Question
Dairy cattle are kept for milk production. Approximately half of all the calves born are male.
(a) Sex is determined in cattle in exactly the same way as it is in humans.
Explain why 50% of all cattle are born male.
You may draw a genetic diagram to help your explanation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[4]
(b) Dairy farmers only need a very small number of male calves. They limit the number by
using sex selection. Sperm cells are identified and sorted before they are used in artificial
insemination (AI).
Explain how artificial insemination is carried out.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(c) Table 2.1 shows the composition of 100 g of cow’s milk compared with the same quantities of
commercial formula milk and human milk.
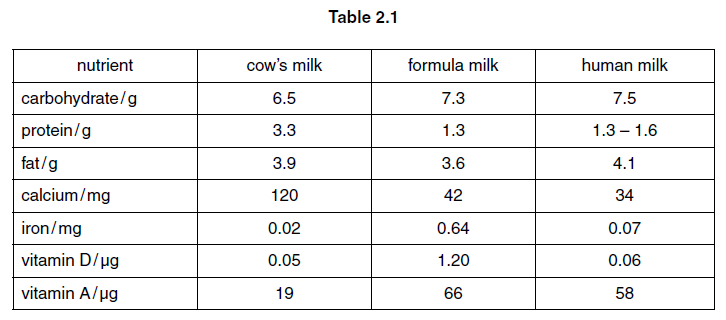
Some women do not breast-feed their babies but bottle-feed them using formula milk. Health
authorities advise against the use of cow’s milk until babies are about 9 months old.
Use the information in Table 2.1 to explain the advantages of using formula milk rather than
cow’s milk.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[4]
One of the components of human milk is the enzyme lysozyme that is present in many body fluids
and is responsible for breaking down the cell walls of bacteria.
(d) Define the term enzyme.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
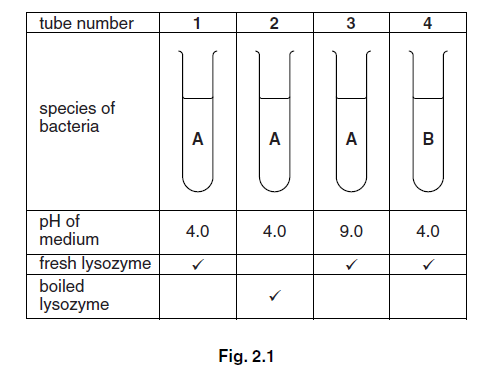
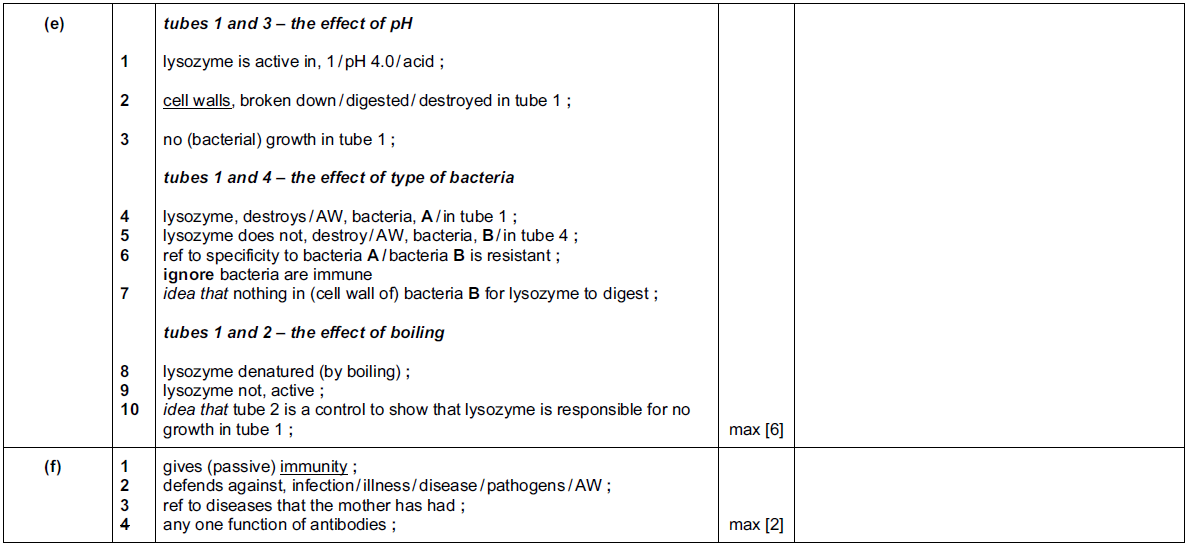
(e) The effect of human lysozyme on two common species of bacteria, A and B, was investigated
at two different values of pH.
The investigation was set up as shown in Fig. 2.1.
The test-tubes were kept at 37 °C for 24 hours.
After 24 hours, samples were taken from each test-tube. Each sample was placed onto
nutrient agar in Petri dishes. The dishes were incubated at 28 °C for a further 24 hours to
allow any bacteria to grow.
The results are shown in Fig. 2.2.
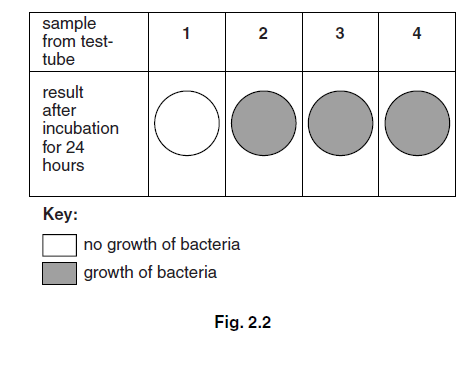
Explain the results shown in Fig. 2.2 by comparing the following pairs:
1 and 3 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
1 and 4 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
1 and 2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
(f) Human milk also contains antibodies. Explain the benefits of antibodies to a newborn child.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:

Question
(a) (i) Table 9.1 contains examples of components of a balanced diet and foods that contain a
high proportion of the component.
Complete Table 9.1 by filling in the blank spaces
(ii) Name two other components of a balanced diet that are not listed in Table 9.1.
(b) Fig. 9.1 shows a picture of food production on a modern farm.

The use of modern technology has increased the amount of food produced.
State two examples of modern technology and explain how each has contributed to the
amount of plants grown for food.
(c) On modern farms crop plants can be grown as large-scale monocultures.
Suggest two negative impacts on an ecosystem for this method of food production.
1
2
Answer/Explanation
Ans
9 (a) (i) 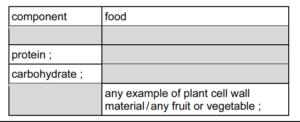
(ii) minerals / ions / named mineral ;
vitamins / named vitamin ;
water ;
(b) 1 use of agricultural machinery / tractors / trucks ;
improved efficiency / greater land area cultivated/plant
more seeds / harvest more of the crop/ harvest faster/
spray pesticides / irrigate the crop ;
2 use of (artificial) fertilisers ;
improved yields /grow faster ;
3 use of herbicides / pesticides / insecticides; no competition from
weeds / pests or increases yields ;
4 selective breeding; improve quality / quantity of produce ;
5 use of glass houses /poly-tunnels ;
protect crops from adverse environment/ provide
optimum growing environment/ grow out of season/
increased yields ;
6 any valid example ;
with improvement ;
(c) 1 death of organisms ;
2 disrupts food chains /webs / eutrophication ;
3 habitat destruction/ soil erosion ;
4 changes in precipitation ;
