Question
What would be the effect of cutting down forests, on the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere?
A Carbon dioxide concentration would fall because of less photosynthesis.
B Carbon dioxide concentration would fall because of more photosynthesis.
C Carbon dioxide concentration would rise because of less photosynthesis.
D Carbon dioxide concentration would rise because of more photosynthesis.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: C – Carbon dioxide concentration would rise because of less photosynthesis.
Forests play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide through the process of photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and use it, along with sunlight and water, to produce energy-rich molecules while releasing oxygen as a byproduct. Cutting down forests reduces the number of trees and plants that can perform photosynthesis, leading to a decrease in the overall capacity of the ecosystem to absorb carbon dioxide. As a result, if forests are cut down, there would be less photosynthesis occurring, and carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere would tend to rise due to the reduced carbon sequestration capacity of the ecosystem.
Question
What are the possible effects of deforestation?
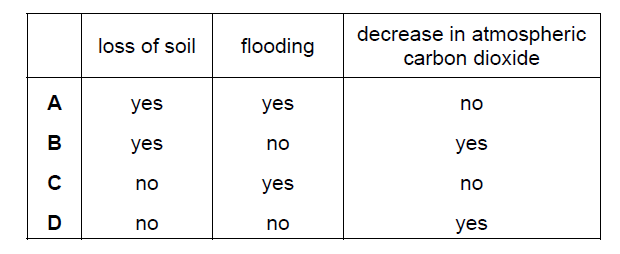
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Deforestation can indeed have various negative effects on the environment, including loss of soil and an increased risk of flooding.
Loss of Soil: Tree roots help hold the soil together, preventing erosion. When trees are removed through deforestation, the soil becomes more vulnerable to erosion by wind and water. Without the protective cover of vegetation, rainwater can wash away the topsoil, which is rich in nutrients and essential for plant growth. This loss of soil fertility can negatively impact agricultural productivity and overall ecosystem health.
Flooding: Trees play a crucial role in regulating the water cycle. They absorb water from the soil and release it into the atmosphere through a process called transpiration. This helps regulate the flow of water in watersheds and reduces the risk of flooding during heavy rains. When trees are removed, the soil’s ability to absorb and hold water is diminished, leading to increased surface runoff and potentially causing floods downstream.
Deforestation can actually contribute to an increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, rather than a decrease. Trees are natural carbon sinks, meaning they absorb CO2 from the atmosphere through photosynthesis and store it as biomass. When trees are cut down and burned or left to decay, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO2, contributing to the greenhouse effect and climate change.
Question
Large areas of tropical forests have been cleared to grow monocultures of palm oil plants.
Which effect will this have on the ecosystem?
A The use of fossil fuels in the area will decrease.
B The use of pesticides in the area will decrease.
C The variety of species in the area will decrease.
D The variety of species in the area will increase.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The monoculture of palm oil plants replacing tropical forests is likely to result in a decrease in the variety of species in the area. Monocultures are characterized by a single type of plant being grown over a large area, which reduces the diversity of plant and animal species that can thrive in the ecosystem. The complex and diverse habitat of the tropical forest, which supports a wide range of species, will be lost as a result of this conversion. This can lead to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and disruption of ecological relationships within the ecosystem.
Question
What describes eutrophication and its effect on a river?
A Nutrients are depleted in the river, causing bacteria to die. This allows plants to grow and
deoxygenate the water.
B Nutrients are depleted in the river, causing plants to die. These decompose, so the water is
deoxygenated.
C Nutrients enter the river, causing algae to grow. These die and decompose, so the water is
deoxygenated.
D Nutrients enter the river, causing plants to grow. These provide extra food for animals, which
deoxygenate the water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Eutrophication is a process in which a body of water, such as a river, becomes enriched with excess nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients can come from sources like agricultural runoff, sewage, and industrial waste. The enrichment of nutrients leads to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants in the water, known as an algal bloom.
As these algae and plants die, they undergo decomposition by bacteria. This decomposition process consumes oxygen from the water, leading to a decrease in dissolved oxygen levels. This reduction in dissolved oxygen can have harmful effects on the aquatic ecosystem, as many aquatic organisms depend on oxygen for survival. In severe cases, the depletion of oxygen can lead to “dead zones” where aquatic life struggles to survive or can’t survive at all.
So, option C is correct: “Nutrients enter the river, causing algae to grow. These die and decompose, so the water is deoxygenated.” This best describes the process of eutrophication and its effect on a river.
Question
Which pollutants of water can lead to eutrophication?
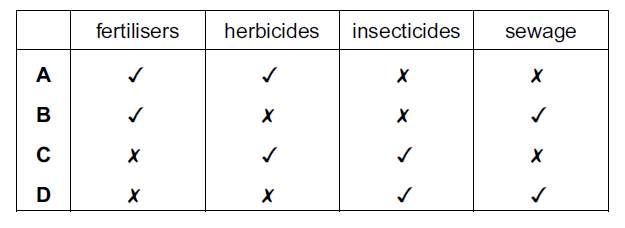
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is B.
Eutrophication is a process that occurs when water bodies, such as lakes, rivers, and oceans, become enriched with excessive nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients can come from various sources, but one of the major contributors is the use of fertilizers in agriculture. When rainwater washes off fields treated with fertilizers, it carries these nutrients into nearby water bodies, promoting the excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants. This overgrowth disrupts the balance of the ecosystem and can lead to harmful algal blooms, oxygen depletion, and ultimately harm to aquatic life.
While herbicides and insecticides can also contribute to water pollution, they are not directly linked to eutrophication in the same way that excessive nutrient enrichment from fertilizers is. Sewage, on the other hand, can contain nutrients and organic matter that contribute to eutrophication if not properly treated before being released into water bodies.
