Question
The student collected four small plants and placed them in beakers filled with water.
A layer of oil was placed on top of the water to prevent evaporation from the beaker itself.
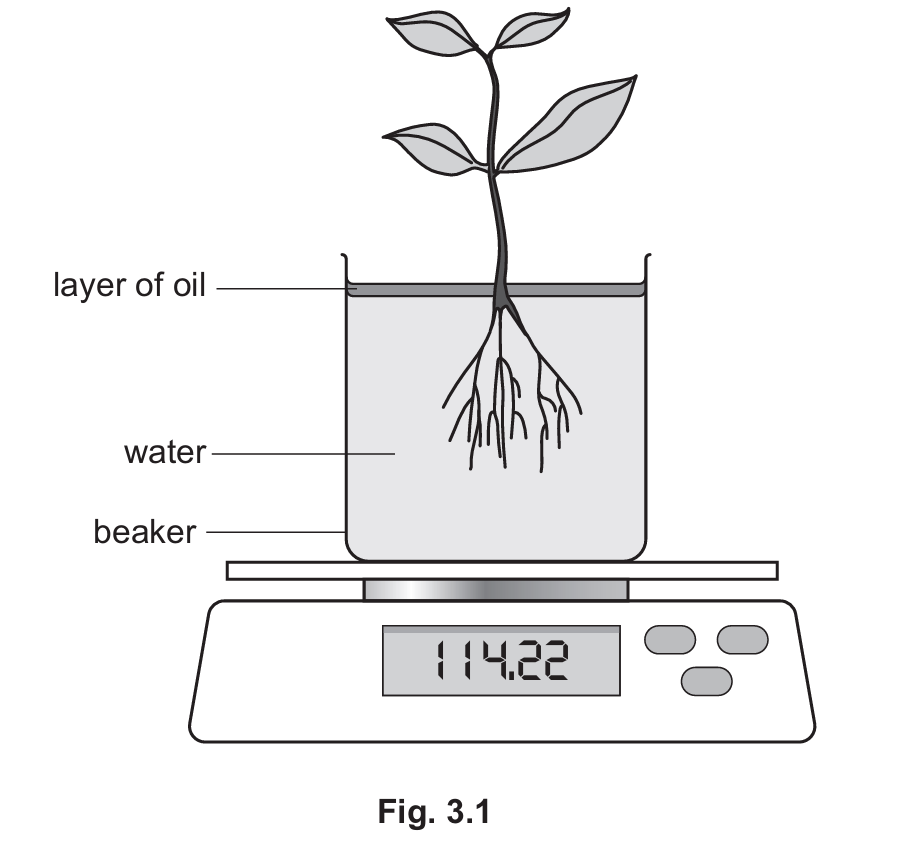
Each plant was placed in a different temperature-controlled room for three hours.
After three hours, the student measured the final masses.
The results are shown in Table 3.1. 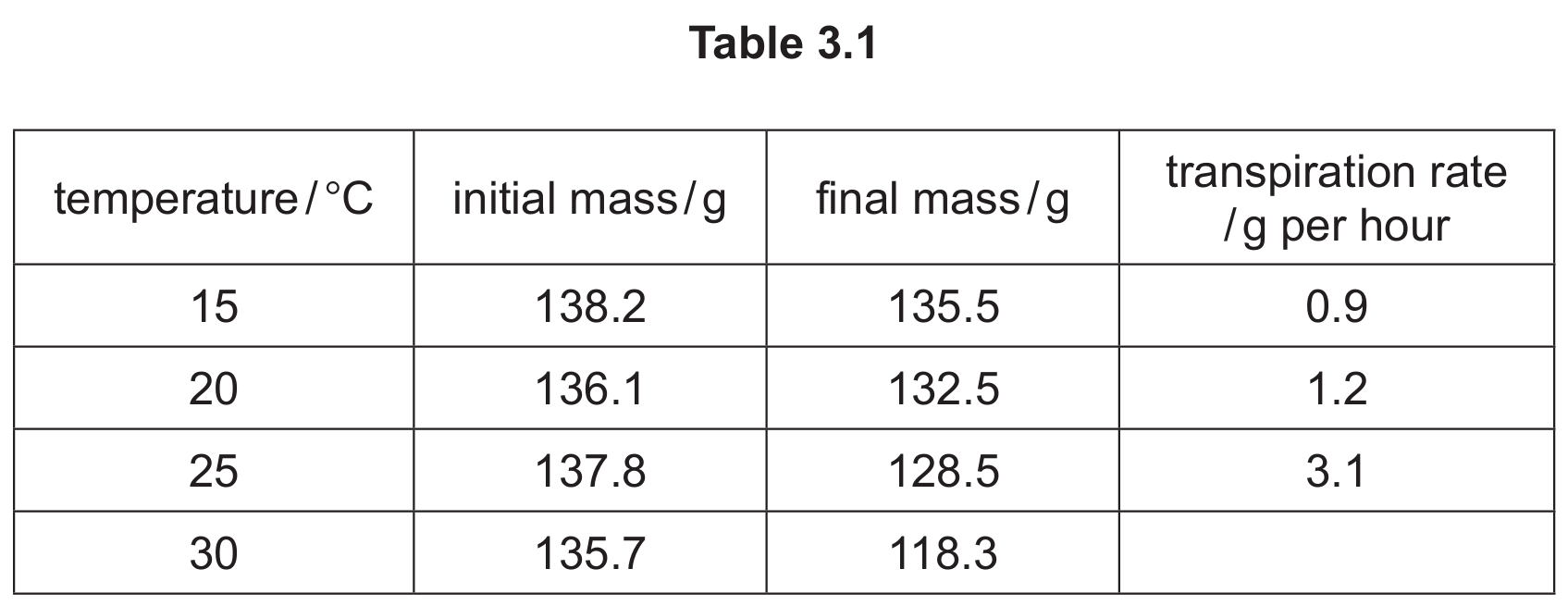
(i) Using the information in Table 3.1, calculate the transpiration rate in the plant kept at \(30^{\circ}\text{C}\).
