Question
(a) (i) State two reasons why bacteria are useful in genetic modification and biotechnology.
(ii) Describe the ways in which genetic modification can improve crop plants.
(b) Scientists investigated two enzymes that could be used in washing powders.
The activity of each enzyme was measured at \(\text{pH}\) values between \(2\) and \(10\).
Fig. 7.1 shows the results of the investigation.
The activity of each enzyme was measured at \(\text{pH}\) values between \(2\) and \(10\).
Fig. 7.1 shows the results of the investigation.

(i) The list shows six conclusions. Tick (\(\checkmark\)) the conclusions that can be made from the data shown in Fig. 7.1.

(ii) Many washing powders have a \(\text{pH}\) of approximately \(9\).
Identify the best enzyme, A or B, to use in these washing powders. Give one reason for your choice.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
(a) (i) Reasons bacteria are useful in biotechnology:
- They have a rapid reproduction rate. Bacteria reproduce asexually via binary fission very quickly (often every 20 minutes), allowing for the mass production of a product in a short time.
- They have the ability to make complex molecules.
- (Alternative point): They contain plasmids (circular DNA), which are easily modified and transferred from one cell to another.
(a) (ii) Ways genetic modification improves crop plants:
- Herbicide resistance: Crops can be modified to withstand weed-killers, allowing farmers to spray fields to kill weeds without harming the crop (e.g., Roundup Ready crops).
- Pest/Insect resistance: Crops can produce their own toxins (e.g., Bt toxin) that kill specific pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
- Increased yield: Modification can lead to larger fruits, faster growth, or resistance to environmental stress like drought.
- Improved nutritional qualities: Crops can be fortified with vitamins (e.g., Golden Rice, which is enriched with Vitamin A precursor).
(b) (i) Conclusions from the graph:
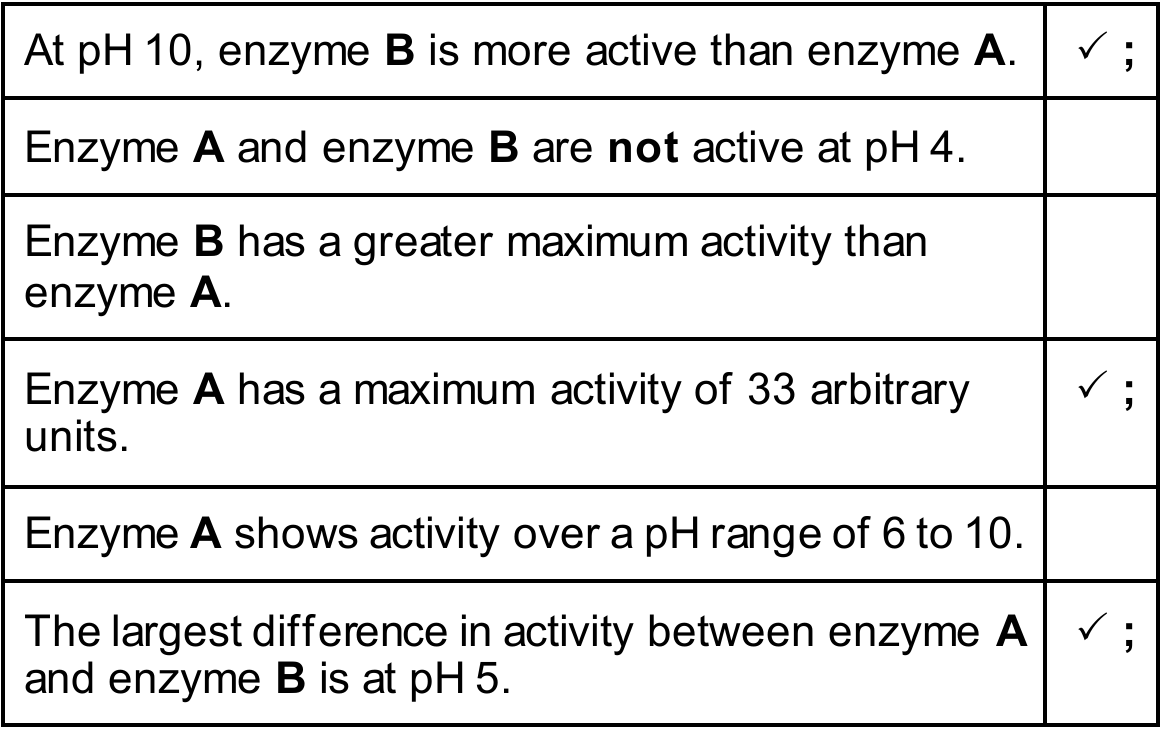
The correct statements based on Fig. 7.1 are:
- At \(\text{pH } 10\), enzyme B is more active than enzyme A. (\(\checkmark\))
Reasoning: Looking at the x-axis at \(10\), the line for Enzyme A is at \(0\), while the dashed line for Enzyme B is at approx \(12\) units. - Enzyme A has a maximum activity of \(33\) arbitrary units. (\(\checkmark\))
Reasoning: The peak of the solid line (Enzyme A) is at \(\text{pH } 5.5\). The y-axis value is \(3\) small squares above \(30\). Since \(5\) squares = \(5\) units, the value is \(33\). - The largest difference in activity between enzyme A and enzyme B is at \(\text{pH } 5\). (\(\checkmark\))
Reasoning: At \(\text{pH } 5\), Enzyme A is at \(30\) units and Enzyme B is at \(0\) units. The difference is \(30\). At any other pH, the gap between the lines is smaller than this.
Why the others are incorrect:
- “Enzyme A and enzyme B are not active at \(\text{pH } 4\)”: Incorrect. Enzyme A is active (value approx \(18\)).
- “Enzyme B has a greater maximum activity than enzyme A”: Incorrect. Peak A is \(33\), Peak B is \(30\).
- “Enzyme A shows activity over a pH range of \(6\) to \(10\)”: Incorrect. It loses activity before \(10\), and starts well before \(6\).
(b) (ii) Washing powder selection:
- Enzyme: B
- Reason: At \(\text{pH } 9\) (the pH of the washing powder), only Enzyme B is active. Enzyme A has denatured and has zero activity at this pH. Alternatively, Enzyme B’s optimum is closer to \(\text{pH } 9\).
