Question
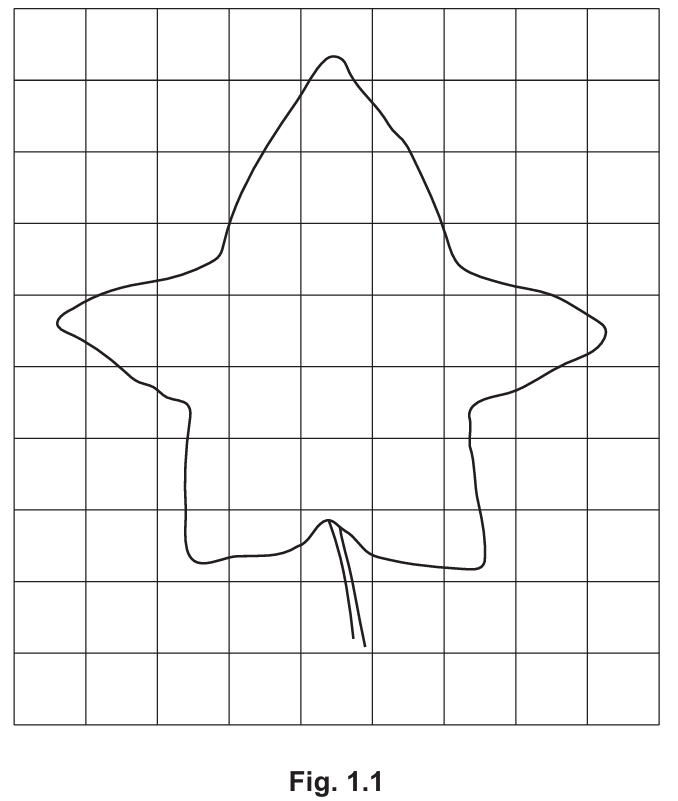
State the unit for this measurement of surface area.
(c) Fig. 1.2 shows a cross-section of part of a leaf.
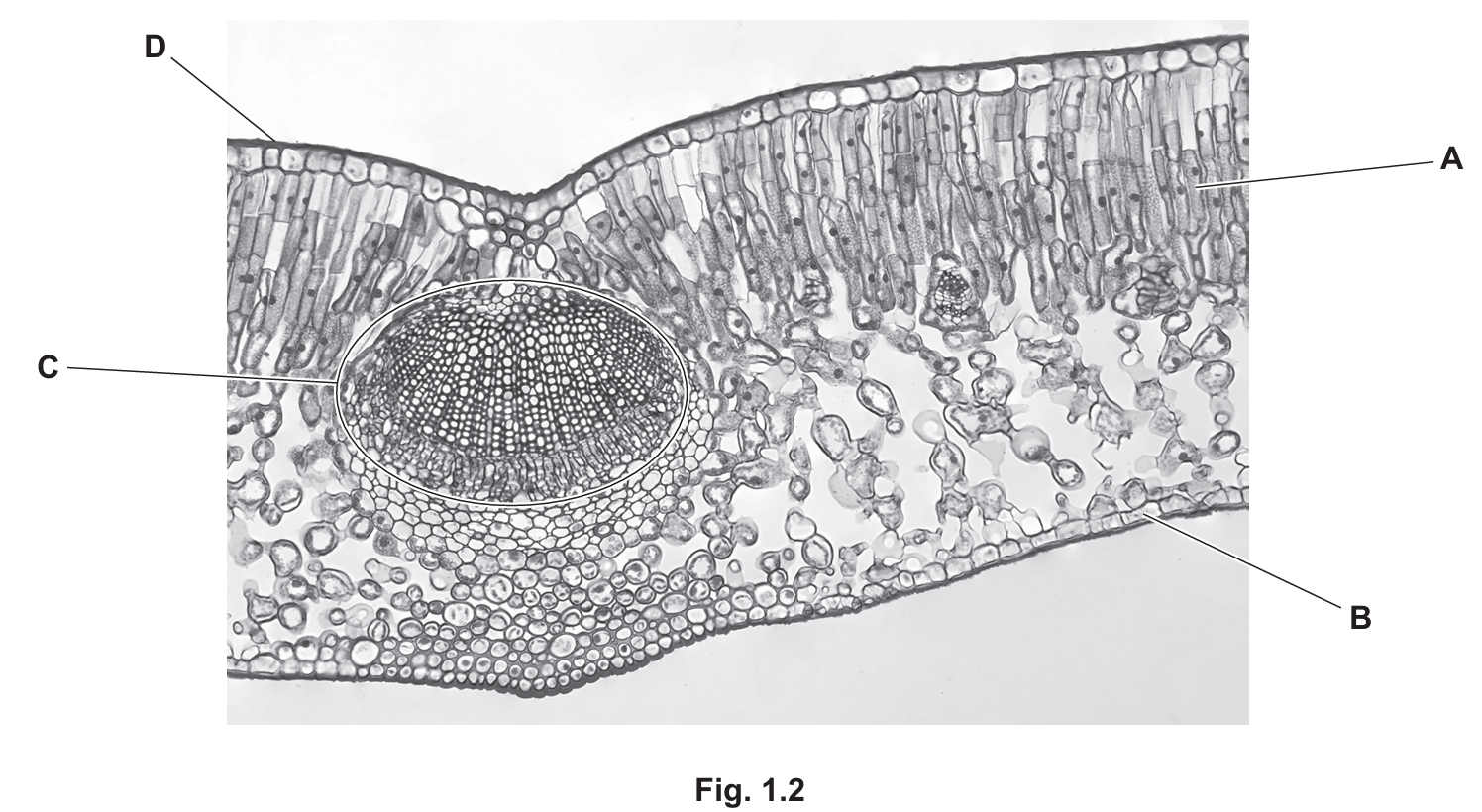
(i) State the names of the structures labelled A, B and D in Fig. 1.2.
