Question
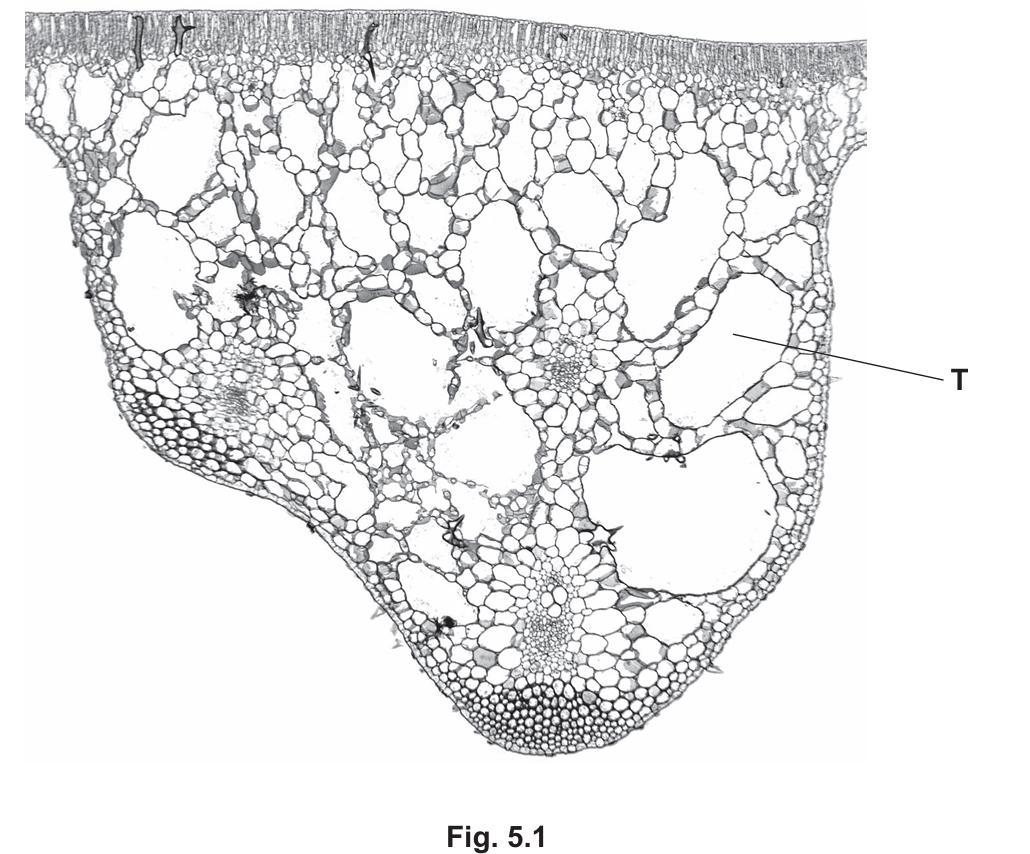
(ii) On Fig. 5.1, draw a label line and the letter X to identify the palisade mesophyll tissue.
(iii) State the name of the cell structure in palisade mesophyll cells where photosynthesis occurs.
(iv) Describe the functions of the tissues in a vascular bundle in a leaf.
(ii) Identify feature T shown in Fig. 5.1 and explain how this feature adapts the leaf to float on the surface of the water.
(iii) Explain one other adaptation of this group of aquatic plants.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Vascular Bundle Location
To answer this correctly on the diagram, you would circle one of the distinct circular structures embedded in the spongy mesophyll layer (the veins). These structures contain the xylem and phloem.
