Question
The board was placed in a clinostat that rotated the board.
The board was rotated continuously as the seeds germinated and the roots grew.
Fig. 6.1 shows the apparatus and results after 5 days.
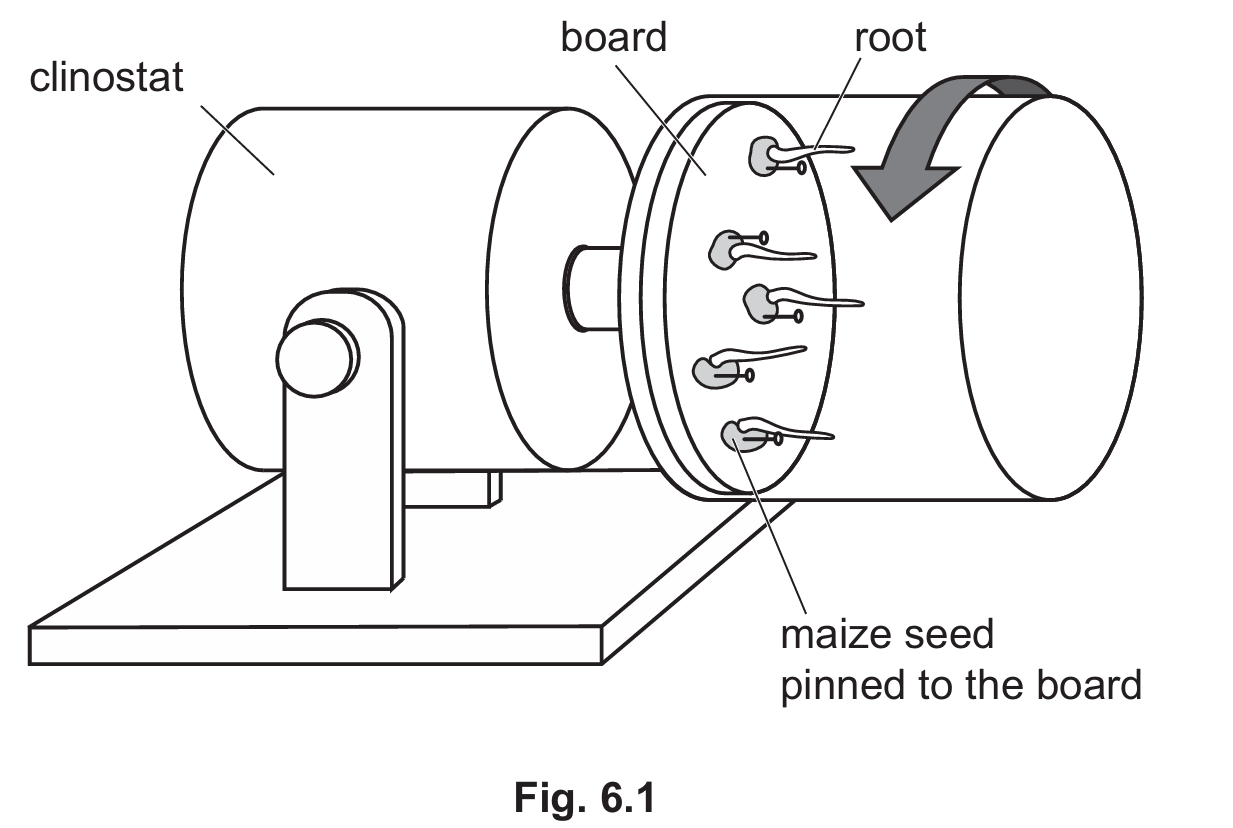
(i) Complete the sentences to explain the root growth in Fig. 6.1.
Auxin is produced in shoot and root ……………… . The auxin travels down the root by the process of ……………… .
As the clinostat rotates, the effect of ……………. on all sides of the root is equal.
This causes the distribution of auxin in the root to be …………….. .
Auxin stimulates cell …………….. causing the roots to grow horizontally.
Predict the change in growth that will occur in the germinating maize seeds in Fig. 6.1.
State and explain the expected appearance of the cells.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
6 (a) (i)
Auxin is produced in shoot and root tips. The auxin travels down the root by the process of diffusion.
As the clinostat rotates, the effect of gravity on all sides of the root is equal.
This causes the distribution of auxin in the root to be equal (or uniform/even).
Auxin stimulates cell elongation causing the roots to grow horizontally.
6 (a) (ii)
The roots will grow downwards (or towards gravity).
6 (a) (iii)
Phototropism
6 (b)
State: The cells will appear flaccid (no longer turgid) or plasmolysed.
Explain:
• There is a lack of turgor pressure.
• The volume of the cytoplasm or vacuole has decreased.
• This is due to a loss of water from the cells (exosmosis) because the water potential outside the cells is lower than inside.
• The cell membrane may pull away from the cell wall (plasmolysis).
Explanation & Key Concepts:
- Clinostats and Tropisms: A clinostat rotates a plant slowly. This rotation negates the directional stimulus of gravity. Under normal conditions, gravity causes auxin to accumulate on the lower side of a root, inhibiting cell elongation there and causing the root to bend downwards (positive gravitropism). By rotating the plant, gravity acts equally on all sides, resulting in an equal distribution of auxin. Consequently, cell elongation occurs at the same rate on all sides, and the root grows straight (horizontally) rather than bending.
- Wilting and Osmosis: Wilting occurs when water loss (transpiration) exceeds water uptake. This causes water to move out of plant cells by osmosis. As water leaves the vacuole, the cell becomes flaccid (soft) because there is no longer turgor pressure pushing the cytoplasm against the cell wall. If water loss is severe, the cell membrane detaches from the wall, a state called plasmolysis.
