Question
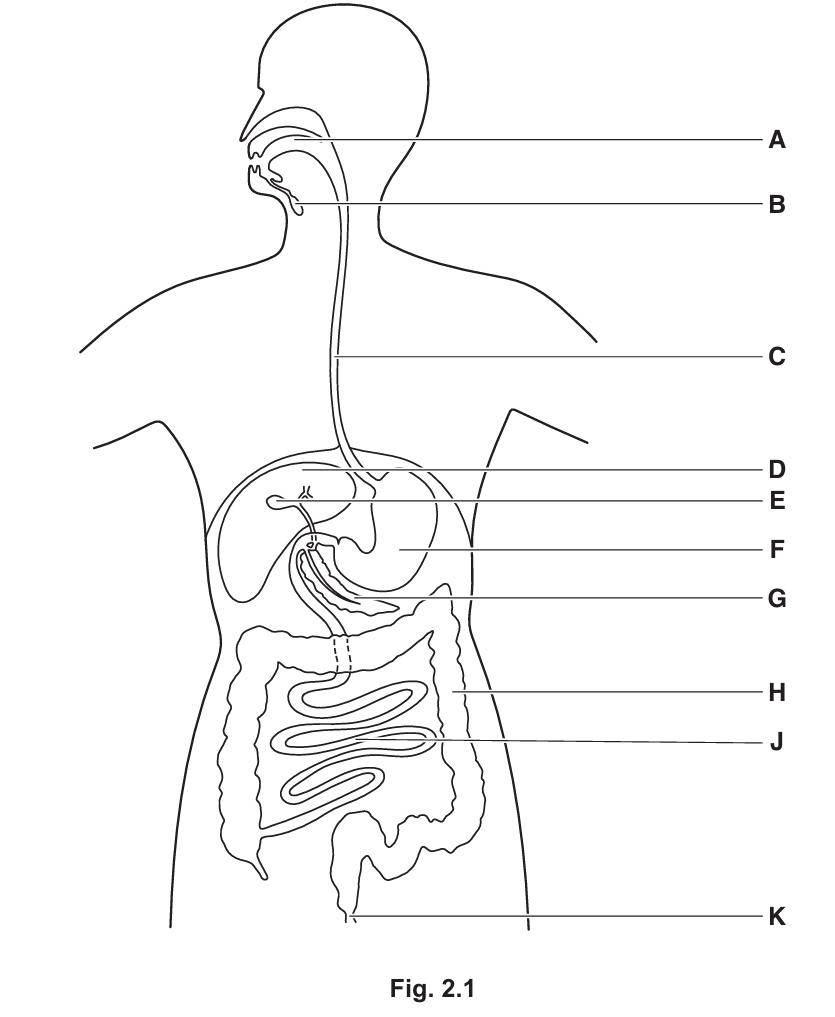
(i) The human digestive system is made up of the alimentary canal and the associated organs.
Food moves through the alimentary canal, but does not move through the associated organs.
The pancreas is one of the associated organs.
State the letter in Fig. 2.1 that identifies the pancreas and state the name of two enzymes secreted by the pancreas.
Name this organ.
State two functions of the small intestine.
