UQuestion
Where does egestion take place?
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Egestion is the process of eliminating undigested waste materials, also known as feces, from the body. In most animals, including humans, egestion takes place in the large intestine, specifically in the final portion called the colon.
After digestion occurs in the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed, the remaining indigestible and unabsorbed material passes into the large intestine. Here, water and electrolytes are absorbed, and the waste materials are compacted to form feces. The feces then move through the colon and into the rectum, where they are temporarily stored until they are ready to be eliminated from the body through the anus during the process of defecation.
Question
Which organ is part of the digestive system?
A colon
B larynx
C trachea
D ureter
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
A
The colon, is an important part of the digestive system. It is a long, muscular tube located at the end of the digestive tract, following the small intestine. The colon’s main function is to absorb water and electrolytes from the remaining indigestible food matter that enters from the small intestine.
Question
A person has their gall bladder removed.
Which statement is correct?
A They cannot eat carbohydrates.
B They can eat fat only in small amounts.
C They can eat only liquid food.
D They must not eat more than one large meal a day.
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
B
Among the given options, option B is the most accurate statement.
After gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy), the body still produces bile to help digest fats, but it is not stored and concentrated in the gallbladder as before. Without the gallbladder, the bile drips continuously into the intestines. However, some individuals may have difficulty digesting larger amounts of fat in one sitting due to the absence of the gallbladder to release a concentrated amount of bile for fat digestion. Therefore, it is often recommended to eat smaller amounts of fat at a time and spread fat intake throughout the day to aid in digestion and prevent discomfort. Other dietary adjustments may also be suggested by a healthcare professional to ensure proper digestion and overall health.
Question
The diagram shows a piece of small intestine during peristalsis.
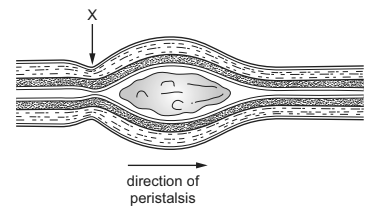
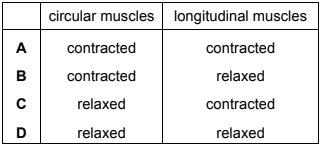
What is happening at X?
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Based on the information given, the diagram is depicting the peristaltic movement in the small intestine. Peristalsis is a coordinated contraction and relaxation of the circular and longitudinal muscles of the digestive tract that helps propel food through the digestive system.
At point X in the diagram, the circular muscles are contracted while the longitudinal muscles are relaxed. This contraction of the circular muscles helps to narrow the diameter of the small intestine, which assists in pushing the food forward through the digestive system. The relaxation of the longitudinal muscles allows for the elongation of the small intestine, accommodating the movement of the food.
Therefore, the correct answer for what is happening at point X is: B ; Circular muscles: Contracted and Longitudinal muscles: Relaxed
Question
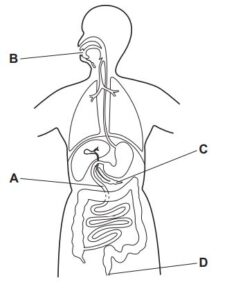
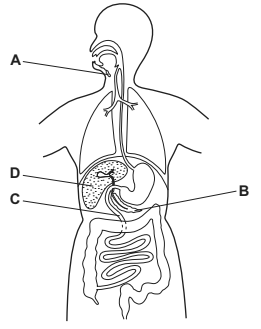
The diagram shows the human alimentary canal.
Which structure does not secrete digestive enzymes?
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Structure D represents the liver. The liver does not directly secrete digestive enzymes into the alimentary canal. Instead, the liver produces bile, a greenish-yellow fluid that contains bile salts, cholesterol, bilirubin, and other substances.
The bile produced by the liver is then transported to the gallbladder for storage and concentration. The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under the liver. When food enters the small intestine, particularly fatty food, the gallbladder contracts, releasing the stored bile into the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine.
Bile is essential for the digestion and absorption of fats. It emulsifies the fat globules into smaller droplets, increasing their surface area. This process aids in the action of pancreatic lipase, an enzyme secreted by the pancreas, which breaks down the fats into fatty acids and monoglycerides, allowing for better absorption.
