Question
The diagram shows a process involving an enzyme in the human stomach.
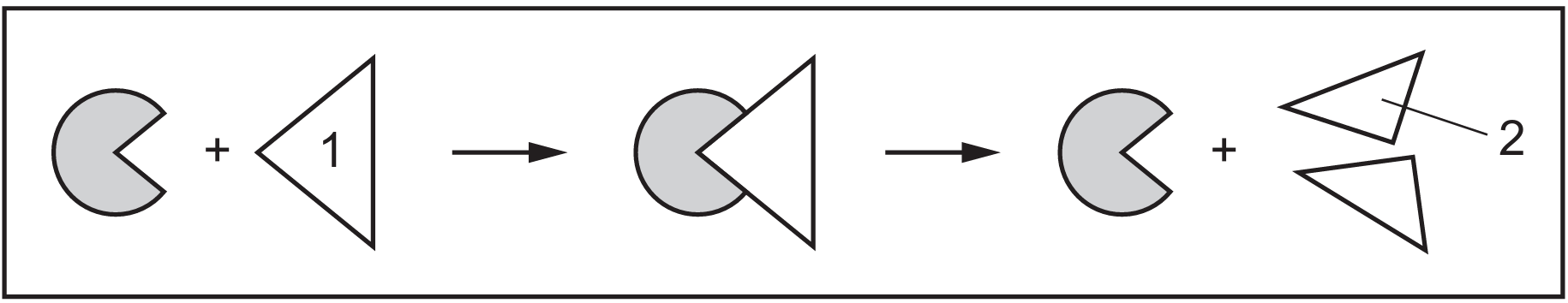
The diagram shows another process, $R$, that affects this enzyme.
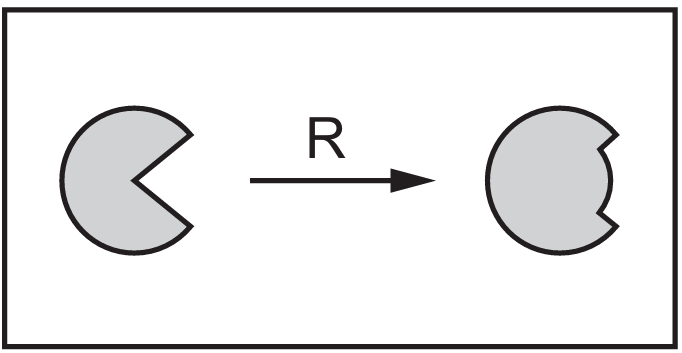
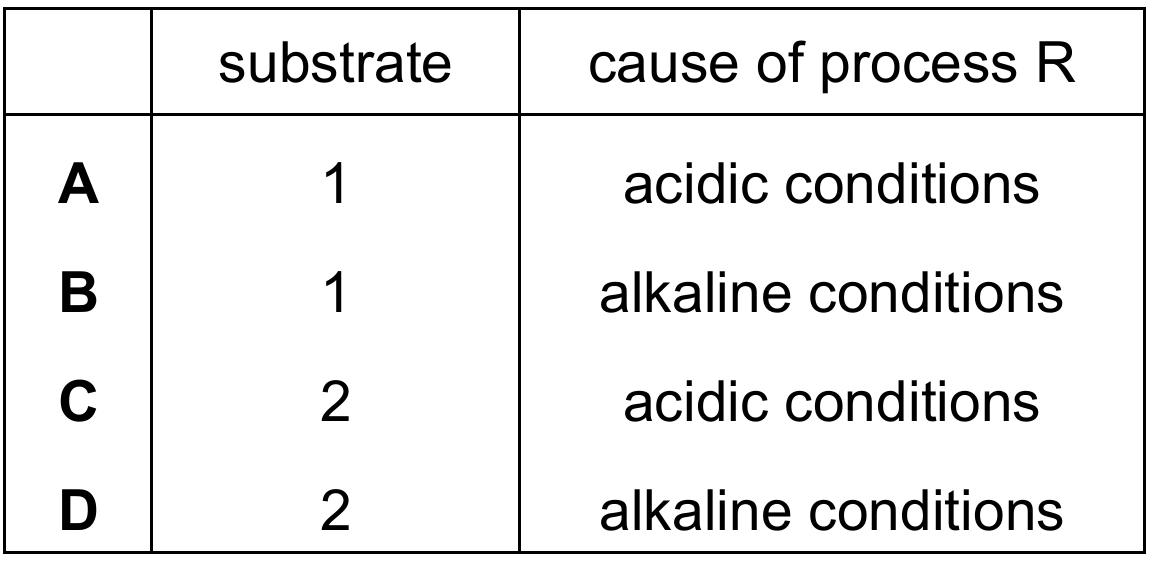
Which row identifies the substrate and the cause of process $R$?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
What is the correct definition of enzymes?
