Question
What is meant by chemical digestion?
A Large insoluble molecules are broken down into small soluble molecules.
B Large soluble molecules are broken down into small insoluble molecules.
C Small insoluble molecules are built up into large soluble molecules.
D Small soluble molecules are built up into large insoluble molecules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The correct answer is A. Chemical digestion refers to the process in which large insoluble molecules are broken down into small soluble molecules. This process occurs in the digestive system and involves the action of various enzymes that break down complex molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids into simpler forms that can be easily absorbed by the body.
Question
The diagram shows two food molecules before and after they have been digested by enzymes.
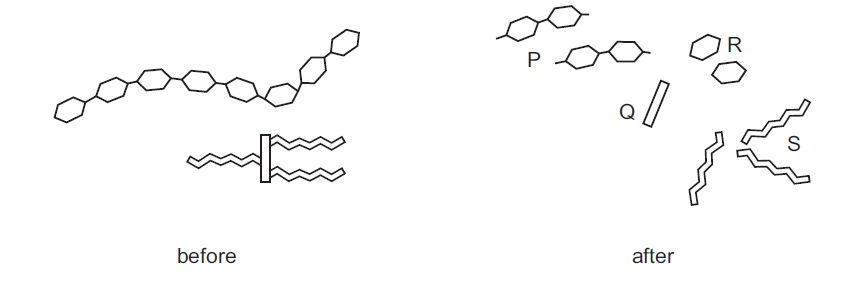
What identifies the products of fat digestion?
A P and R B P and S C Q and R D Q and S
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
During fat digestion, triglycerides (the primary form of dietary fats) are broken down into their constituent components: fatty acids and glycerol. When fats are digested, they undergo a process called lipolysis, which involves the breakdown of triglycerides into their component parts. Triglycerides are large molecules consisting of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol molecule.Therefore, the fat digestion products are Q : glycerol and S : fatty acids.
During digestion, enzymes called lipases break down triglycerides into individual fatty acids and glycerol. These smaller molecules can then be absorbed through the intestinal lining and transported to various cells in the body for energy production or storage.
Question
Which chemical reaction takes place in the stomach?
A Proteins are digested by protease.
B Proteins are digested into fatty acids.
C Starch is digested into amino acids.
D Starch is digested by lipase.
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
A
The correct answer is A: Proteins are digested by protease.
In the stomach, the primary chemical reaction that takes place is the digestion of proteins. Proteins are large molecules made up of amino acids. In order to break down these proteins into smaller, more easily absorbable molecules, the stomach produces an enzyme called protease (specifically pepsin) that catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds between amino acids. This process converts proteins into smaller peptide fragments.
It’s important to note that the digestion of starch (a complex carbohydrate) does not occur in the stomach but rather starts in the mouth with the enzyme amylase, and continues in the small intestine with pancreatic amylase. Starch is broken down into simpler sugars (such as glucose) through the action of amylase enzymes, not lipase.
Therefore, the correct answer is A: Proteins are digested by protease.
Question
In which organ is alcohol broken down?
A brain
B kidney
C liver
D stomach
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
C
Alcohol is primarily broken down in the liver. The liver contains enzymes, such as alcohol dehydrogenase, that metabolize alcohol into acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is further metabolized into acetate by the enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase. Acetate can then be converted into carbon dioxide and water, which are eliminated from the body. While small amounts of alcohol can be metabolized in the stomach by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, the majority of alcohol metabolism occurs in the liver.
Question
The diagram shows a large food molecule changing into smaller molecules.
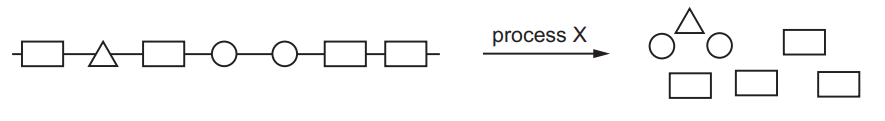
What is process X?
A absorption
B chewing
C digestion
D secretion
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
C
Digestion is the process by which large food molecules are broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by the body. This process occurs in several steps and involves various organs and enzymes.
The digestion of food begins in the mouth, where mechanical digestion occurs through chewing and the mixing of food with saliva. Saliva contains enzymes, such as amylase, which begins the chemical digestion of carbohydrates.
From the mouth, the food travels down the esophagus and enters the stomach. In the stomach, muscular contractions and the secretion of gastric juices help break down the food further. Gastric juices contain hydrochloric acid and enzymes, such as pepsin, which start the digestion of proteins.
After the stomach, the partially digested food enters the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption take place. The small intestine receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver to aid in the breakdown of nutrients. The enzymes break down proteins into amino acids, fats into fatty acids and glycerol, and carbohydrates into simple sugars.
The final step of digestion occurs in the small intestine, where the absorption of the small molecules takes place. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous tiny, finger-like projections called villi, which greatly increase the surface area available for absorption. The small molecules, such as amino acids, fatty acids, and simple sugars, are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to cells throughout the body to be used for energy, growth, and repair.
