Question
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from leaves.
Water evaporates from the surfaces of the ……………….. cells into the ……………. spaces.
Water vapour moves out of the leaves through the …………………. by the process of ………………….. .
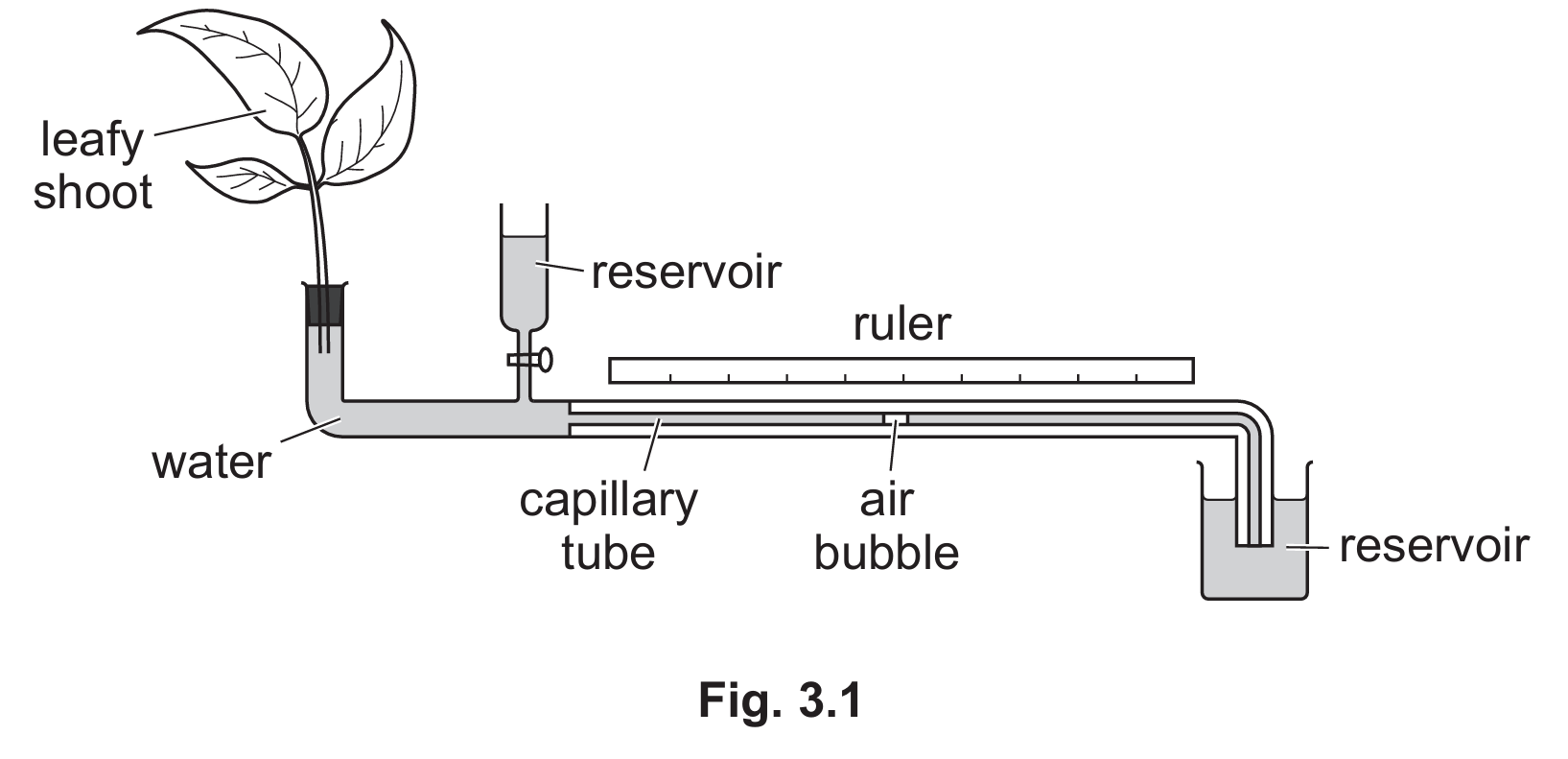
The results are shown in Table 3.1
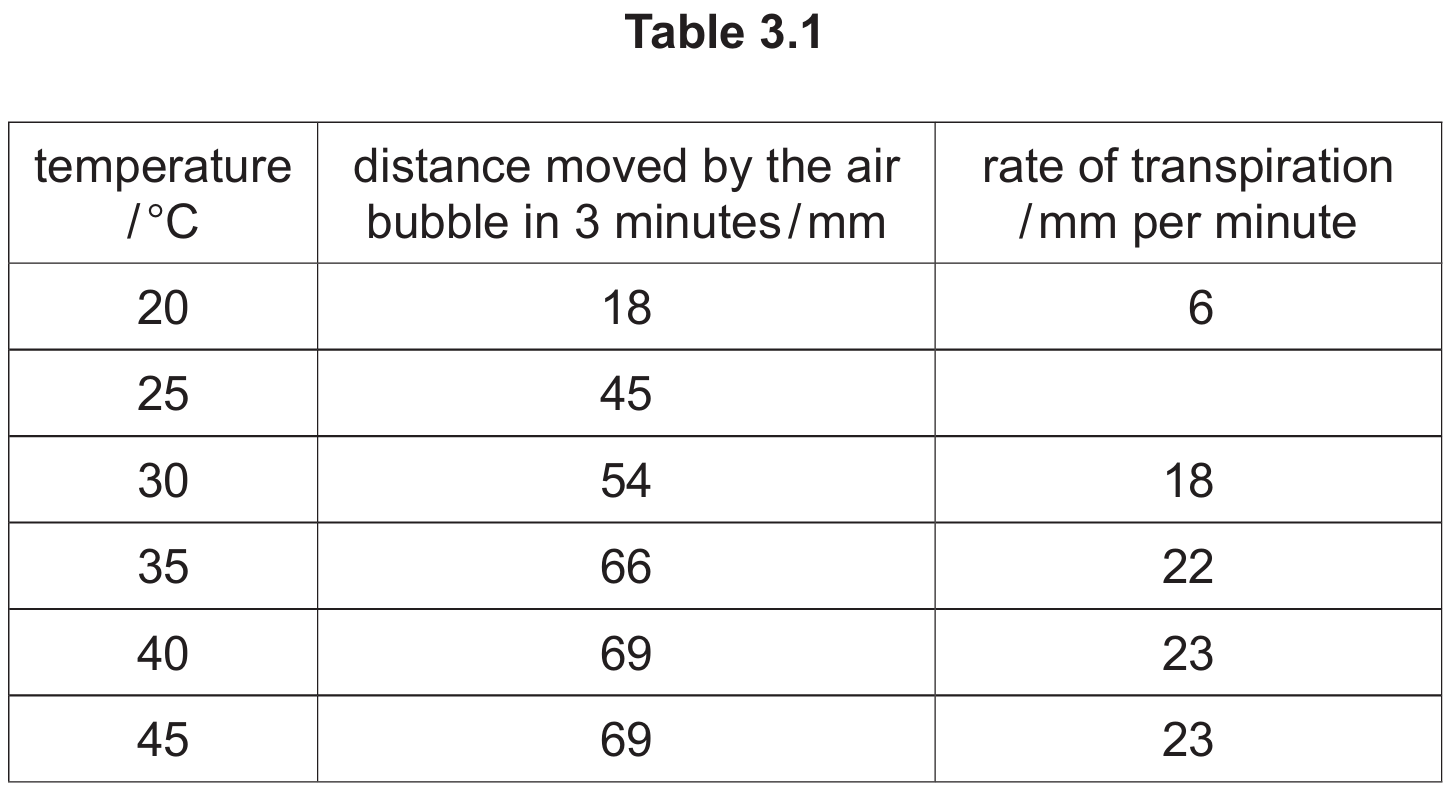
(i) Using the data in Table 3.1, calculate the rate of transpiration at (25^\circ\text{C}).
(ii) The list shows six conclusions. Tick ((\checkmark)) three conclusions for the data shown in Table 3.1.

▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Water evaporates from the surfaces of the mesophyll cells into the air spaces.
Water vapour moves out of the leaves through the stomata by the process of diffusion.
Explanation: The syllabus states that water evaporates from the surfaces of mesophyll cells into air spaces and then diffuses out of the leaves through stomata as water vapour. This process is driven by the random movement of molecules.
(b)(i)
(15) (mm per minute)
Explanation: The rate is calculated by dividing the distance moved by the time taken. At (25^\circ\text{C}), the distance is (45) mm over (3) minutes.
(b)(ii)
The correct conclusions are:
- As temperature increases, the rate of transpiration increases and then remains constant.
(The rate increases from (6) to (23) mm/min as temperature goes from (20^\circ\text{C}) to (40^\circ\text{C}), then stays at (23) mm/min at (45^\circ\text{C}).) - From (20^\circ\text{C}) to (30^\circ\text{C}), the rate of transpiration triples.
(At (20^\circ\text{C}) rate is (6). At (30^\circ\text{C}) rate is (18). (6 \times 3 = 18).) - From (20^\circ\text{C}) to (45^\circ\text{C}), the rate of transpiration increases by (17) mm per minute.
(Rate at (45^\circ\text{C}) is (23). Rate at (20^\circ\text{C}) is (6). Difference: (23 – 6 = 17).)