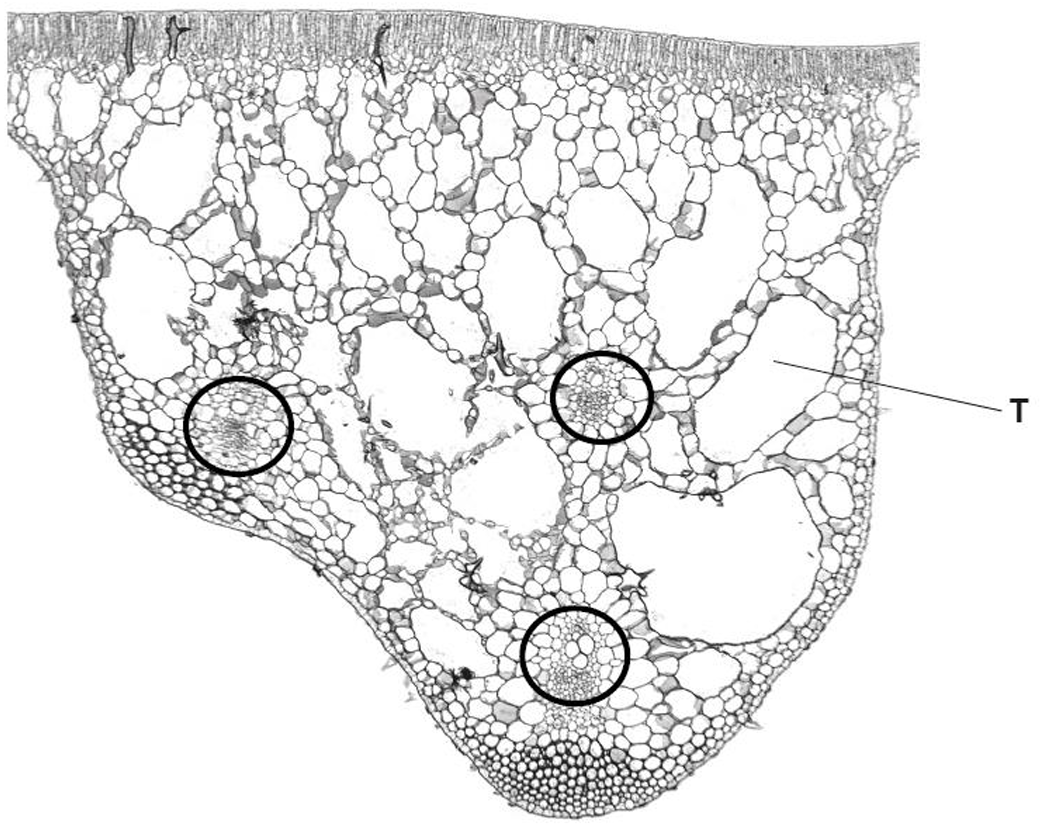
(a)(ii) Palisade Mesophyll Location
The label line X should point to the layer of cells immediately below the upper epidermis. These cells are distinctive because they are elongated, rectangular, and packed tightly together to maximize light absorption.
(a)(iii)
Chloroplasts
Explanation: The palisade mesophyll is the primary site of photosynthesis. These cells contain a high density of chloroplasts, the organelles containing chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy.
(a)(iv)
The vascular bundle contains two main tissues with distinct functions:
- Phloem: Responsible for translocation, which is the transport of sucrose and amino acids from sources (leaves) to sinks (roots/fruits).
- Xylem: Responsible for the transport of water and dissolved mineral ions from the roots to the leaves. Xylem vessels also provide structural support to the plant due to their lignified walls.
(b)(i)
Hydrophyte
Explanation: This is the specific biological term for plants adapted to live in aquatic environments (either submerged or floating).
(b)(ii)
Feature T: Air space (or aerenchyma).
Explanation: These large air gaps reduce the overall density of the leaf. This creates buoyancy, allowing the leaf to float on the water surface to access sunlight for photosynthesis.
(b)(iii)
Acceptable answers include:
- Stomata on the upper epidermis: In land plants, stomata are usually on the bottom to prevent water loss. In floating plants, they must be on top to access the air for gas exchange ($CO_2$ intake and $O_2$ release).
- Thin or no cuticle: Since the plant is in water, there is no risk of desiccation (drying out), so the thick waxy cuticle found in terrestrial plants is unnecessary.
