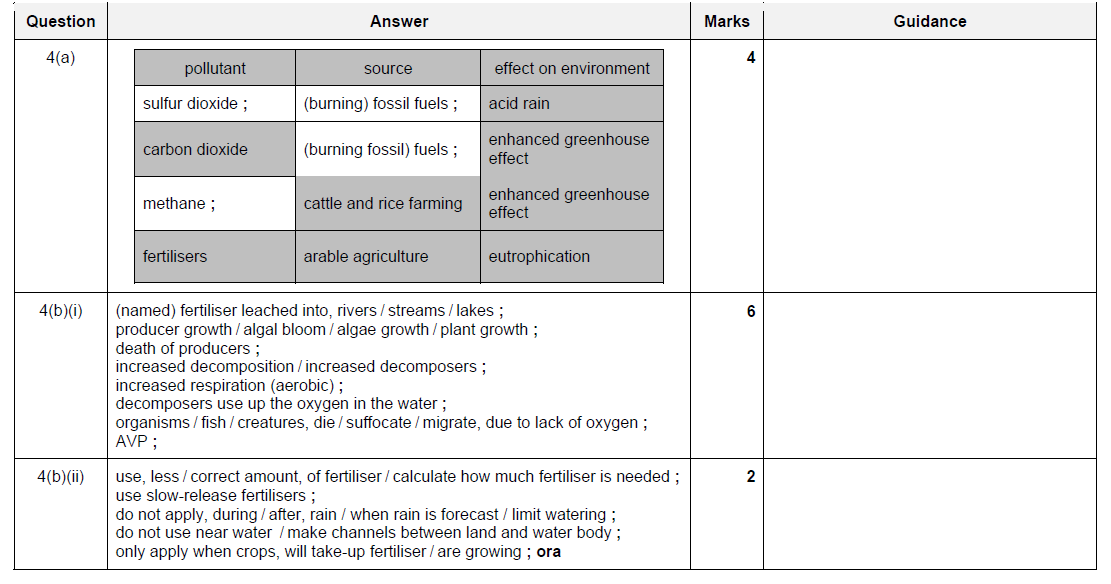
Question
Pollution is the harm done to the environment by the release of substances from human activities.
Table 4.1 shows the names of some pollutants, their sources and their effects on the environment.
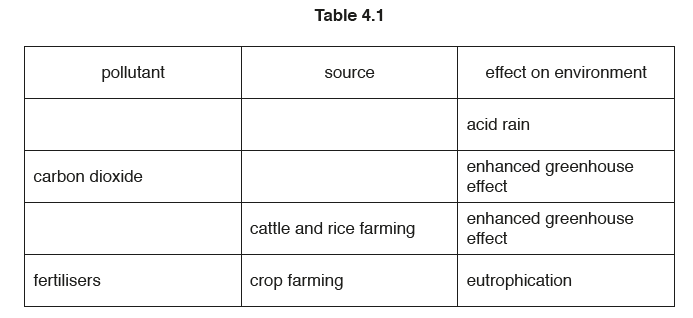
(a) Complete Table 4.1. [4]
(b) When fertiliser is applied to fields, it can lead to eutrophication in lakes and rivers.
(i) Describe and explain what happens in lakes when eutrophication occurs.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [6]
(ii) Suggest ways in which a farmer could reduce the chances of eutrophication occurring
when applying fertilizer to crops.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Large quantities of plastic waste are polluting the oceans.
(a) A survey published in March 2018 showed the increase in plastic waste in the Pacific Ocean.
One area of the Pacific Ocean is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch (GPGP).
Data were collected from areas inside and outside the GPGP between 1965 and 2015 to
estimate the quantity of plastic waste.
The results are shown in Fig. 2.1.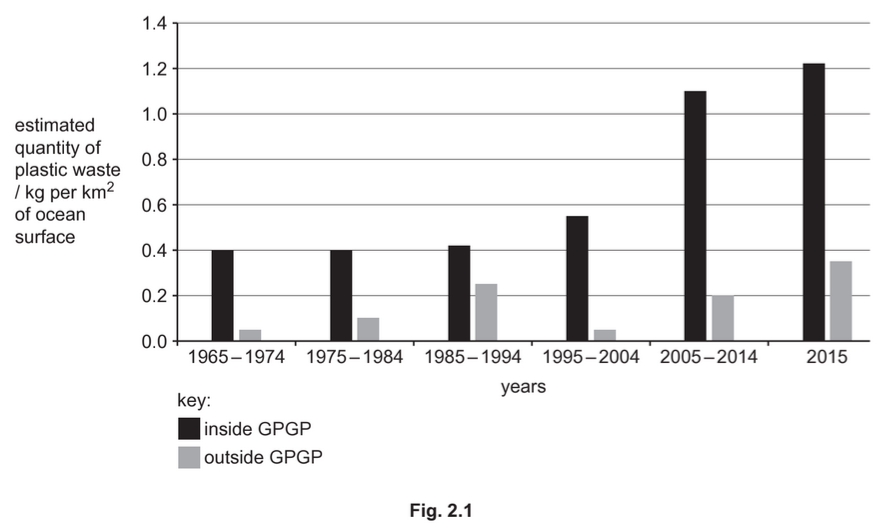
Describe the results of the survey shown in Fig. 2.1.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The green turtle, Chelonia mydas, is a species of marine animal that is harmed by plastic
waste.
