Question
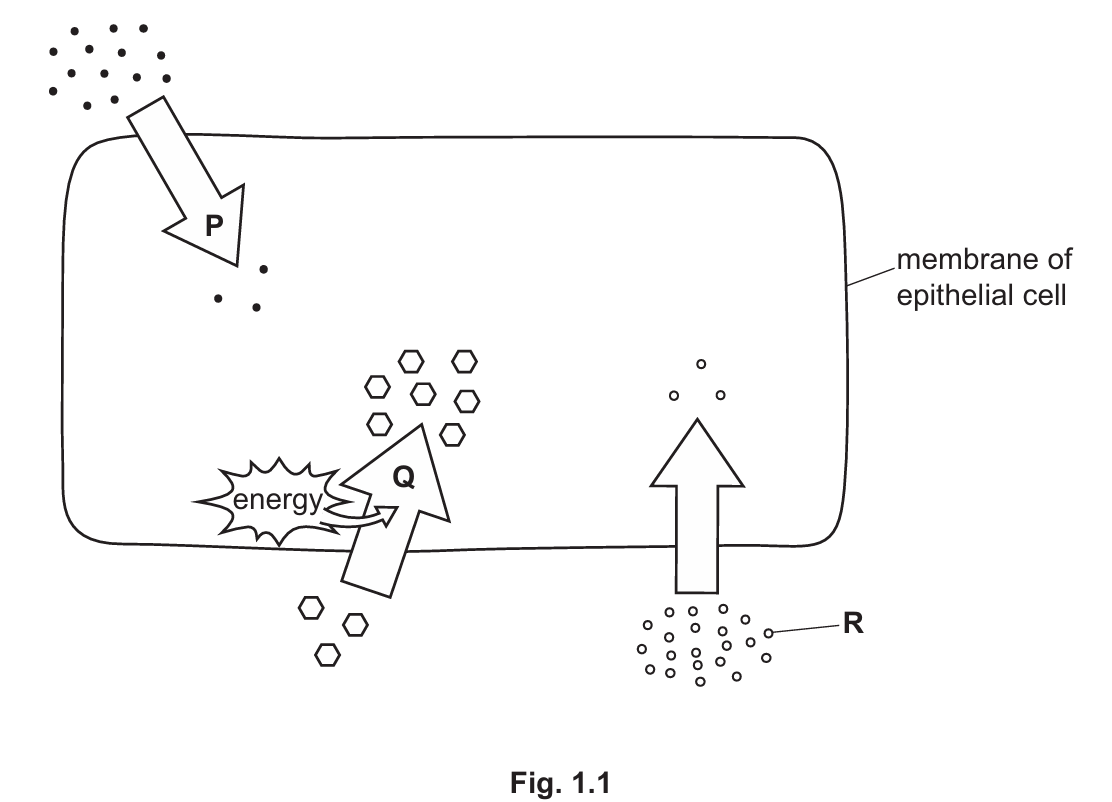
Fig. 1.1 shows the movement of particles through an epithelial cell in the small intestine.
(i) Describe what is meant by the term diffusion.
(i) State the name of the process in human cells that produces carbon dioxide.
(c) In Fig. 1.1, arrow Q represents another type of particle movement.
Identify the type of particle movement represented by arrow Q. Explain your answer.
Suggest why particle R cannot be starch.
(e) Fig. 1.2 is a photomicrograph of red onion cells.
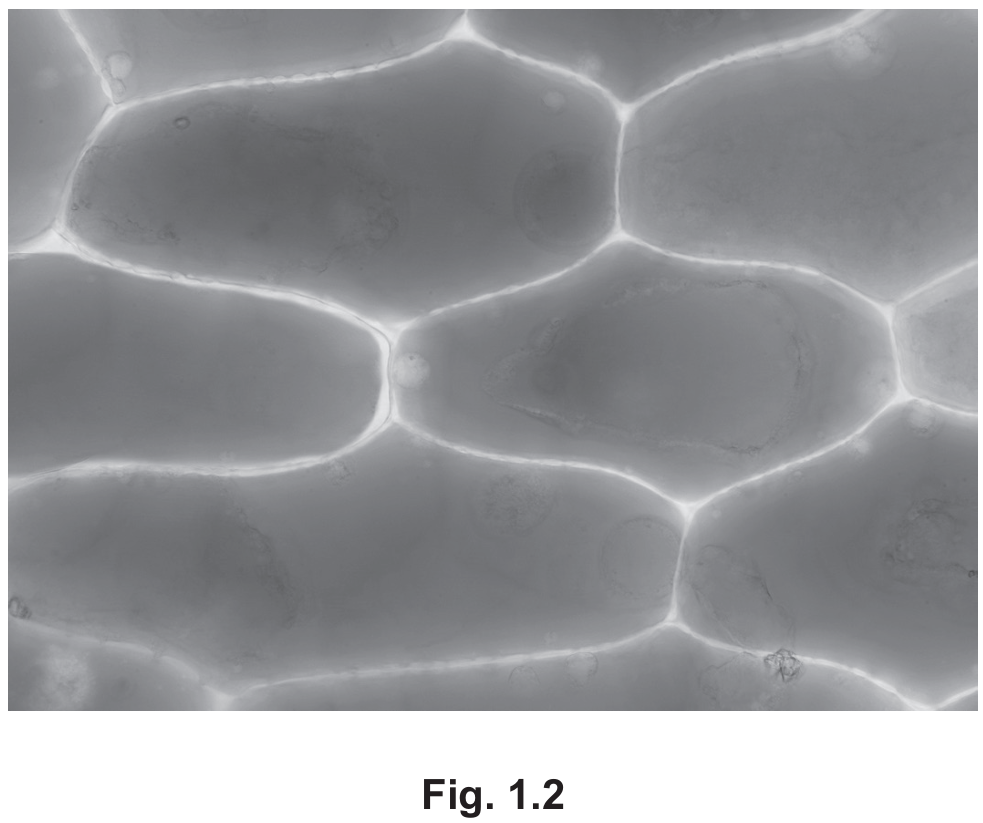
Fig. 1.3 is a photomicrograph of the same red onion cells after being immersed in a salt solution.
