Question
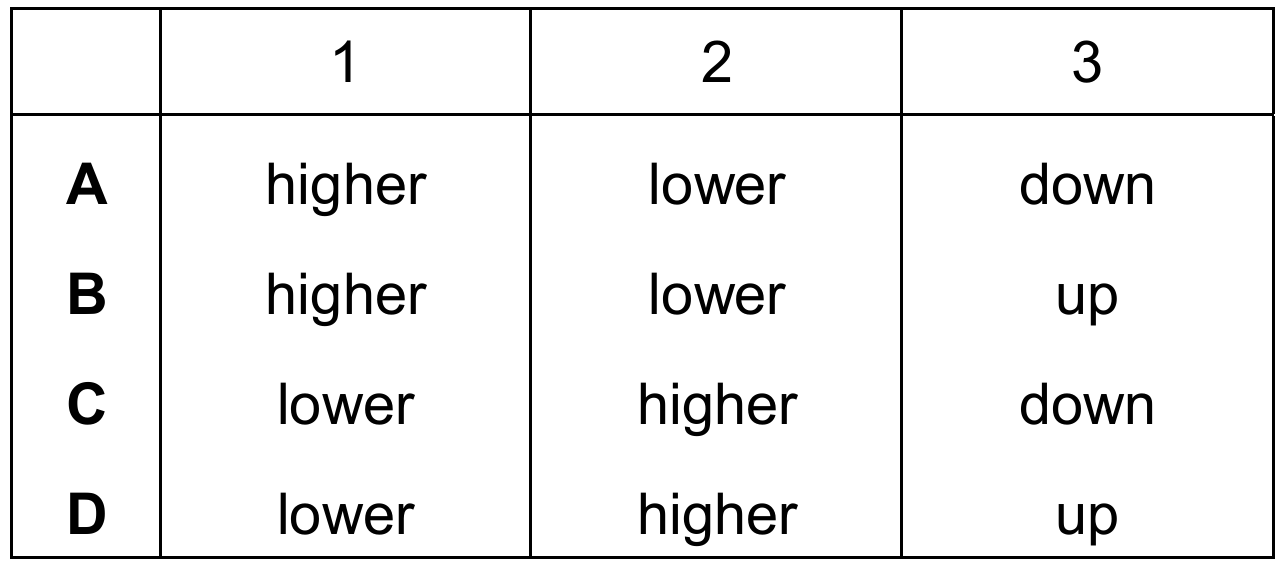
Diffusion may be defined as the net movement of particles from a region of their ……$1$…… concentration, to a region of their ……$2$…… concentration, where movement is ……$3$…… a concentration gradient.
Which words complete gaps $1$, $2$ and $3$?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Diffusion is a passive process where particles move from an area where they are more crowded to an area where they are less crowded. This means they move from a higher concentration ($1$) to a lower concentration ($2$). Since the particles are following the natural slope of concentration, the movement is described as going down ($3$) the concentration gradient. This process does not require energy input because it relies on the random kinetic energy of the particles. Therefore, the sequence that correctly fills the gaps is higher, lower, and down.
✅ Answer: (A)
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
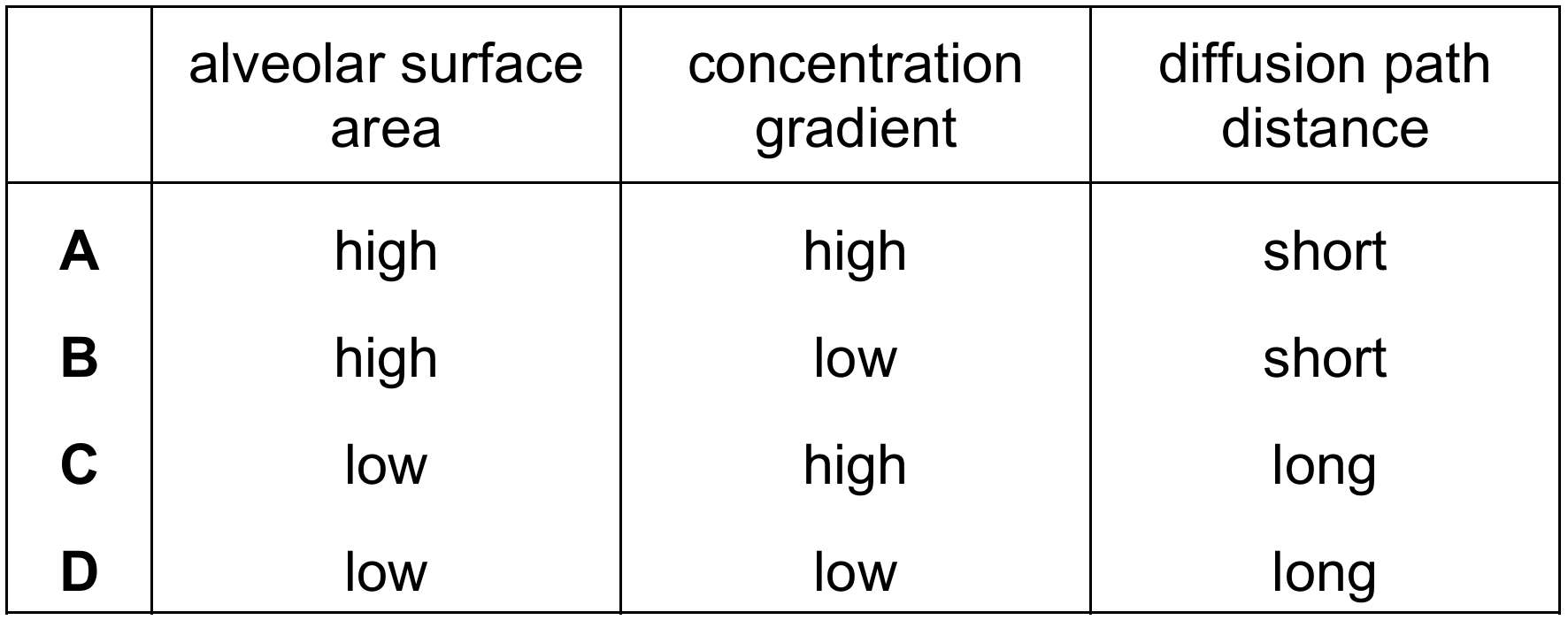
Which row shows the conditions when diffusion of oxygen into the blood is fastest?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The rate of diffusion is governed by Fick’s Law, which states that diffusion is faster when the surface area is large and the concentration gradient is steep (high). Conversely, diffusion is slower when the diffusion path distance (membrane thickness) is long. Therefore, the fastest diffusion occurs when there is a high surface area for more molecules to pass through, a high gradient to drive the movement, and a short distance to travel.
✅ Answer: (A)
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
The graph shows the results of an investigation into the effect of oxygen on the uptake of glucose by cells.

Which conclusion can be made about these data?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Solution
Ans: C
The graph shows glucose uptake occurs both with and without oxygen. Active transport requires energy (oxygen), while diffusion doesn’t. Since uptake happens in both conditions, both mechanisms must be operating. Osmosis (D) involves water, not glucose.