(ii) State the names of the two types of tissue that make up structure C in Fig. 1.2.
(d) Fig. 1.3 shows part of the lower surface of a leaf.
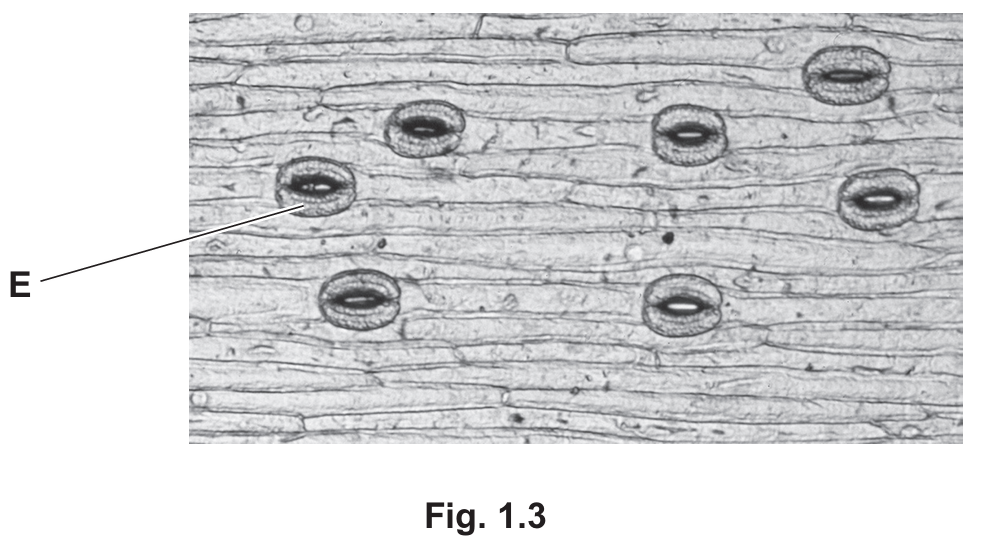 (i) State the name of the cell labelled E in Fig. 1.3.
(i) State the name of the cell labelled E in Fig. 1.3.
(ii) Describe how cell E adapts the leaf for photosynthesis.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Chloroplast
Photosynthesis takes place inside organelles called chloroplasts, which contain the enzymes and pigments necessary for the reaction.
(a)(ii) Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is the green pigment located inside the chloroplasts. Its function is to absorb light energy required to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
(b)(i) (\text{cm}^2)
Since the side of one square is (1 , \text{cm}), the area of one square is (1 , \text{cm} \times 1 , \text{cm} = 1 , \text{cm}^2). Therefore, the total surface area is measured in square centimeters.
(b)(ii) Explanation of adaptation:
A large surface area allows for maximum absorption of light. By spreading out, the leaf exposes more chloroplasts to sunlight, increasing the rate of photosynthesis.
(c)(i) Labels:
A: Palisade mesophyll (The layer of elongated cells packed with chloroplasts near the top of the leaf).
B: Lower epidermis (The protective layer of cells at the bottom of the leaf).
D: Cuticle (The waxy, waterproof layer on the upper surface that reduces water loss).
(c)(ii) Xylem and Phloem
Structure C represents the vascular bundle (vein). It consists of:
- Xylem: Transports water and mineral ions from the roots to the leaves.
- Phloem: Transports soluble sugars (sucrose) and amino acids (translocation).
(d)(i) Guard cell
Cell E is a guard cell. These are found in pairs surrounding the stomata (pores) on the leaf surface.
(d)(ii) Adaptation mechanism:
Guard cells control gas exchange by changing shape to open and close the stomata.
- They open the stomata to allow carbon dioxide ((\text{CO}_2)) to diffuse into the leaf for photosynthesis.
- They can close the stomata to prevent excessive water loss via transpiration (e.g., in hot or dry conditions).
