Question
Fig. 1.1 shows a diagram of a cross-section of a dicotyledonous leaf, as seen using a light microscope.
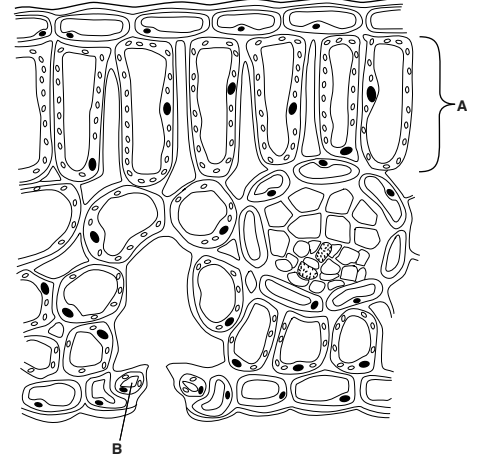
(a) (i) Name tissue A and cell B.
(ii) Describe two ways in which tissue A is adapted for maximum photosynthesis.
(b) Plants use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
(i) Describe where and how carbon dioxide enters a leaf.
(ii) State the two products of photosynthesis.
(c) Hydrophytes are plants that grow in water. Fig. 1.2 shows a photograph of Indian lotus, Nelumbo nucifera, which is a hydrophyte.

Describe and explain two adaptations of hydrophytes to their environment.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) A palisade/mesophyll (layer/cells) ;
B guard (cell) ;
(ii) (palisade cells)
contain many chloroplasts / lots of chloroplasts ;
are tightly packed ;
are located near the top of the leaf ;
arranged ‘on end’/ vertically / lengthways / columnar ;
(b) (i) through stomata ;
by diffusion ;
from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ;
guard cells bend/ become turgid ;
(ii) glucose and oxygen ;
(c) submerged leaves are divided ;
providing large area for, photosynthesis / absorption ;
OR
leaves have large surface area to float ;
OR
(floating leaves so) little xylem/ little lignin ;water provides support ;
OR
little/ no roots /root hairs ;
roots for anchorage only / no need for roots to absorb water or mineral ions ;
OR
little/ no, cuticle ;10 no need to conserve water ;
OR
stomata only on upper surface ;
only upper surface exposed to air/ to allow diffusion of gases ;OR
lots of air spaces (between cells) ;
for flotation/ buoyancy ;
OR
floating leaves ;
to allow, diffusion/AW of (named) gas(es) ;
OR
aerial roots ;
to allow roots to receive oxygen ;
Question
A student carried out an investigation to find the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis of an aquatic plant.
The apparatus that the student used is shown in Fig. 2.1. The student was advised to use a light meter positioned at the same distance from the lamp as the pond plant. The student counted the number of bubbles produced by the cut end of the stem.
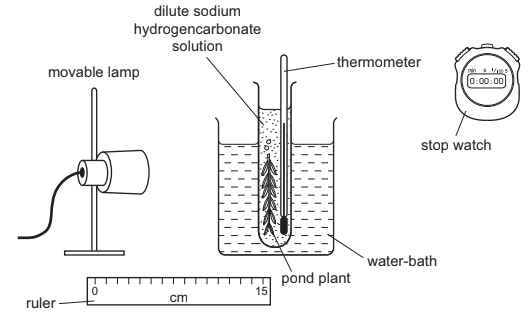
Fig. 2.1
(a) Explain why the student included the following in the apparatus.
(i) The beaker of water and the thermometer.
(ii) The light meter and the ruler.
(b) The results obtained by the student are shown in Fig. 2.2.
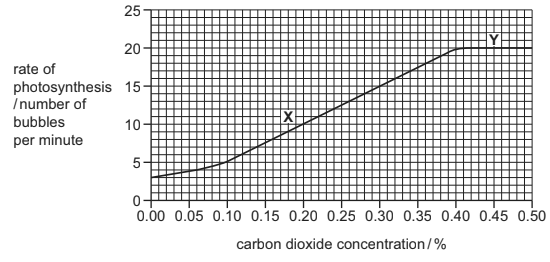
Fig. 2.2
(i) Describe the student’s results.