Predict the effect of these conditions on the transpiration rate.
Explain your prediction.
(iv) Complete the sentences about water movement through the xylem.
The xylem transports water and ………………… .
Xylem cells form a long continuous ………………….. with thick walls containing cellulose and ………………… .
Water moves upwards in the xylem because of transpiration ………………….. .
This draws up a …………….. of water molecules, held together by …………………. between water molecules.
Fig. 3.2 is a photomicrograph of a cross-section of a marram grass leaf.
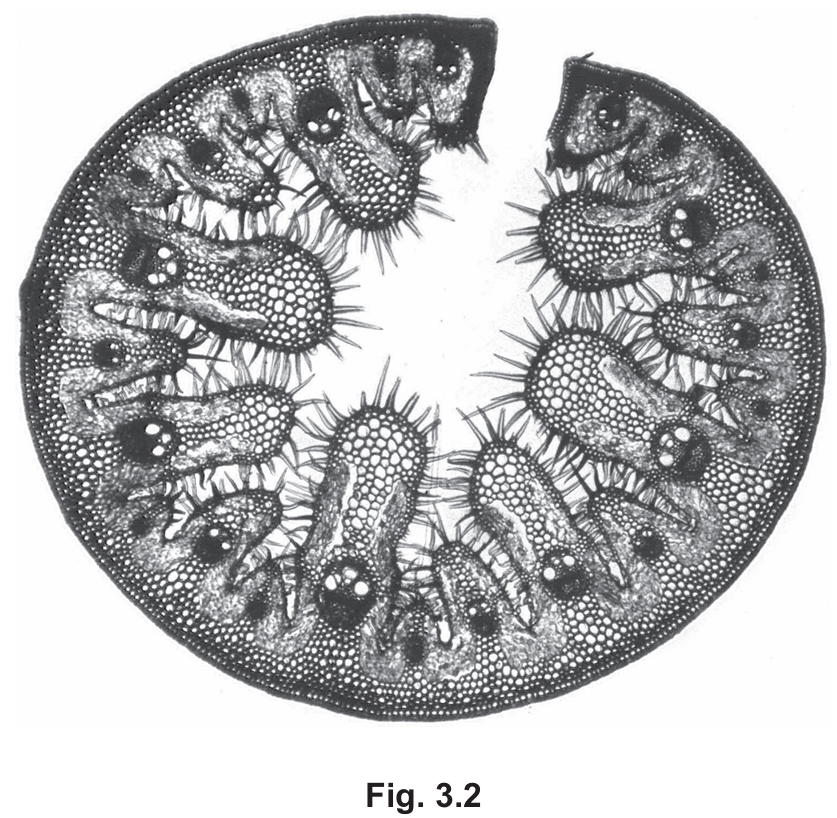
Explain one way that the marram grass leaf shown in Fig. 3.2 is adapted to reduce transpiration.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Water enters the plant through the root hair cells by osmosis. It then moves through the root cortex cells before reaching the xylem vessels.
(b)(i)
First, calculate the total mass lost: \(135.7 \text{ g} – 118.3 \text{ g} = 17.4 \text{ g}\).
The experiment lasted for 3 hours, so divide the total loss by the time:
\(\frac{17.4}{3} = \mathbf{5.8} \text{ g per hour}\).
(b)(ii)
Description: The rate of transpiration is higher at \(25^{\circ}\text{C}\) (\(3.1 \text{ g/hr}\)) compared to \(15^{\circ}\text{C}\) (\(0.9 \text{ g/hr}\)). As temperature increases, the rate of water loss increases.
Explanation: At higher temperatures, water molecules possess more kinetic energy. This increases the rate of evaporation from the surface of mesophyll cells into the air spaces. Consequently, the rate of diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf through the stomata increases.
(b)(iii)
Prediction: The transpiration rate will increase.
Explanation: Lower humidity outside the leaf increases the concentration gradient (or water potential gradient) between the moist air spaces inside the leaf and the dry air outside. A steeper gradient causes water vapour to diffuse out of the stomata more rapidly.
(b)(iv)
The xylem transports water and mineral ions.
Xylem cells form a long continuous tube (or vessel) with thick walls containing cellulose and lignin.
Water moves upwards in the xylem because of transpiration pull.
This draws up a column of water molecules, held together by forces of attraction (or cohesion) between water molecules.
(c)(i)
Wilting occurs when the rate of water loss (transpiration) is greater than the rate of water uptake by the roots. This causes water to move out of the plant cells by osmosis. The cells lose their turgor pressure (becoming flaccid) or undergo plasmolysis. Since non-woody plants rely on turgor pressure against cell walls for support, the loss of pressure causes the plant to droop.
(c)(ii)
The marram grass leaf is rolled (or curled). This adaptation traps moist air (water vapour) inside the leaf roll near the stomata. This reduces the concentration gradient between the inside of the leaf and the immediate external environment, thereby reducing the rate of diffusion of water vapour out of the leaf. Other acceptable answers based on the image include the presence of hairs (which also trap moisture) or sunken stomata.
