Question
(a) Define diffusion.

(b) Fig. 3.1 shows an apparatus that was used to investigate the effect of concentration of
a chemical on the rate of diffusion.
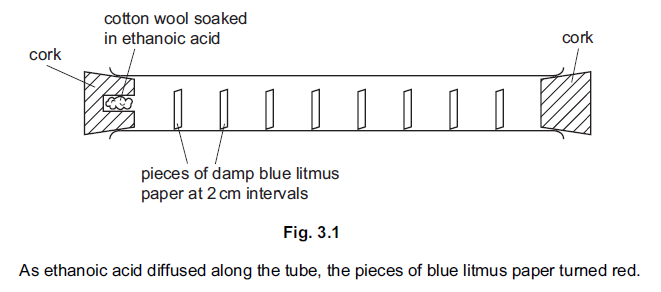
Two different samples of ethanoic acid, A and B, were used in this apparatus. The two
samples had different concentrations. The results are shown in Fig. 3.2.
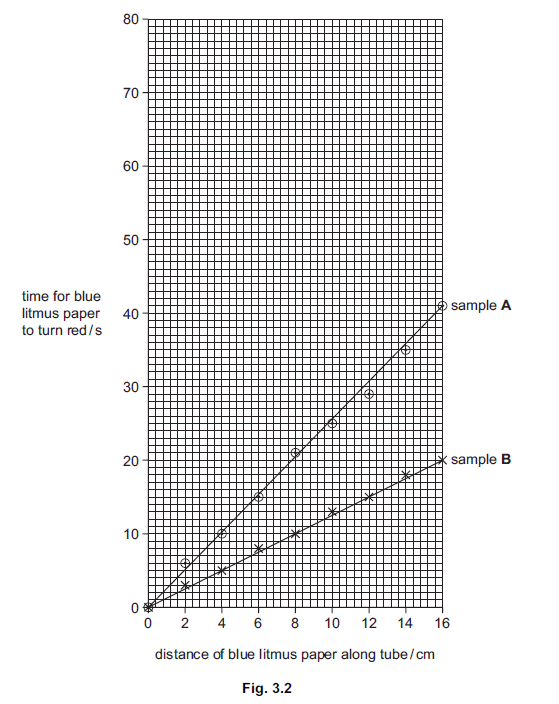
Table 3.1 shows the results for a third sample, C, of ethanoic acid.
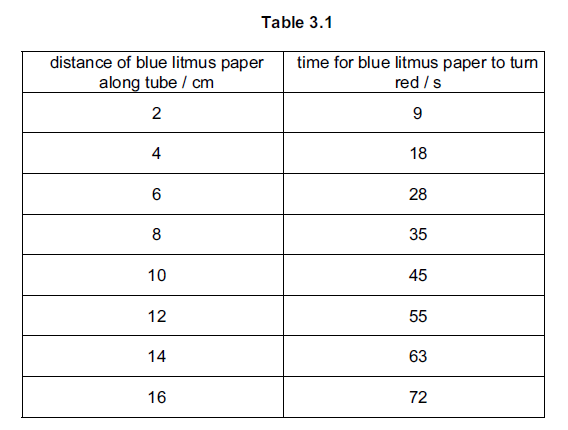
(i) Complete Fig. 3.2 by plotting the results shown in Table 3.1.
Plot the results shown in Table 3.1 on the grid, Fig. 3.2, on page 6. [3]
(ii) State which sample of ethanoic acid, A, B or C, took the longest time to travel
8 cm along the tube.
![]()
(iii) State and explain which sample of ethanoic acid was the most concentrated.

(c) Substances can enter and leave cells by either diffusion or by osmosis.
State two ways in which osmosis differs from diffusion.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Rhabdostyla is a single-celled organism that has no cell wall and no chlorophyll.
(a) Gases are exchanged across the cell membrane of Rhabdostyla.
Name:
the gas produced by Rhabdostyla …………………………………………………………………………
the process that produces the gas ………………………………………………………………………..
the method of removal of the gas …………………………………………………………………………. [3]
Rhabdostyla lives in freshwater habitats, such as ponds, lakes and rivers.
Freshwater has a very low concentration of solutes.
Rhabdostyla has a contractile vacuole that fills with water and empties at intervals as shown in
Fig. 4.1. The contractile vacuole removes excess water.
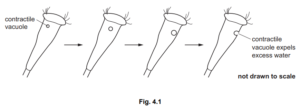
(b) Explain, using the term water potential, why Rhabdostyla needs to remove excess water.
In an investigation, individual Rhabdostyla were placed into different concentrations of sea water.
The rate of water excreted by the contractile vacuole of each organism was determined. The results
are shown in Fig. 4.2.
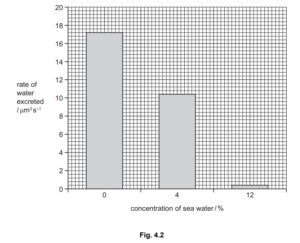
(c) Explain the results shown in Fig. 4.2.
(d) Single-celled organisms with cell walls do not have contractile vacuoles. Suggest why.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
4 (a) carbon dioxide/CO2 ;
(aerobic) respiration ;
(simple) diffusion ;
(b) water enters by osmosis ;
down a water potential gradient/high(er) to low(er) water potential ;
through partially permeable membrane ;
needs to remove water to prevent bursting ;
(c) as concentration of sea water increases the removal of water decreases ;
as concentration of sea water increases the water potential gradient
decreases ;
therefore less water enters at higher concentrations of sea water ;
less excess water ;
(d) cell walls, inelastic / do not stretch/rigid/ inflexible/ keep shape of cell ;
cells, are turgid/ have high turgor pressure ;
resist any increase in, volume/ pressure ;
these cells do not absorb excess water ;
the cells will not burst ;