(B) carbohydrates that act as substrates
(C) proteins that act as biological catalysts
(D) proteins that act as substrates
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Enzymes are specialized proteins synthesized by living cells to speed up metabolic reactions. They function as biological catalysts, meaning they lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur without being consumed in the process. While carbohydrates serve as energy sources or structural components, they do not possess catalytic properties. Similarly, a substrate is the specific molecule that an enzyme acts upon, rather than the enzyme itself. Therefore, the most accurate definition identifies them as protein-based catalysts.
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
The graph shows how enzyme activity is affected by temperature.
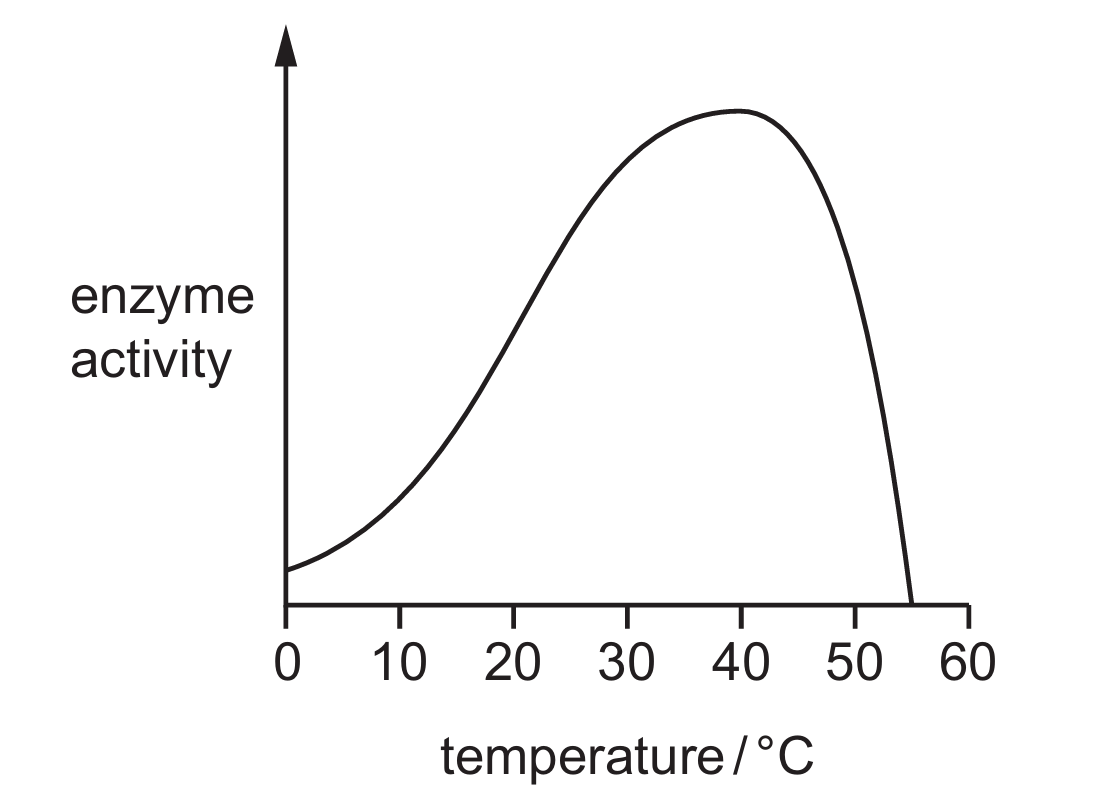
Why is enzyme activity lower at $55$ °C than it is at $40$ °C?
(B) The enzyme has been used up.
(C) The reactants are moving faster.
(D) The substrate is less likely to fit into the active site.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (D)
