Question
Fig. 3.1 shows a photomicrograph of a section of a root.
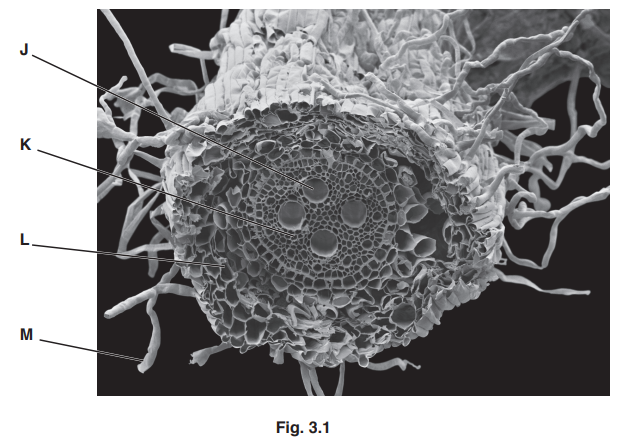
(a) Structure J is a xylem vessel.
The xylem vessels conduct water from the roots to the stems.
State the features of xylem vessels that enable them to conduct water.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[3]
(b) Describe the pathway of water from outside the root to the xylem vessels (J) at the centre of
the root. Use the letters in Fig. 3.1 in your answer.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..[5]
(c) Scientists wanted to determine the flow-rate of water in roots.
They measured the flow-rate in three zones of onion roots as shown in Fig. 3.2.
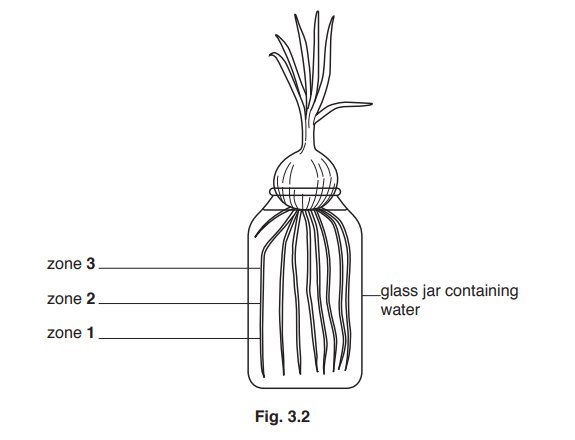
They measured the flow-rate in healthy roots and roots that had been treated with a toxic
solution.
Their results are shown in Table 3.1.
(i) Calculate the percentage increase in the average flow-rate between zone 1 and 3 for
healthy roots.
Give your answer to two significant figures.
Show your working.
…………………………………………………… %
[2]
(ii) The scientists observed that the xylem vessels nearer the root tip were narrower than
the xylem vessels higher up the root.
Describe how the width of xylem vessels in different zones of a root affects the average
flow-rate of water. Use the information in Table 3.1 in your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[3]
(iii) Suggest why there was little difference in the flow-rate in healthy roots and in roots
treated with the toxic solution.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………[2]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Phloem is used to transport sucrose and amino acids in plants. Sucrose is a carbohydrate.
(a) Describe the uses of carbohydrates and amino acids in plants.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… [4]
(b) Fig. 2.1 shows a diagram of a plant. The arrows point to circles containing magnified
cross-sections of those parts of the plant.
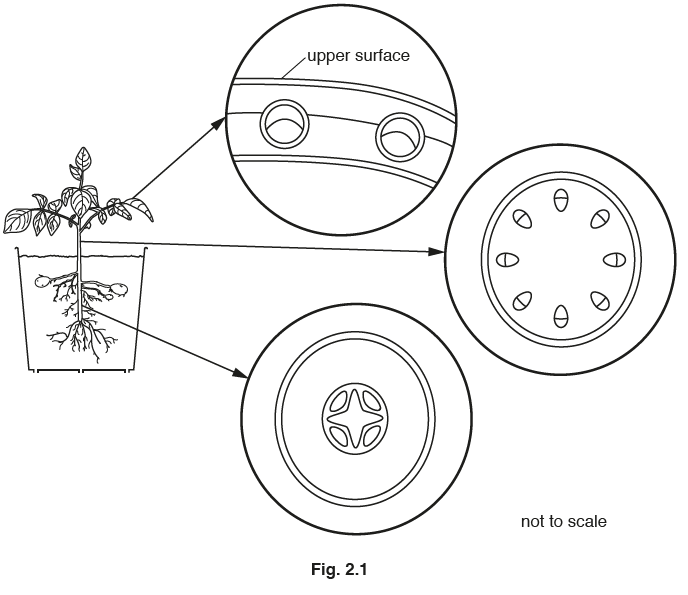
Label the position of the phloem in each of the three magnified sections in Fig. 2.1.
Use a label line and the letter P for each section.
(c) Aphids are used by investigators to discover how plants transport sucrose.
Fig. 2.2 shows an aphid with its mouthparts inserted into a plant stem to feed on the liquid in
the phloem.

