Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Advantages of intensive livestock production:
Intensive farming is highly efficient because it requires less land compared to extensive farming, which can help reduce deforestation as fewer trees need to be cut down for pasture. This method provides a higher yield and more consistent quality of products (like meat or milk), leading to increased food security and higher profits for the farmer.
(b) Need for antibiotics:
Because animals are kept in close proximity or overcrowded conditions, diseases can spread very rapidly. Antibiotics are used to treat or prevent the spread of these bacterial infections to maintain a healthy herd.
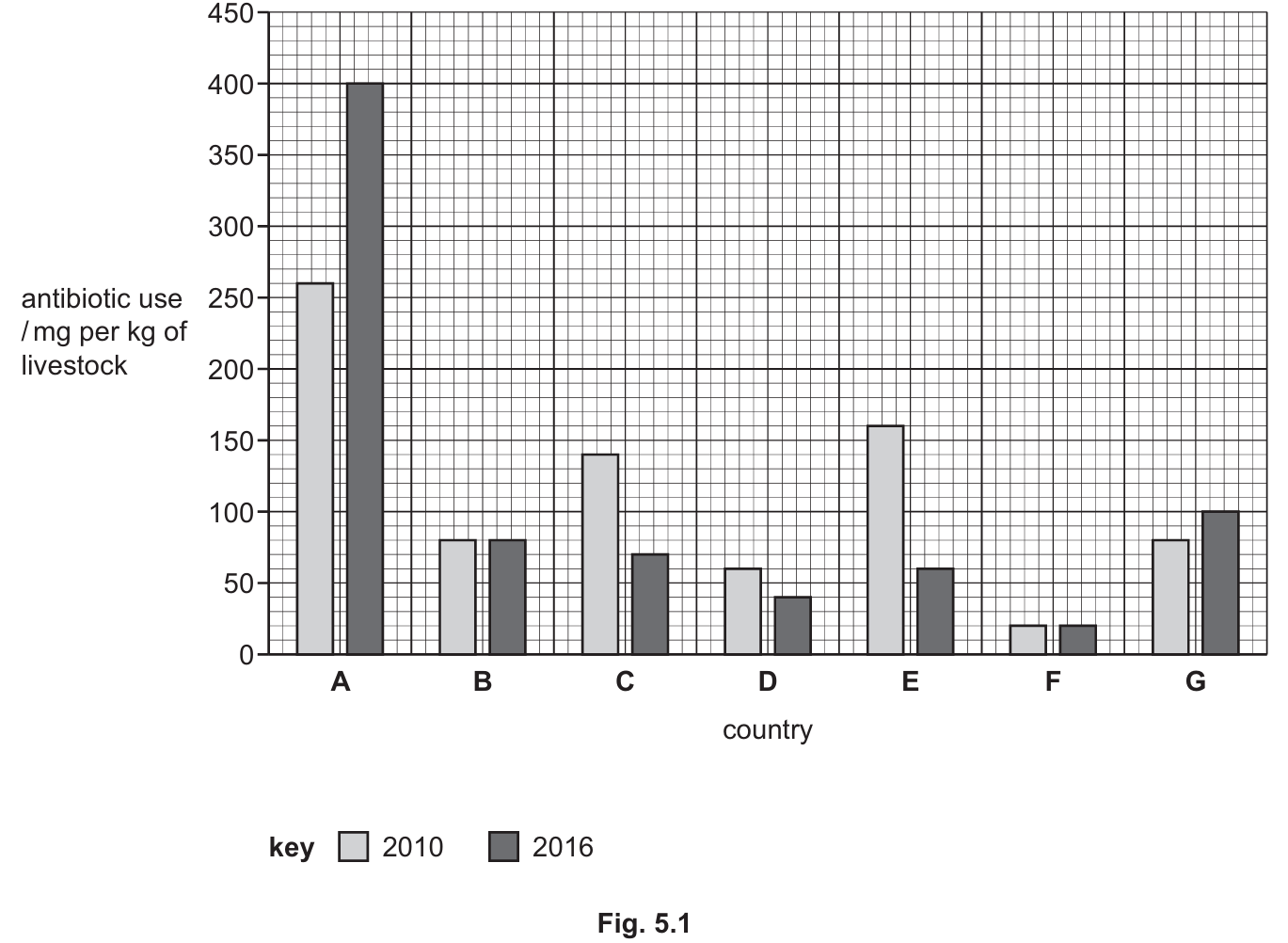
(c)(i) Countries below the limit ($50\text{ mg/kg}$):
Looking at the dark grey bars (2016) in Fig. 5.1, the countries below the $50$ line are D and F.
(c)(ii) Percentage Increase Calculation:
• Value in 2010 (Country A): $260\text{ mg/kg}$
• Value in 2016 (Country A): $400\text{ mg/kg}$
• Increase: $400 – 260 = 140$
• Percentage Increase: $\frac{140}{260} \times 100 \approx 53.846\%$
• To two significant figures, the answer is $54\%$.
(c)(iii) Development of antibiotic resistance:
This is a process of natural selection. It begins when a random mutation occurs in the DNA of a bacterium, giving it resistance to an antibiotic. When the antibiotic is applied, it kills the non-resistant bacteria, while the resistant bacteria survive. These survivors then reproduce and pass on the alleles for resistance to their offspring. Over time, the frequency of the resistant allele increases in the population, making the antibiotic ineffective.