You will gain credit if you use data from Fig. 2.2 in your answer.
(ii) State the factor that is limiting the rate of photosynthesis in region X of the graph.
(iii) Suggest and explain the reasons for the shape of the graph in region Y.
(c) Counting bubbles may not be the best way to measure the rate of photosynthesis. The volume of the bubbles is not always exactly the same.
Suggest and explain one alternative way of measuring the gas given off to solve this problem.
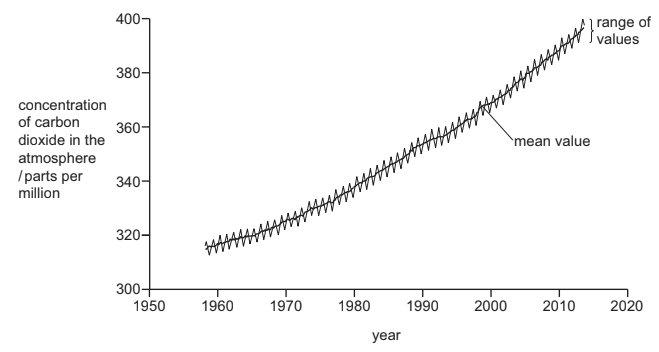
Fig. 2.3
(i) Explain why the concentration of carbon dioxide has increased between 1959 and 2013.
(ii) Global warming is largely due to this increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide. Explain how increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations contribute to global warming.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) (i) maintain constant temperature/ prevent heat from the lamp heating
the water/absorbs heat from the lamp/ heat shield ;
(thermometer) to measure/ check / monitor/record, water ;
prevent temperature (change), influencing/ affecting, the results /
rate of photosynthesis ;
temperature is a, control(led)/ standardised, variable ;
(ii) maintain constant light intensity ;
(light meter) to measure/ check /monitor/record, the light intensity ;
prevent light intensity (change) influencing/ affecting the, results / rate of photosynthesis ;
make sure the lamp is always, in the same place/ at right distance ;
light, intensity / level, is dependent on distance ;
light intensity is, a controlled/ standardised, variable ;
(b) (i) rate/photosynthesis / bubbles:
increases as carbon dioxide concentration increases and then, levels off AW ;
increases to 0.40 % ; A rate remains constant above 0.40%
little / slow, increase up to 0.1 % ; ora
one data quote with CO2 concentration and rate with units ;
(ii) carbon dioxide/CO2, concentration/%/ level/ availability ;
(iii) ref to limiting factor in suitable context ;
carbon dioxide (concentration), is no longer limiting/AW ;
light, intensity / level, could be limiting/AW ;
reference to light providing energy for photosynthesis ;
temperature could be limiting/AW ;
reference to temperature influencing the activity of enzymes ;
chloroplast/ chlorophyll/ number of leaves / size of plant, could be limiting factor ;
(c) measure volume (of oxygen/ gas) ;
use, inverted test-tube/ measuring cylinder/ syringe (barrel) ;
reference to, graduations /markings ; A ‘take readings from…’/ ‘record results…’
filled with water ;
gas collects at the top and pushes out the water/ downward displacement of water;
gas syringe ;
attached by (delivery) tube to, flask /AW ;
oxygen sensor ;
data logger for any other suitable electronic method ;
reference to equilibration/ described ;
reference to time period ; A rate = volume divided by time
(d) (i) use/ combustion/ burning, of fossil fuels ;
reason for increased demand for energy ;
carbon dioxide from, volcanic activity / volcanoes ;
deforestation ;
burning of, forests / trees ;
(ii) carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas ;
(enhanced) greenhouse effect (in context of carbon dioxide) ;
heat/infra-red/ long wavelength radiation, radiated/ emitted, from /
absorbed/ trapped/AW, by, carbon dioxide/ greenhouse gases ;
travels /AW, back to the surface ;
heat cannot, leave (from the atmosphere)/ pass into outer space ;