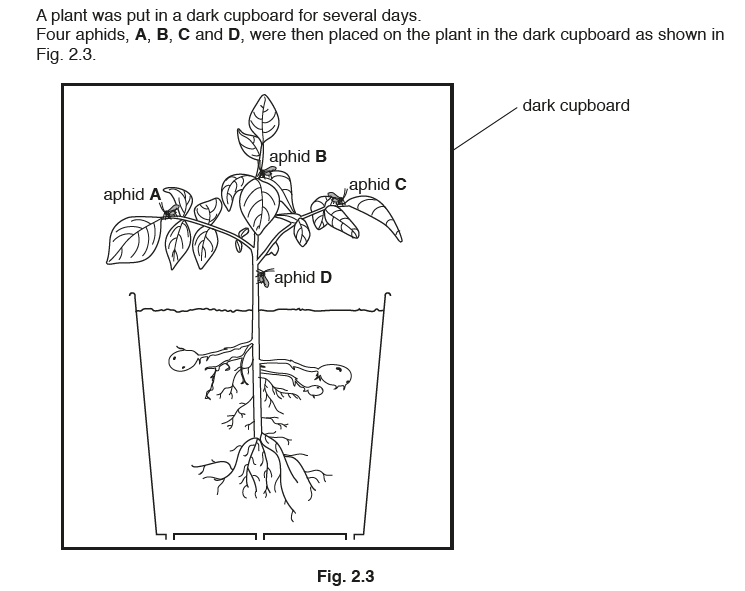
(i) Immediately after the aphids were placed on the plant it was observed that:
• all the aphids ingested the same volume of liquid from the phloem
• aphid D ingested the highest concentration of sucrose.
Explain why aphid D ingested the highest concentration of sucrose.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
(ii) Many crop farmers try to prevent insects such as aphids from damaging their plants.
Describe how modern technology is used to reduce damage to crop plants by insects.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
(iii) Other insects are useful to crop farmers.
Give one example of how insects are useful to farmers.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:

Question
a) Phloem and xylem are two types of tissue in plants.
Fig. 9.1 shows a section through a plant stem, A, and a plant leaf, B.
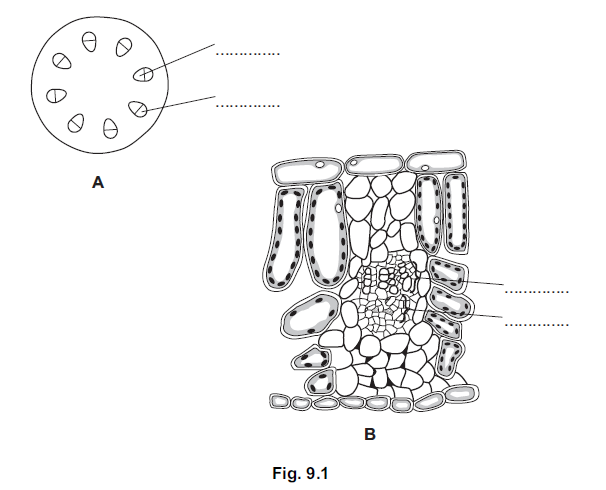
(i) Label the phloem (P) and the xylem (X) on both A and B on Fig. 9.1.
Write the letters P and X on both A and B on Fig. 9.1. [2]
(ii) Describe two functions of the xylem.

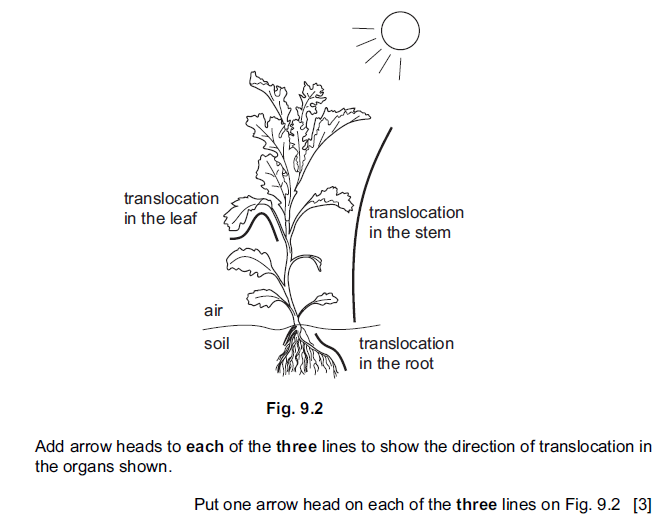
(b) Translocation takes place in the phloem tissue.
(i) State which materials are translocated in the phloem.

(ii) Fig. 9.2 shows a plant in the sunlight. The three lines (________) are arrows, with
no arrow heads, showing the translocation of materials within parts of the plant.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:

