Question
A student wanted to investigate the effect of humidity on transpiration. She set up two sets of apparatus with identical-sized plants of the same species.
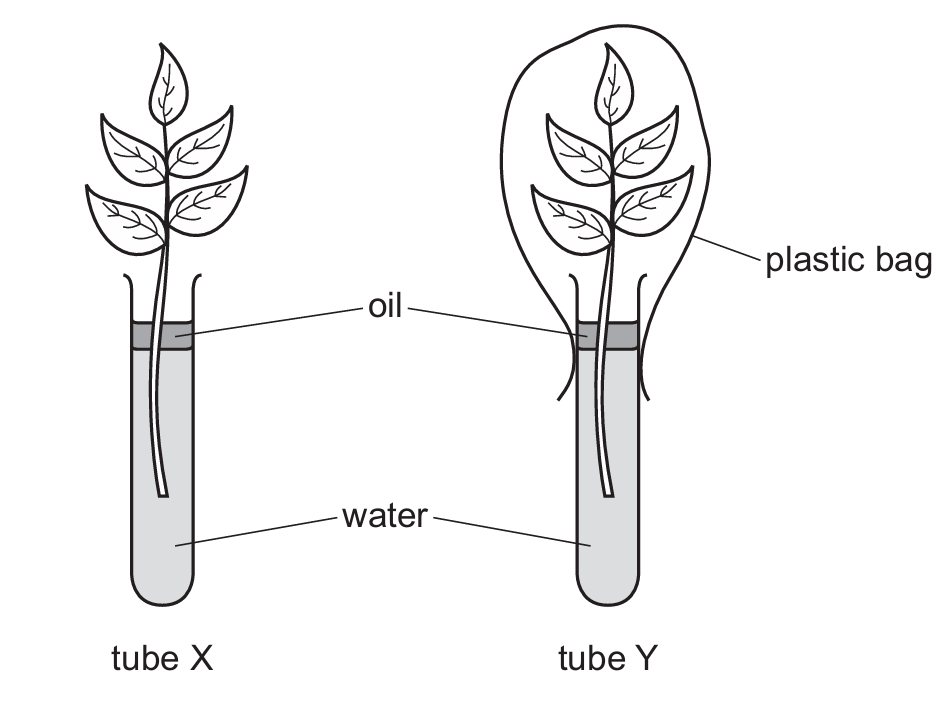
The masses of the water in both tubes were measured at the start of the investigation and again after five days. The table shows the results of the investigation.

Which statement describes and explains these results?
(B) Transpiration in tube $Y$ was higher than in tube $X$ as the plastic bag increased the humidity.
(C) Transpiration in tube $Y$ was lower than in tube $X$ as the plastic bag decreased the humidity.
(D) Transpiration in tube $Y$ was lower than in tube $X$ as the plastic bag increased the humidity.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
The mass of water lost from a plant was investigated. The leaves of the plant were covered with a type of grease that acts as a waterproof barrier. The environmental conditions remained the same throughout the experiment. The table shows the results of the investigation.
| treatment | mass lost in seven days / $g$ |
|---|---|
| no grease applied | $12.0$ |
| grease applied only to the upper surface of every leaf | $8.7$ |
| grease applied to both surfaces of every leaf | $0.0$ |
What is the mean daily rate of water loss through the upper surface of the leaves?
(B) $1.24 \text{ g / day}$
(C) $1.71 \text{ g / day}$
(D) $3.30 \text{ g / day}$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which conditions cause the highest rate of transpiration?
(B) high temperature, high wind speed and low humidity
(C) low temperature, low wind speed and low humidity
(D) low temperature, low wind speed and high humidity
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Transpiration is the evaporation of water from leaf surfaces, which is driven by a concentration gradient. High temperatures increase the kinetic energy of water molecules, speeding up evaporation. High wind speeds prevent water vapor from accumulating near the leaf, maintaining a steep diffusion gradient between the inside and outside of the leaf. Conversely, low humidity ensures the surrounding air is dry, further maximizing the rate at which water diffuses out of the stomata. Therefore, the combination of hot, windy, and dry conditions results in the maximum water loss.
✅ Answer: (B)
