Question
(a) Complete the sentences about diffusion.
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of their …………………….. concentration to a region of their ………………… concentration (down a concentration …………………).
The energy for diffusion comes from the …………………… energy of the ……………………. movement of molecules.
(b) Glucose diffuses into cells.
Glucose can be made into starch to be stored in plant cells.
(i) State the chemical elements that make up starch.
(ii) State the name of one other molecule that is made from glucose in plant cells.
(c) A student made a model of a cell using dialysis tubing. The student used the model cell to investigate the diffusion of starch and glucose.
Dialysis tubing only allows small molecules to pass through.
Fig. 6.1 shows the apparatus used.
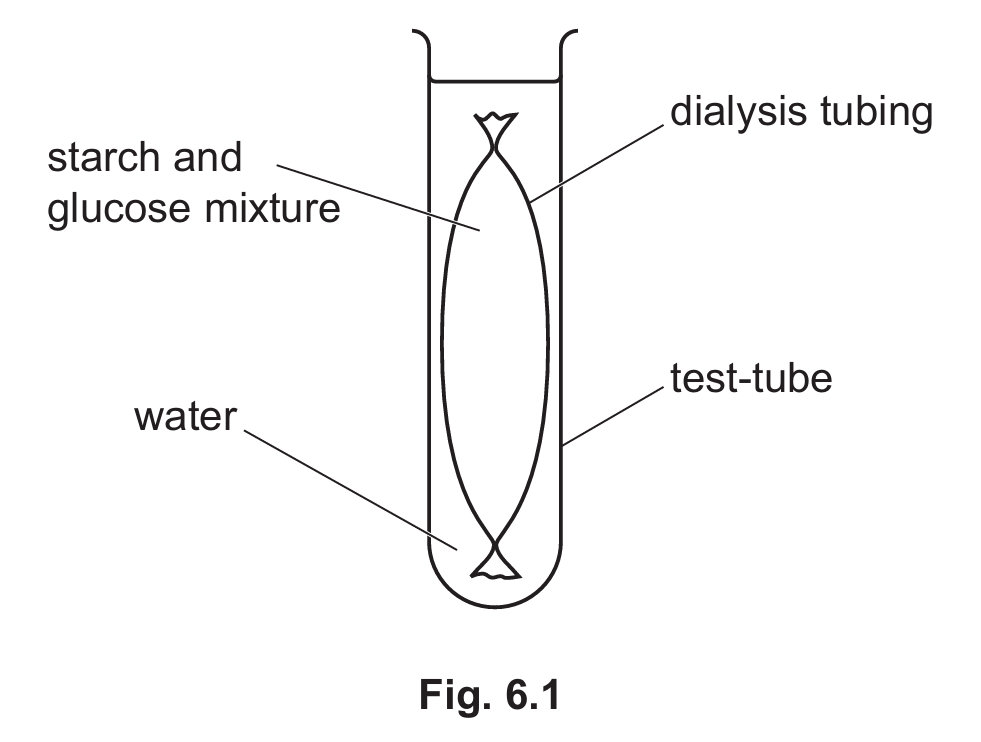
(i) State the name of the cell structure that the dialysis tubing represents.
(ii) After 10 minutes, the student tested the water outside the dialysis tubing for glucose and starch.
The results showed that glucose was present and starch was absent.
Explain these results.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
6 (a)
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration (down a concentration gradient) .
The energy for diffusion comes from the kinetic energy of the random movement of molecules.
6 (b)(i)
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen .
Note: All carbohydrates (including starch, glycogen, and cellulose) and fats are made of these three elements.
6 (b)(ii)
Cellulose (or sucrose, fructose) .
Explanation: Plants synthesize cellulose from glucose to build cell walls. Sucrose is also made from glucose for transport in the phloem .
6 (c)(i)
Cell membrane .
Explanation: The dialysis tubing is a partially permeable membrane that controls which substances can enter or leave the model cell, similar to a cell membrane’s function .
6 (c)(ii)
Glucose moved out because it is a small, soluble molecule that can fit through the pores of the dialysis tubing. Starch did not move out because it is a large, insoluble molecule (polymer) that is too big to pass through the pores.
6 (d)
Amylase .
Explanation: Amylase is the enzyme responsible for breaking down starch into simple reducing sugars (maltose).
