Question
(b) Fig. 1.1 is a diagram of the human digestive system.
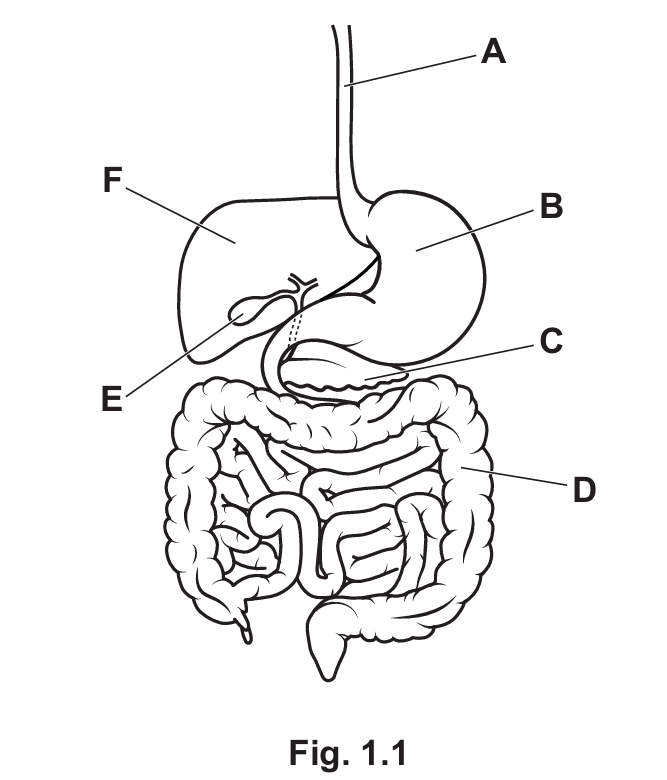
State the letter from Fig. 1.1 that shows one part where:
- physical digestion occurs ……………………
- glucagon is produced ……………………
- bile is produced ……………………
State the names and functions of two types of human teeth.
(e) Fig. 1.2 is a photomicrograph of part of one villus in the small intestine.
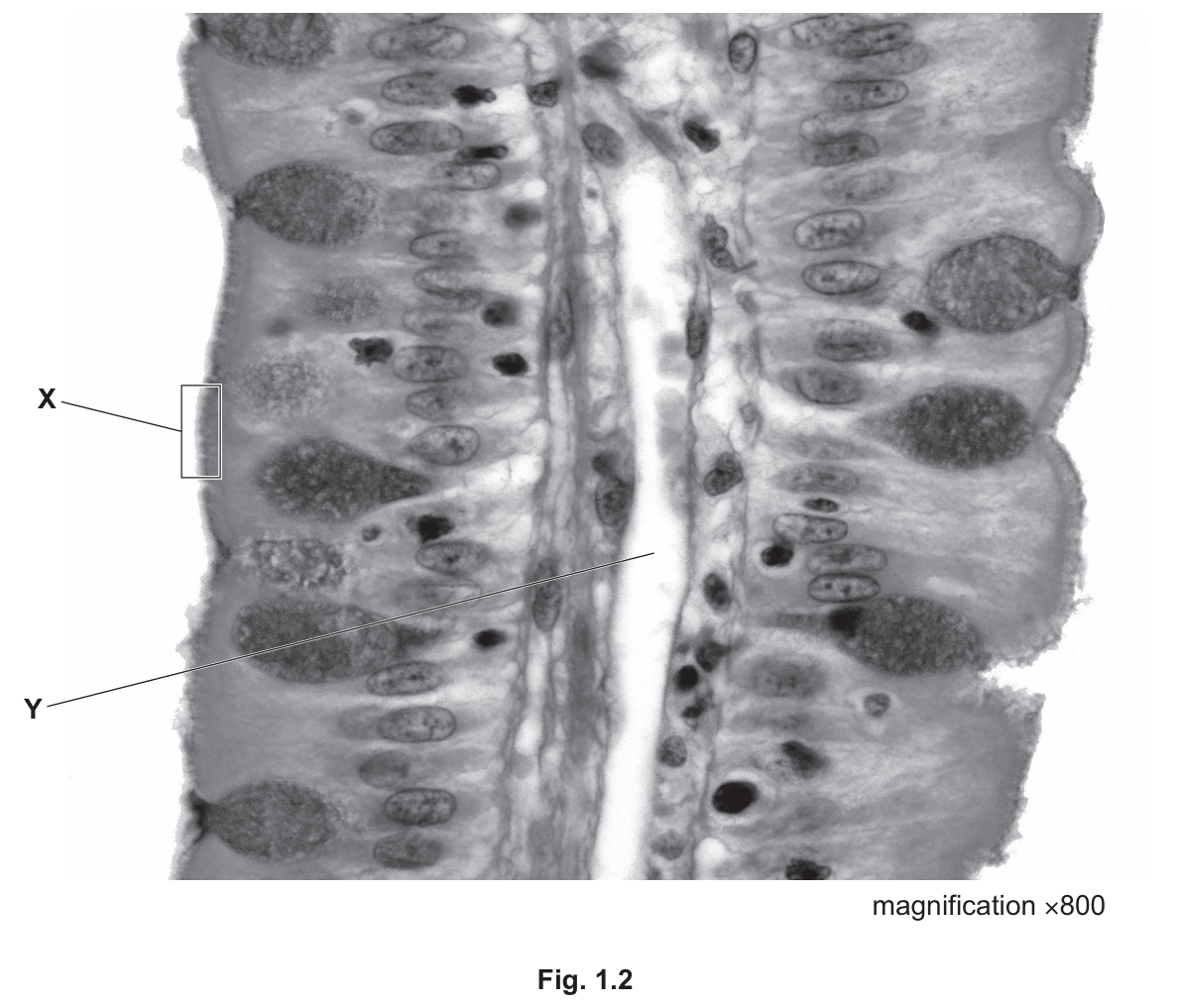
Identify and explain the roles of the parts labelled X and Y in Fig. 1.2.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Physical digestion is the breakdown of food into smaller pieces without any chemical change to the food molecules. This process increases the surface area for enzymes to work on later.
(b)
- Physical digestion occurs: B (The Stomach). The stomach walls churn the food, mechanically breaking it down.
- Glucagon is produced: C (The Pancreas). The pancreas is an endocrine gland that secretes glucagon and insulin to regulate blood sugar.
- Bile is produced: F (The Liver). Note that while bile is stored in the gall bladder (E), it is produced in the liver.
(c)
Bile plays a crucial role in physical digestion through emulsification. It breaks down large drops of fat into smaller droplets. This significantly increases the surface area of the fat, allowing the enzyme lipase to digest fats into fatty acids and glycerol more rapidly.
(d)
(Any two of the following pairs are acceptable):
- Incisors: Used for biting, cutting, or piercing food.
- Canines: Used for tearing, piercing, or holding food.
- Premolars: Used for grinding, chewing, or crushing food.
- Molars: Used for grinding, chewing, or crushing food.
(e)
- Part X (Microvilli): These are tiny projections on the surface of the epithelial cells. Their role is to increase the surface area significantly to maximize the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood. They also contain enzymes (like maltase) for the final stages of digestion.
- Part Y (Lacteal): This is a lymphatic vessel found in the center of the villus. Its function is the absorption of fatty acids and glycerol (the products of fat digestion), which eventually enter the bloodstream via the lymphatic system.
