Question
Which process only involves the movement of water through the partially permeable membrane
of a cell?
A absorption
B evaporation
C osmosis
D transpiration
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The process that only involves the movement of water through the partially permeable membrane of a cell is option C: osmosis. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of lower solute concentration (hypotonic solution) to an area of higher solute concentration (hypertonic solution) through a semipermeable membrane, such as the cell membrane. This process occurs to equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane and maintain osmotic balance within the cell.
Question
Which structures must be present in a cell for osmosis to take place?
A cell (sap) vacuole and cell wall
B cell wall and cell membrane
C chloroplast and cytoplasm
D cytoplasm and cell membrane
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
The correct answer is D: cytoplasm and cell membrane.
Osmosis is the process of water moving across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. In cells, osmosis occurs through the cell membrane, which is the selectively permeable barrier surrounding the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm, which contains various solutes, including dissolved ions and molecules, is responsible for establishing the concentration gradient necessary for osmosis.
Question
The diagram shows apparatus which can be used to demonstrate osmosis.
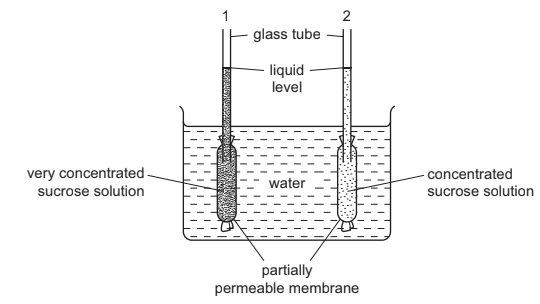
After one hour, what would happen to the liquid levels in the glass tubes?

▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Based on the given information, the liquid levels in both glass tubes are likely to rise after one hour.
In this apparatus, where tube 1 contains a very concentrated sucrose solution compared to tube 2, osmosis will occur. Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules (in this case, water) from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration through a partially-permeable membrane.
Since tube 1 contains a highly concentrated sucrose solution, which has a lower water concentration compared to tube 2, water molecules will move from tube 2 (higher water concentration) to tube 1 (lower water concentration) through the partially-permeable membrane. This movement of water will result in an increase in the liquid level in both tubes.
The liquid level in tube 1 will rise because water is moving into it from tube 2, diluting the concentrated sucrose solution. The liquid level in tube 2 will also rise because water is leaving it, reducing the water concentration.
Question
The diagram represents two liquids, separated by a membrane through which osmosis can occur.
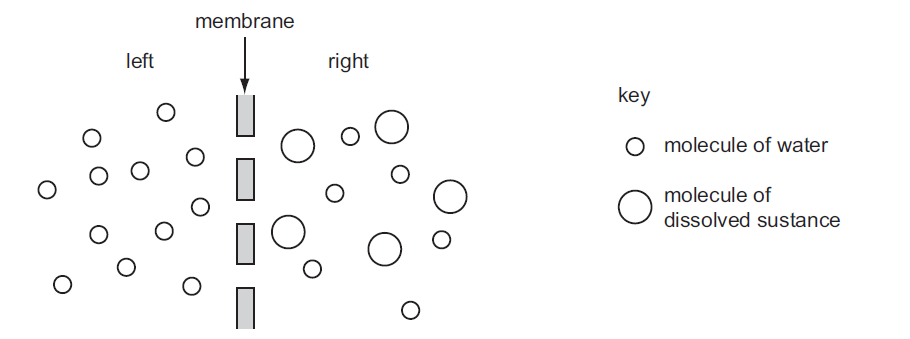
What movement of molecules will occur?
A Molecules of dissolved substance move from left to right.
B Molecules of dissolved substance move from right to left.
C Overall, water molecules move from left to right.
D Overall, water molecules move from right to left.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is C. Overall, water molecules move from left to right.
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules, usually water, from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration across a semipermeable membrane. In this case, the left side has small-sized water molecules, while the right side has both small and large molecules of dissolved substances.
Since the membrane is semipermeable, it allows the passage of water molecules but restricts the movement of larger dissolved substances. As a result, water molecules will tend to move from the side with lower solute concentration (left) to the side with a higher solute concentration (right) in an attempt to equalize the concentration on both sides of the membrane.
Therefore, the overall movement of molecules in this scenario is that water molecules move from left to right.
Question
Which diagram shows the changes in appearance of a plant cell when it remains in a
concentrated sugar solution for thirty minutes?
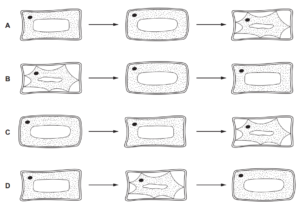
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
When a plant cell is placed in a concentrated sugar solution for thirty minutes, several changes can occur in its appearance. These changes are a result of the process known as plasmolysis, where water leaves the cell due to osmosis. Here’s what typically happens:
1. Cell Shrinkage: As water leaves the cell, the protoplast (cell contents) shrinks and pulls away from the cell wall. This is because the cell wall is more rigid compared to the flexible protoplast, causing the protoplast to collapse inward.
2. Wrinkled Cell Membrane: The cell membrane, which surrounds the protoplast, becomes wrinkled or shriveled due to the loss of water. This occurs because the cell membrane detaches from the cell wall, resulting in a wrinkled appearance.
3. Vacuole Contraction: The central vacuole, which is responsible for maintaining cell turgidity, undergoes significant contraction. The decrease in water content within the vacuole causes it to shrink in size, leading to a noticeable reduction in the overall cell volume.
4. Loss of Turgidity: Turgor pressure, which is the pressure exerted by the cell contents against the cell wall, decreases as water exits the cell. As a result, the plant cell loses its firmness and becomes flaccid or limp.
These changes occur due to the high concentration of sugar solution surrounding the cell. The sugar molecules attract water molecules, causing water to move out of the cell through osmosis. If the cell is placed back into a normal isotonic solution, it may regain its original appearance and turgidity through the process of rehydration.