Fig. 2.2 shows a green turtle swimming past a plastic bag in the Pacific Ocean.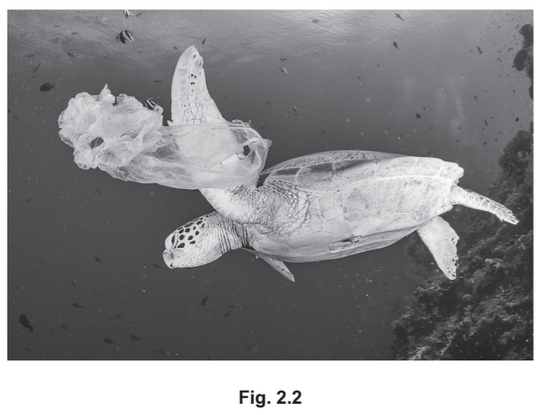
(i) Turtles are classified as reptiles.
State one feature shown by all reptiles that is not found in amphibians.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Outline the dangers of non-biodegradable plastic waste to marine animals, such as
green turtles.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Suggest ways to reduce the quantity of plastic waste.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
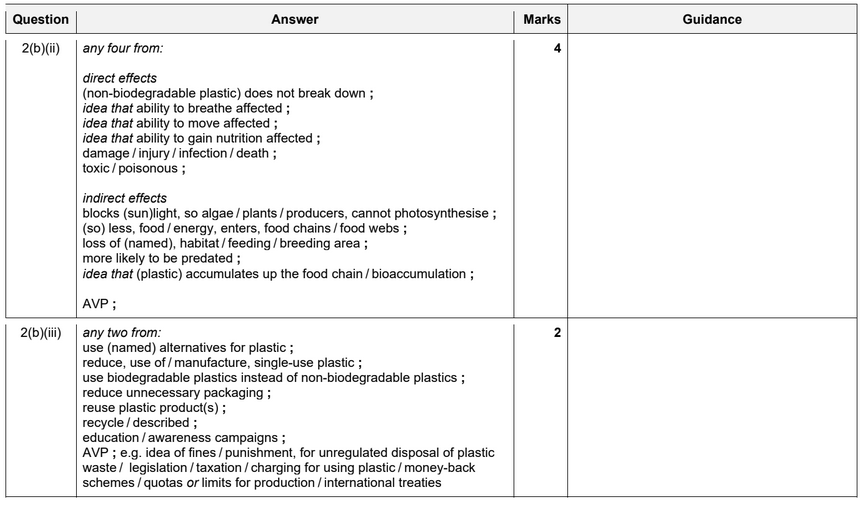
(a) Pollutants can affect the environment.
Draw one line from each pollutant listed to an effect it might have on the environment.
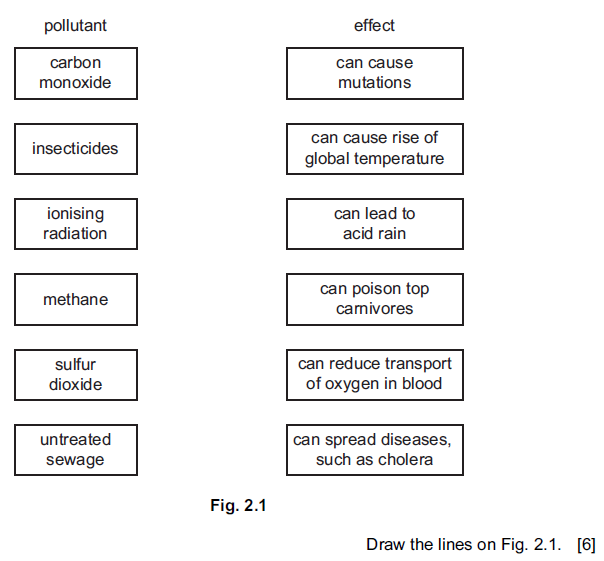
(b) Suggest one major source for each of the following pollutants.