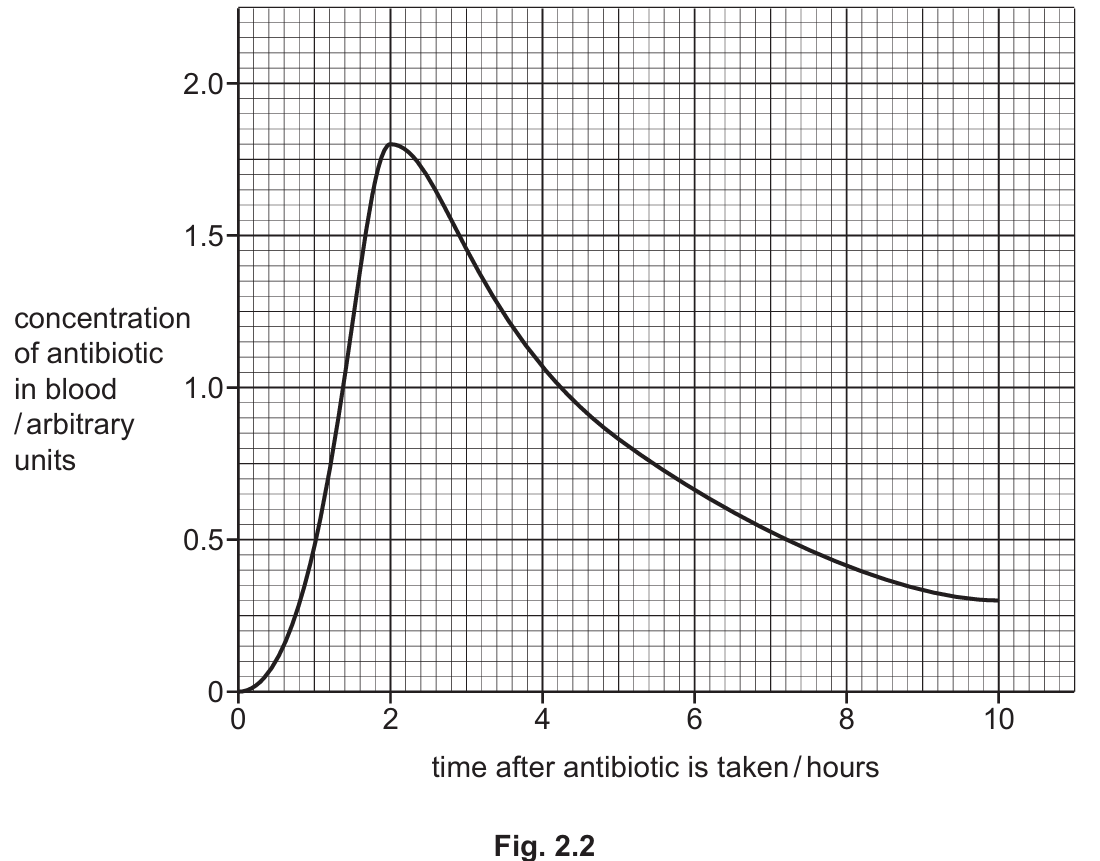
Fig. 2.2 shows the concentration of antibiotic in the blood after a tablet is taken.
(ii) Circle the name of the process of taking substances into the body.
assimilation digestion egestion excretion ingestion
State the name of the component of blood that transports substances such as nutrients, hormones and antibiotics.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
Letter: G
Enzymes: Amylase, Protease (or trypsin), Lipase (any two).
Explanation: In Fig. 2.1, G points to the pancreas, a leaf-shaped gland located just below the stomach (F). The pancreas acts as an accessory organ by secreting digestive enzymes into the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). These enzymes include amylase (digests starch), protease/trypsin (digests proteins), and lipase (digests fats).
(a)(ii)
Letter: D Name: Liver
OR
Letter: E Name: Gall bladder
OR
Letter: B Name: Salivary glands
Explanation: Associated organs help in digestion but food does not pass through them. D is the liver (produces bile), E is the gall bladder (stores bile), and B represents the salivary glands near the mouth.
(a)(iii)
1. Chemical digestion (breakdown of large molecules into small molecules).
2. Absorption of nutrients (movement of digested food molecules into the blood).
Explanation: Structure J is the small intestine. It is the primary site where enzymatic digestion is completed (using enzymes from the pancreas and its own lining) and where digested nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream through structures called villi.
(b)(i)
The concentration of antibiotic increases rapidly to a peak of $1.8$ arbitrary units at $2$ hours. After the peak, the concentration decreases gradually/slowly but remains in the blood (around $0.3$ units) after $10$ hours.
Explanation: The graph shows an initial absorption phase where the drug enters the blood, followed by a metabolism/excretion phase where the level drops.
(b)(ii)
Ingestion should be circled.
Explanation: Ingestion is defined as “the taking of substances, e.g., food and drink, into the body” (usually through the mouth). Digestion is the breakdown of food; egestion is the removal of undigested waste; excretion is the removal of metabolic waste.
(b)(iii)
Plasma
Explanation: Plasma is the liquid component of blood (mostly water) responsible for transporting dissolved substances, including glucose, amino acids, hormones, carbon dioxide, urea, and drugs like antibiotics.
(b)(iv)
Bacteria
Explanation: Antibiotics are chemical substances that kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. They are ineffective against viruses because viruses lack the cell structures (like cell walls or ribosomes) that antibiotics target.
