Question
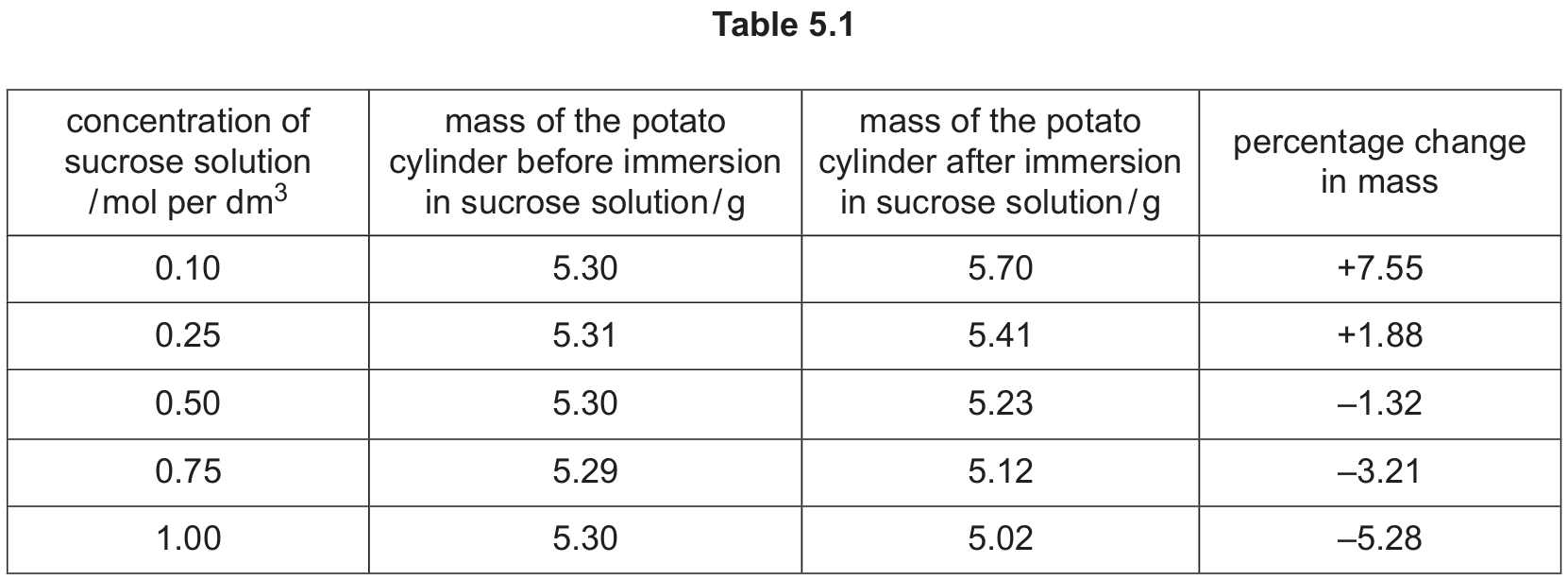
The mass of a potato cylinder was measured before immersion and after being immersed for \(60\) minutes.
Table 5.1 shows the results.
(i) The student has written several conclusions for the results shown in Table 5.1. Tick (\(\checkmark\)) all the correct conclusions.

(c) Water is important as part of a balanced diet.
(i) Circle two uses of water in the body.
for phagocytosis for transport
(ii) State two other components of a balanced diet.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
The correct conclusions to be ticked are:
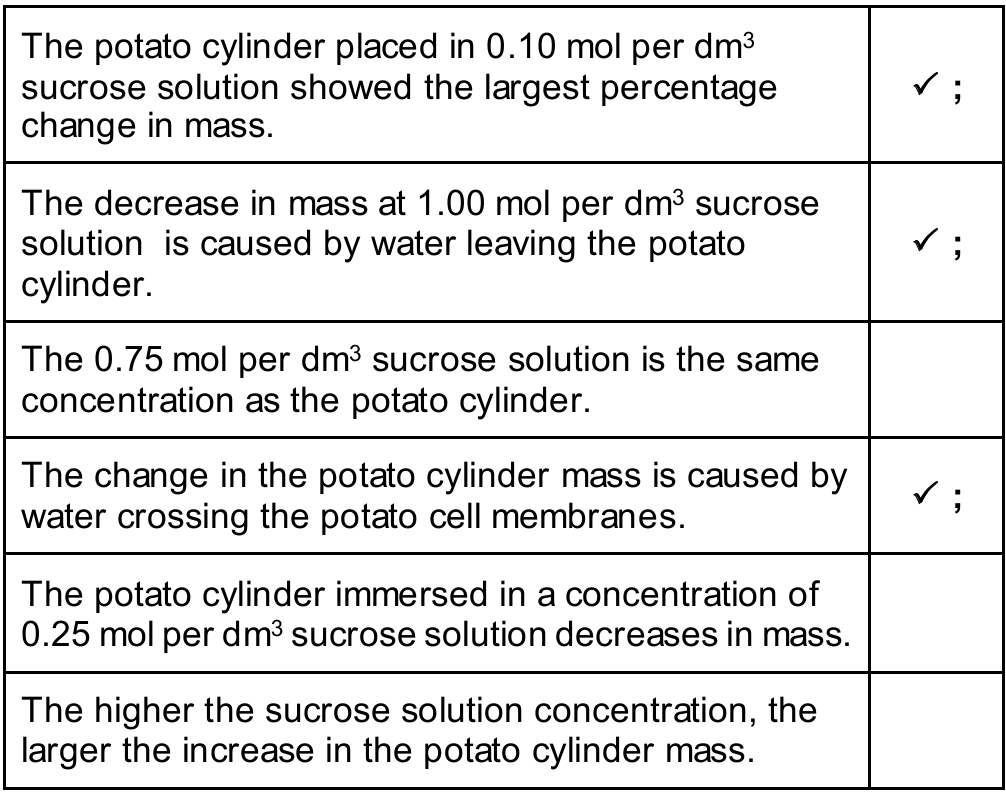
- The potato cylinder placed in \(0.10\,\text{mol per dm}^3\) sucrose solution showed the largest percentage change in mass.
Explanation: Comparing the values in the “percentage change” column, \(+7.55\%\) has the largest magnitude (absolute value) compared to the others. - The decrease in mass at \(1.00\,\text{mol per dm}^3\) sucrose solution is caused by water leaving the potato cylinder.
Explanation: A decrease in mass indicates that water has moved out of the potato cells into the surrounding hypertonic solution via osmosis. - The change in the potato cylinder mass is caused by water crossing the potato cell membranes.
Explanation: Osmosis is the movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane (the cell membrane) down a water potential gradient.
(a)(ii)
Osmosis.
Explanation: The experiment demonstrates the movement of water across a partially permeable membrane due to differences in solute concentration (sucrose).
(a)(iii)
Any two of the following factors:
- Temperature (Higher temperature increases kinetic energy and the rate of diffusion/osmosis).
- Surface area (Larger surface area allows more molecules to cross the membrane per unit of time).
(b)
(Cell) wall.
Explanation: The cell wall is a rigid structure made of cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane in plant cells. It resists the outward pressure (turgor pressure) exerted by the swelling vacuole and cytoplasm when water enters, preventing the cell from lysing (bursting).
(c)(i)
The two circled uses of water should be:
- as a solvent (Water is the universal solvent for metabolic reactions).
- for transport (Water is the main component of blood plasma and xylem sap, transporting substances around the body/plant).
(c)(ii)
Any two of the following components of a balanced diet (excluding water):
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats (Lipids)
- Vitamins
- Minerals
- Fibre (Roughage)