(i) carbon monoxide

(ii) carbon dioxide

(iii) ionising radiation

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
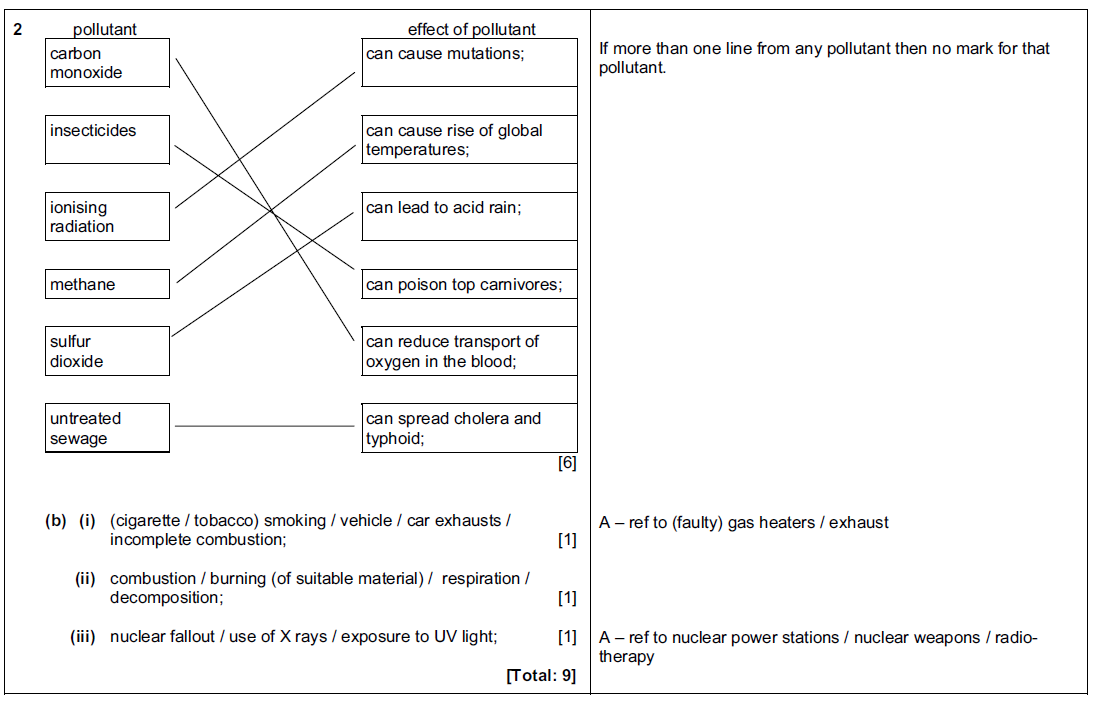
Question
(a) Describe how deforestation harms the environment.
(b) Humans are polluting the environment.
Complete Table 4.1 by naming two examples of pollutants in each part of the environment.
You should name different pollutants for each part of the environment.
Table 4.1
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) desertification/AW ; soil erosion/ landslides / land unstable/AW ;
(rapid run-off leads to) local flooding ;
rivers silt up ;
less transpiration ;
(dry air) so less rainfall ;
climate change/ changed weather patterns / disruption of water cycle ;
carbon dioxide added to atmosphere by burning trees / AW ;
less photosynthesis so less carbon dioxide removed from atmosphere / more carbon dioxide remains ;
more carbon dioxide leads to, global warming/ greenhouse effect/ sea levels rising ;
lack of food/ shortage of shelter/ homes / nesting sites / loss of habitat ;
organisms die/ extinction of species / loss of bio-diversity / food chains disrupted/nutrient cycles disrupted/reference to migration ;
(b) air: carbon dioxide/ carbon monoxide/ oxides of sulfur/ methane/ oxides of nitrogen/CFCs / oxides of lead/ozone/ smoke/dust/AVP ;
land: sewage / pesticides /herbicides / insecticides (or
examples)/ fertilisers / nuclear waste/ chemical waste/land-fill/ litter or
rubbish/ oil spillage/ heavy metals /AVP ;
water: fertilisers / pesticides / herbicides / insecticides / human
excrement/ nuclear waste/reproductive hormones / antibiotics / chemical waste
/ industrial waste/ litter or rubbish/ chlorine/ oil spillage/AVP ;
Question
(a) Fig. 5.1 shows a power station. Power stations release waste gases into the atmosphere when they burn fossil fuels.
Name two gases that cause pollution when released into the atmosphere. State one effect of each of these gases on the environment.
gas ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
effect ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
gas ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
effect ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) In some countries wood is an important fuel. Wood may be collected by cutting down trees in forests. State three undesirable effects of deforestation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) carbon dioxide;
global warming/ greenhouse effect;
sulfur dioxide;
acid rain/ acidification/trees and plants die/aquatic organisms die/ leaches minerals from soil;
nitrogen oxides;
global warming/ acid rain/ trees and plants die/ aquatic organisms die/ leaches minerals from soil;
methane;
global warming;
ozone;
decrease in level of photosynthesis / decrease in flower and fruit production;
AVP;;
(b) extinction of species / loss of biodiversity / loss of habitat;
disruption of food chains;
increase in carbon dioxide resulting in global warming;
loss of soil/ soil erosion;
flooding;
loss of potential medicines / useful chemicals;
changes to water cycle/weather patterns / desertification;
AVP;
