Question
Pepsin is a protease enzyme found in the alimentary canal.
(a) (i) Name the product formed from the digestion of proteins by protease enzymes.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(ii) State the organ in the alimentary canal where pepsin is secreted.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[1]
(b) A biologist performed an experiment to find the optimum pH for the activity of pepsin.
The enzyme activity was measured in four test-tubes. Each test-tube contained a 1cm3 cube
of cooked egg white which contains protein.
Fig. 3.1 shows the four test-tubes.
The biologist measured the time taken for the complete digestion of the cubes of cooked egg
white.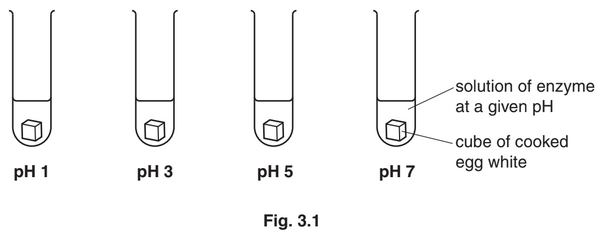
(i) The biologist ensured all the cubes of cooked egg white were exactly the same size.
Suggest why.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
(ii) Temperature must be controlled in this experiment.
Describe how temperature could be controlled.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
10
© UCLES 2016 0610/41/O/N/16
(c) The same experiment was performed with trypsin, another protease enzyme.
Predict the optimum pH for trypsin.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[1]
(d) Enzymes, such as proteases, are important in digestion.
Describe in detail how enzymes function, using other digestive enzymes as examples.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) Dialysis tubing is an artificial membrane, which is similar to the lining of the intestine.
A student investigated the diffusion of glucose through dialysis tubing by using the apparatus
shown in Fig. 3.1.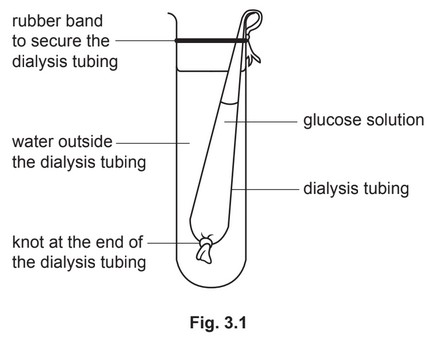
The student took samples of the water outside the dialysis tubing at 5 minute intervals and
tested the samples with Benedict’s solution.
The results are shown in Table 3.1.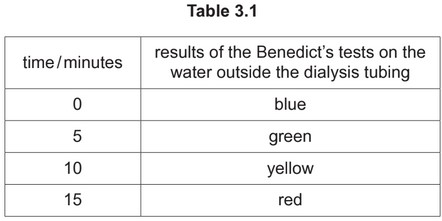
(i) Describe and explain the results shown in Table 3.1.
(ii) The student repeated the investigation with a higher concentration of glucose in the dialysis tubing.
Predict the results that the student would observe.
(b) Fig. 3.2 shows a drawing of a cell from the lining of the small intestine. The lumen is the
space inside the intestine where food is digested.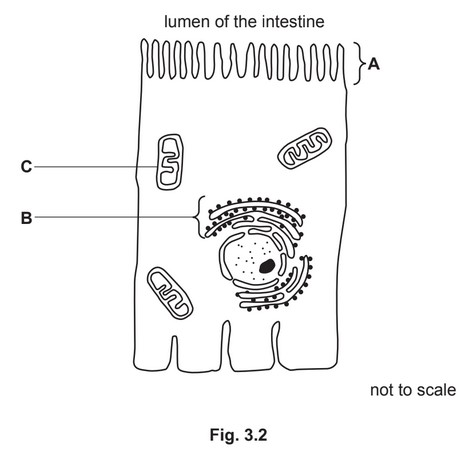
State the names of the three labelled structures in Fig. 3.2 and describe the role of each
structure in the intestinal cell.
(c) The cholera bacterium can survive in the small intestine and the large intestine. The bacterium
releases a toxin that interacts with receptors on the surface of cells.
Fig. 3.3 shows the effect of the toxin. The arrows indicate the direction of movement.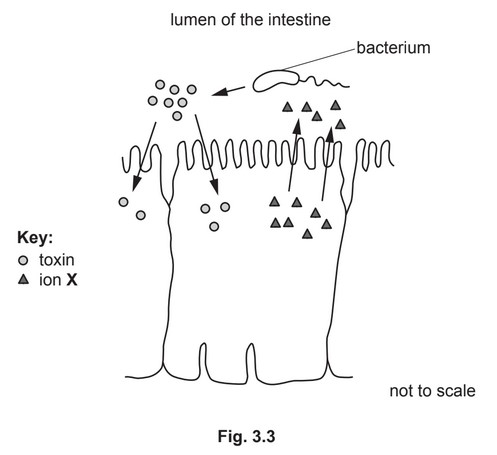
The toxin stimulates the secretion of ion X out of the intestinal cell.
(i) State the name of ion X.
(ii) Describe the effects on the body of the secretion of ion X into the lumen of the intestine.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) any three from:
blue at time 0 indicates no glucose present ;
ensures that no glucose on outer surface of dialysis tubing / in water, as a result of an error ;
green / yellow / red, indicates presence of glucose ;
glucose, diffuses / moves, out of dialysis tubing / into water ;
(movement is) down the concentration gradient / high to low concentration ;
dialysis tubing is permeable to glucose ;
AVP ;
(ii) idea that (Benedict’s solution) changes colour quicker / gives more intense colour / AW ;
(b) A are microvilli ;
function: allow movement of substances into the cell / increase surface area for absorption by diffusion OR active
transport / have proteins in the membrane for active transport ;
B is the (rough) endoplasmic reticulum / (R)ER ;
function: site of protein synthesis / modify proteins / assemble amino acids in a specific sequence to make (named)
protein ;
C is a mitochondrion ;
function: aerobic respiration / provides energy for (named) cell process(es) ;
(c) (i) chloride ;
(ii) any four from:
loss of water ;
by osmosis / down water potential gradient ;
diarrhoea ;
dehydration ;
loss of other, (named) ions / salt(s) ;
AVP ;
