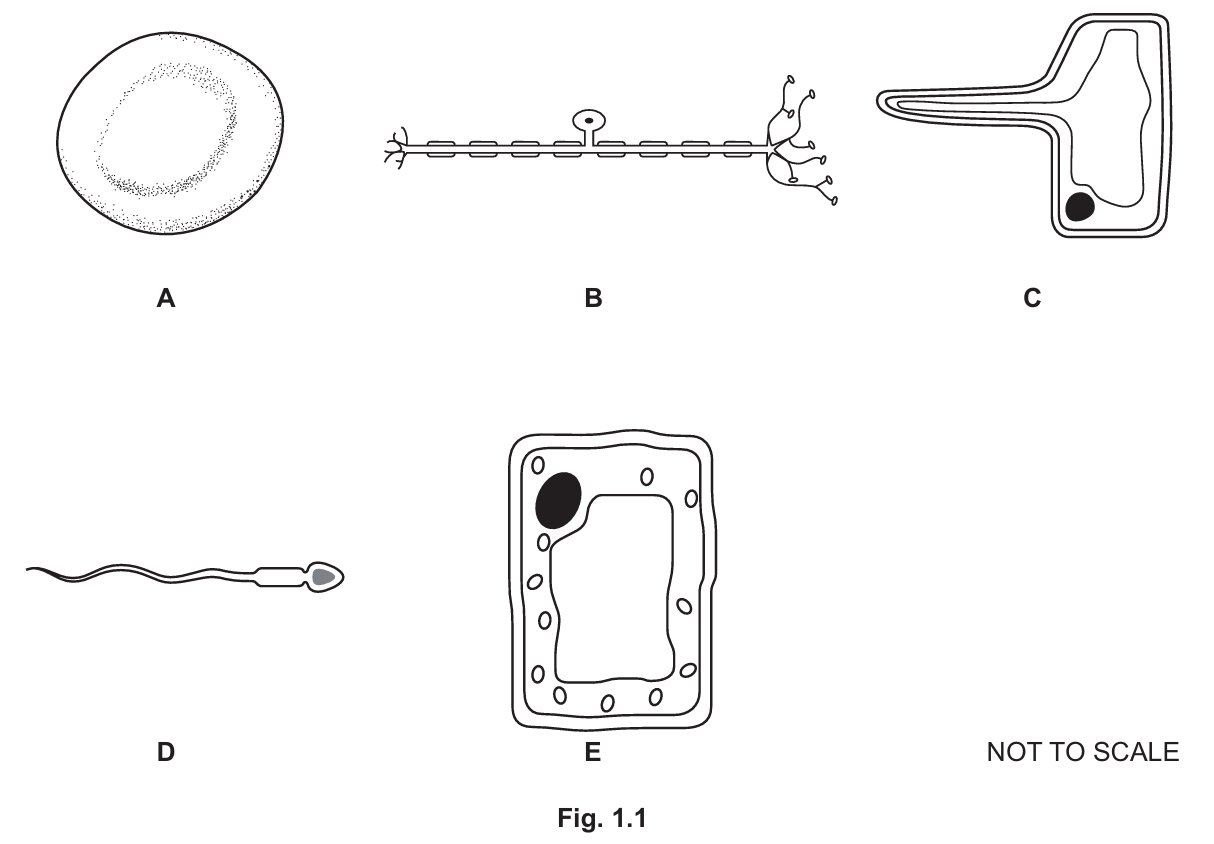
- contain an acrosome ……………………..
- contain haemoglobin ……………………..
- are found in plants ………………… and ………………
- are found in the peripheral nervous system ……………
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
• D (contain an acrosome)
• A (contain haemoglobin)
• C and E (are found in plants)
• B (are found in the peripheral nervous system)
Explanation:
Cell D is a sperm cell; the acrosome is a vesicle containing enzymes. Cell A is a red blood cell containing haemoglobin. Cell C (root hair cell) and Cell E (palisade mesophyll cell) are plant cells; both have cell walls (E also has chloroplasts). Cell B is a neurone (nerve cell).
(b)(i)
Controls the activities of the cell / Contains genetic material (DNA/chromosomes)
(b)(ii)
Any two from:
• Cell membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Ribosomes
Note: Cell A (Red Blood Cell) lacks a nucleus and mitochondria, and animal cells (A, B, D) lack cell walls. Therefore, only the cell membrane and cytoplasm are universally present in these mature cells (ribosomes are present in developing RBCs but lost in mature ones, though often accepted in broad mark schemes; cell membrane and cytoplasm are the safest answers).
(c)
• Has a long extension / projection / hair-like structure
• Increases the surface area
• For the absorption of water and mineral ions
(d)
• Magnification
• Image size (or length of the cell in the image)
Formula: \( \text{Actual size} = \frac{\text{Image size}}{\text{Magnification}} \)
