Question
(b) Complete the sentences about pollution of the air by writing the appropriate words or phrases in the spaces provided.
Methane is a pollutant gas that contributes to the enhanced ………………… and climate change. Methane is released into the atmosphere from cattle and from the farming of ……………….. crops.
……………… is a gas that is absorbed by trees in the process of ………………. . This gas is released into the atmosphere by the …………………. of fossil fuels, where it also contributes to climate change.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
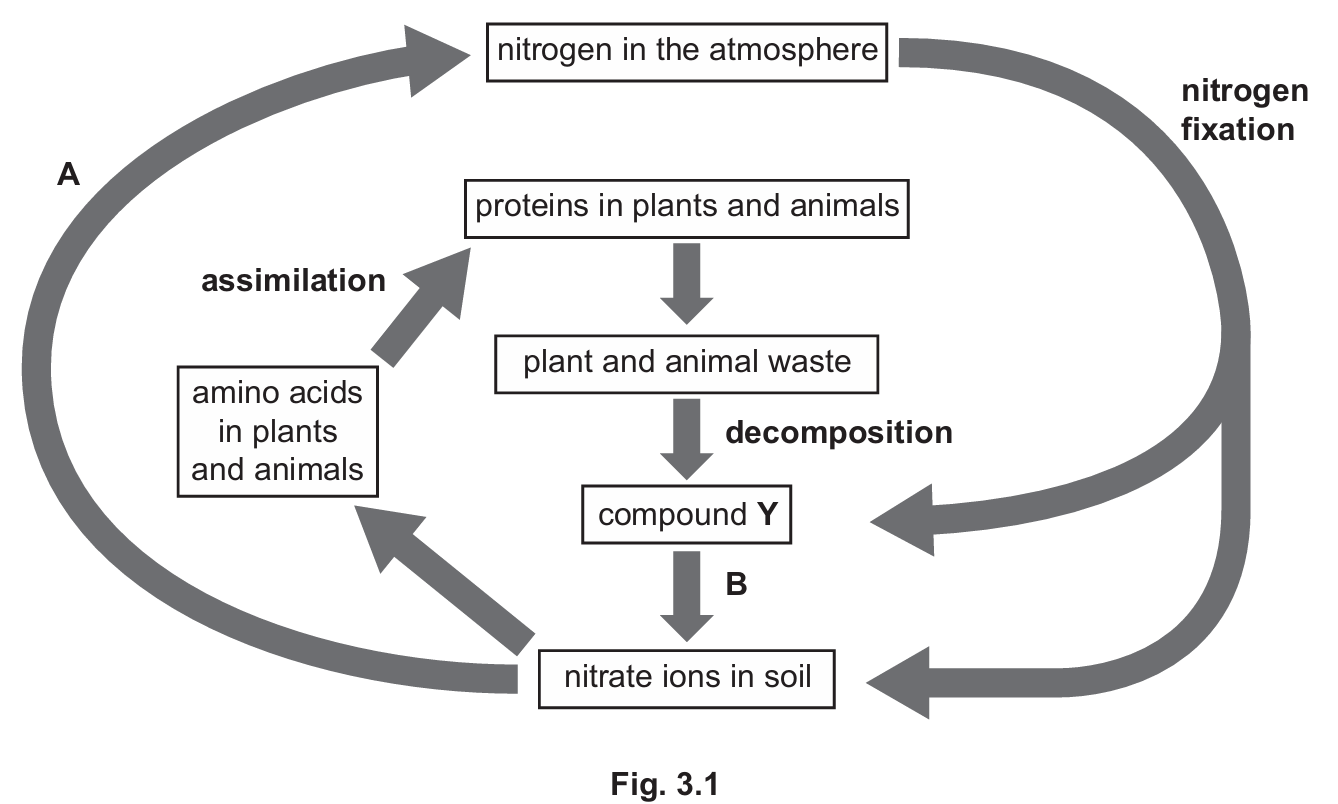
(a) (i)
A: Denitrification
B: Nitrification
(ii)
$1.$ Lightning
$2.$ Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium in root nodules)
(iii)
Ammonia / Ammonium ions
(iv)
Liver
(v)
Deamination is the removal of the nitrogen-containing part (the amino group) of amino acids. This process occurs when there is an excess of protein intake, as amino acids cannot be stored. The removed nitrogen is converted into urea to be excreted by the kidneys.
(b)
Methane is a pollutant gas that contributes to the enhanced greenhouse effect and climate change. Methane is released into the atmosphere from cattle and from the farming of rice crops.
Carbon dioxide is a gas that is absorbed by trees in the process of photosynthesis. This gas is released into the atmosphere by the burning / combustion of fossil fuels, where it also contributes to climate change.
(c)
Eutrophication occurs when untreated sewage or fertilizers (rich in nitrates/phosphates) leach into water bodies.
1. This leads to an increased availability of nutrients, causing an algal bloom.
2. The thick layer of algae blocks sunlight, preventing submerged plants from performing photosynthesis, leading to their death.
3. Decomposing bacteria feed on the dead organic matter and multiply rapidly.
4. These bacteria respire aerobically, using up the dissolved oxygen in the water.
5. This results in anoxic conditions where aquatic organisms like fish die due to suffocation.
Conceptual Explanation:
The nitrogen cycle is essential for converting inert atmospheric $N_2$ into forms usable by living organisms (like nitrates). Nitrification (Process B) turns ammonia into nitrates, which plants can absorb. Conversely, denitrification (Process A) converts nitrates back into atmospheric gas, usually in waterlogged soils. In animals, the liver is the metabolic hub where assimilation (incorporating nutrients into cells) and deamination (breaking down excess amino acids) occur to maintain chemical balance and remove toxic nitrogenous waste.
