Question
(a) The list shows some of the organs in the digestive system.
large intestine liver oesophagus
pancreas salivary gland stomach
The words in the list can be used once, more than once or not at all.
State the name of one organ from the list that:
- is where physical digestion occurs ………..
- releases hydrochloric acid …………
- secretes protease and amylase …………….
- secretes insulin. …………..
(b) State two functions of hydrochloric acid in the digestive system.
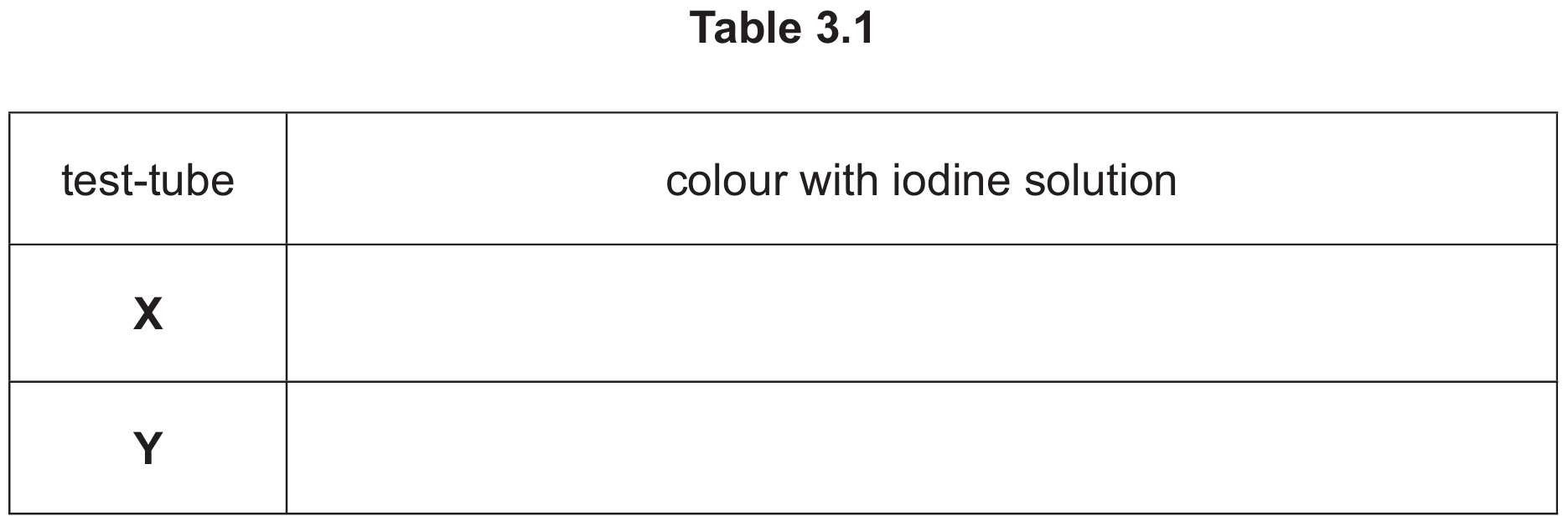
Test-tube X contained starch only.
Test-tube Y contained starch and amylase.
After 30 minutes the contents of test-tubes X and Y were tested with iodine solution.
The contents of test-tubes X and Y turned different colours.
(i) Complete Table 3.1 with the expected results.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
- Physical digestion occurs: stomach. (The muscular walls of the stomach churn food).
- Releases hydrochloric acid: stomach. (Secreted by the gastric glands in the stomach wall).
- Secretes protease and amylase: pancreas. (The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice containing these enzymes into the small intestine).
- Secretes insulin: pancreas. (Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to regulate blood glucose).
(b)
Hydrochloric acid has two primary functions in the stomach:
- It kills harmful microorganisms (pathogens) present in food.
- It provides an acidic pH (optimum pH) for the enzyme pepsin (a protease) to work effectively.
(c)
Protease is important because it breaks down large, insoluble protein molecules into small, soluble amino acids. This allows the nutrients to be absorbed through the wall of the small intestine into the blood for use by the body (e.g., for growth and repair).
(d)(i)
| test-tube | colour with iodine solution |
| X | blue-black |
| Y | yellow-brown (or orange/brown) |
(d)(ii)
The colours are different because in test-tube Y, the enzyme amylase has broken down (digested) the starch into simple sugars (maltose). Since starch is no longer present, the iodine solution remains its original yellow-brown colour. In test-tube X, there is no amylase, so the starch remains undigested, causing the iodine to turn blue-black.