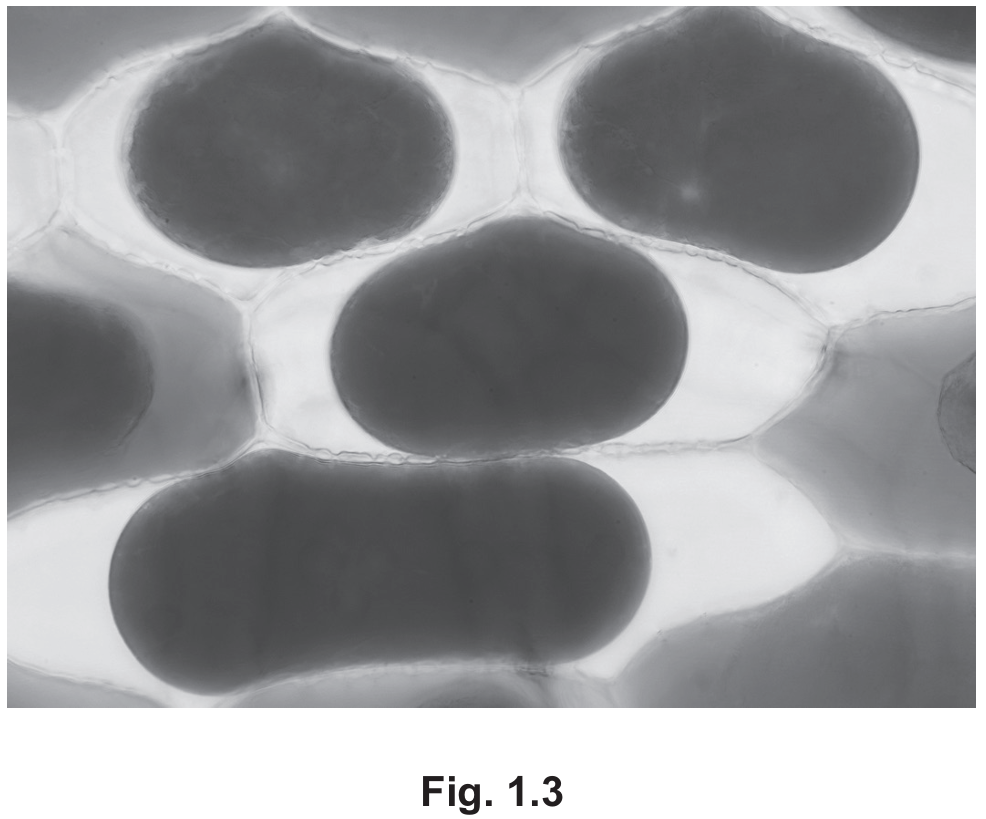
Using Fig. 1.2 and Fig. 1.3, describe and explain the difference in appearance of the cells before and after immersion in salt solution.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration (down a concentration gradient), as a result of their random movement.
Explanation: Molecules are constantly in motion due to kinetic energy. While they move randomly, the statistical probability results in them spreading out until they are evenly distributed.
(a)(ii)
Kinetic energy.
Explanation: Diffusion is a passive process; it relies on the inherent motion (kinetic energy) of the particles themselves, not on metabolic energy (ATP) produced by the cell.
(b)(i)
Aerobic respiration.
Explanation: This is the chemical reaction in mitochondria where glucose reacts with oxygen to release energy, producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
(b)(ii)
The arrow should be drawn pointing from the inside of the epithelial cell to the outside (towards the blood/tissue fluid).
Explanation: Since cells produce \(CO_2\) during respiration, the concentration is highest inside the cell. Therefore, \(CO_2\) diffuses out down its concentration gradient.
(c)
Type of movement: Active transport.
Explanation: The particles are moving from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (against the concentration gradient). The diagram also shows the use of energy, which is required for this process.
Additional Note: Active transport typically involves specific protein carriers in the cell membrane that use energy (from ATP) to pump substances against the gradient.
(d)
Particle R cannot be starch because:
1. Starch molecules are too large.
2. Starch is insoluble.
3. Starch molecules cannot pass through the cell membrane (they must be digested into simple sugars like glucose first).
Explanation: The cell membrane is partially permeable, allowing small molecules like glucose or amino acids to pass, but blocking large polymers like starch.
(e)
Description:
- Before immersion (Fig 1.2), the cells are turgid; the cytoplasm pushes fully against the cell wall.
- After immersion (Fig 1.3), the cells are plasmolysed or flaccid. The cell membrane and cytoplasm have pulled away from the cell wall.
- The vacuole/cytoplasm appears darker or more concentrated after immersion.
Explanation:
- This change is due to osmosis.
- The salt solution surrounding the cells is hypertonic (concentrated), meaning it has a lower water potential than the cell cytoplasm.
- Water moves out of the cell, from a region of higher water potential (inside) to a region of lower water potential (outside), through the partially permeable membrane.
- The loss of water causes a decrease in turgor pressure, leading to the cytoplasm shrinking.
