Question
Which chemical tests should a student use to test lemon juice for reducing sugars and vitamin C?
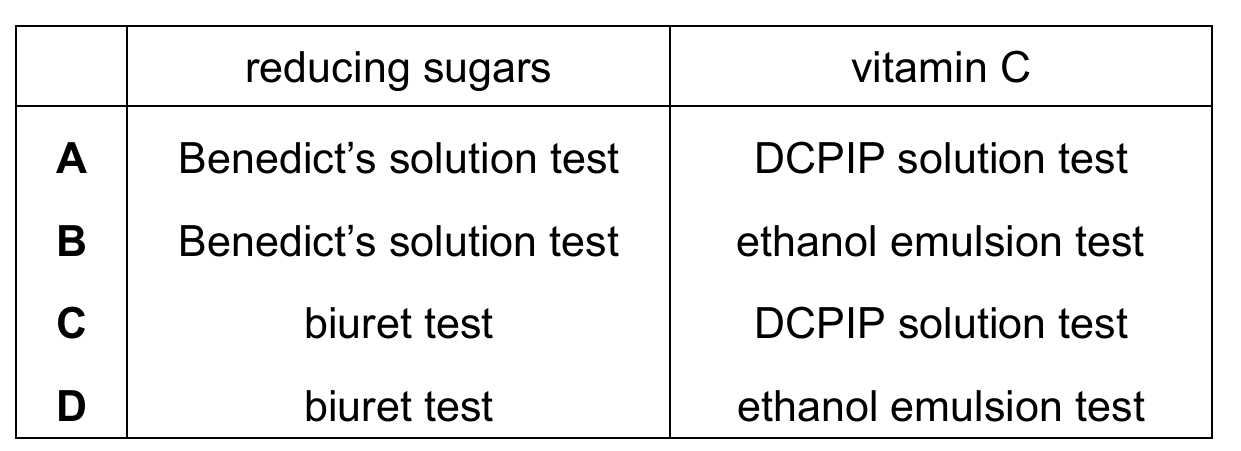
▶️ Answer/Explanation
To identify reducing sugars, the standard food test is the Benedict’s solution test, which involves heating the sample to see a color change from blue to brick-red. For vitamin C (ascorbic acid), the specific test uses DCPIP solution, which decolors from blue to colorless in the presence of the antioxidant. Other options like the biuret test are used for proteins, and the ethanol emulsion test is used for lipids. Therefore, the combination of Benedict’s and DCPIP is the only correct path for testing lemon juice for these specific nutrients.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which carbohydrate is used to build plant cell walls?
(B) glycogen
(C) starch
(D) sucrose
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Cellulose is a complex polysaccharide consisting of thousands of $\beta$-glucose units linked together. Its linear, rigid structure allows it to form tough microfibrils that provide structural support and tensile strength to plant cell walls. While starch and sucrose are used for energy storage and transport in plants, and glycogen is the storage carbohydrate in animals, only cellulose serves as a primary structural component. This makes it the most abundant organic polymer on Earth, essential for maintaining the integrity of plant cells.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
A student placed amylase and starch solution in a test-tube.
After some minutes, the student tested samples of the liquid in the test-tube. They recorded the colour of the samples after testing for starch and reducing sugar.
Which row shows the test used and the expected results?
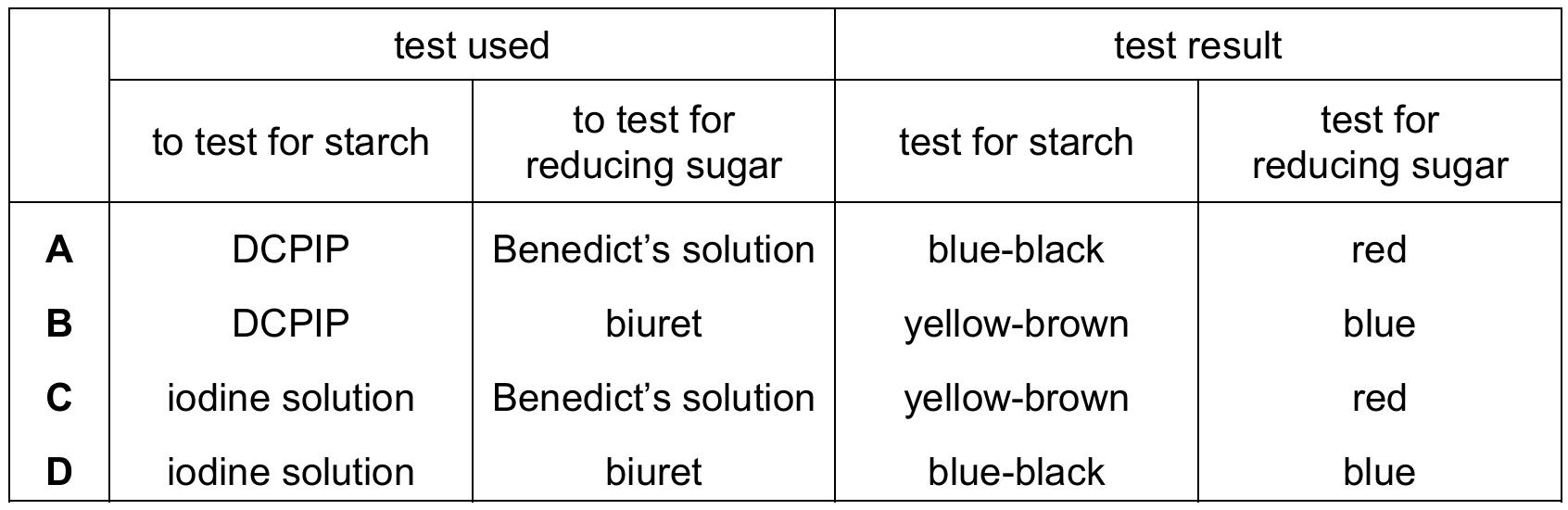
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is C.
To determine the correct answer, we must identify the correct chemical reagents for the specific food tests and understand the enzymatic reaction occurring in the test-tube.
- The Reaction: Amylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of starch into reducing sugars (specifically maltose). Since the question states “after some minutes,” we can infer that the enzyme has had time to work, converting the starch into reducing sugar.
1. Identifying the Correct Tests:
- Test for Starch: The standard reagent used to test for the presence of starch is iodine solution.
- Positive result (Starch present): Blue-black.
- Negative result (Starch absent): Yellow-brown (the colour of the iodine solution itself).
- Test for Reducing Sugar: The standard reagent used to test for reducing sugars (like maltose) is Benedict’s solution.
- Positive result: A colour change from blue to green, yellow, orange, or red (depending on concentration).
- Negative result: Blue.
2. Analyzing the Options:
- A: Incorrect. DCPIP is used to test for Vitamin C, not starch.
- B: Incorrect. DCPIP is incorrect for starch, and the Biuret test is used for proteins, not reducing sugars.
- C: Correct.
- Tests used: Iodine solution (for starch) and Benedict’s solution (for reducing sugar) are the correct reagents.
- Results: Since amylase has broken down the starch, the starch test should be negative (yellow-brown). Since reducing sugars (maltose) have been produced, the Benedict’s test should be positive (red).
- D: Incorrect. While iodine is correct for starch, the Biuret test is for proteins, not reducing sugars.
