Question
Scientists investigated the effect of cuticle thickness on water loss from the leaves of the balsam
fir tree, Abies balsamea.
The leaves were divided into three groups:
A – thick cuticle
B – medium cuticle
C – thin cuticle
Samples of leaves from each group were weighed. The leaves were placed on a tray in dry air at
20 °C. The samples of leaves were reweighed, at intervals, over 15 hours.
The scientists calculated the mass of each sample of leaves as a percentage of the initial mass.
Fig. 5.1 shows the results.
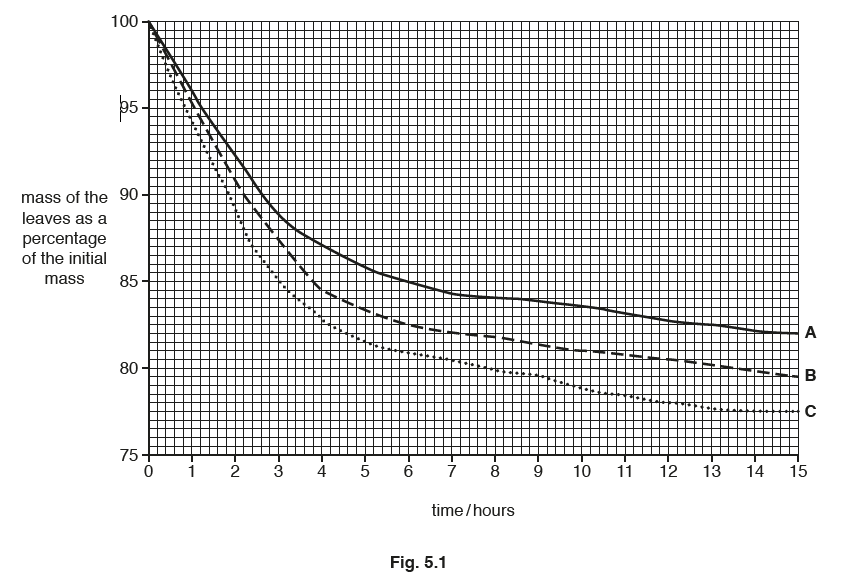
(a) (i) Describe and explain the results shown in Fig. 5.1.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [5]
(ii) The investigation was repeated on a day when the air humidity was higher.
Suggest and explain the effect that this would have on the results.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [3]
(b) The leaves of pine trees show xerophytic features. Stems and roots also show xerophytic
adaptations.
State one adaptation of the stem and one adaptation of the root in xerophytes.
stem …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
root ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[2]
(c) Water is one of the raw materials needed for the production of sugars in photosynthesis.
(i) State the name of the other raw material needed for photosynthesis.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) State three ways a plant uses the sugars produced in photosynthesis.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
[3]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Transpiration occurs in plants.
(a) Explain what is meant by the term transpiration.
(b) Fig. 9.1 shows a healthy plant and its appearance three hours later when it has started to wilt.
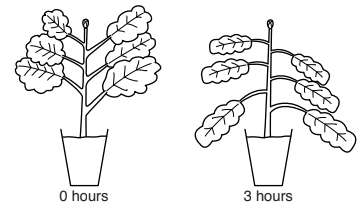
Fig. 9.1
State and explain two changes a student could make to the environment of the plant that would stop it wilting any further.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) evaporation of water ;
(from) mesophyll (cells / tissue) ;
water vapour loss ;
by diffusion ;
through stomata ;
(b) add water ;
to restore turgor to cells / AW ;
put in the dark / put in shade / AW ;
stomata close so, less water loss / less transpiration ;
lower temperature ;
reduces KE of water molecules ;
protect from draughts / wind / method of ;
to reduce diffusion gradient ;
increase humidity / method of ;
to reduce diffusion gradient ;
Question
(a) A scientist investigated the effect of temperature on the mass of leaves picked from a
tea plant, Camellia sinensis.
• Three samples of leaves were picked and the mass of each sample of leaves was
recorded.
• Each sample of leaves was kept at a different temperature for four hours.
• After four hours, the mass of each sample of leaves was measured and recorded
again.
• The scientist then calculated the final mass as a percentage of the initial mass for
each sample.
Fig. 3.1 shows the results.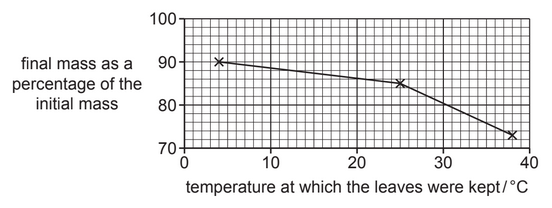
(i) Explain the results shown in Fig. 3.1.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) State one factor, other than temperature, that would affect the loss of mass from the
leaves of a plant.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) Fig. 3.2 is a photomicrograph of the tissue that transports water and mineral ions in a plant.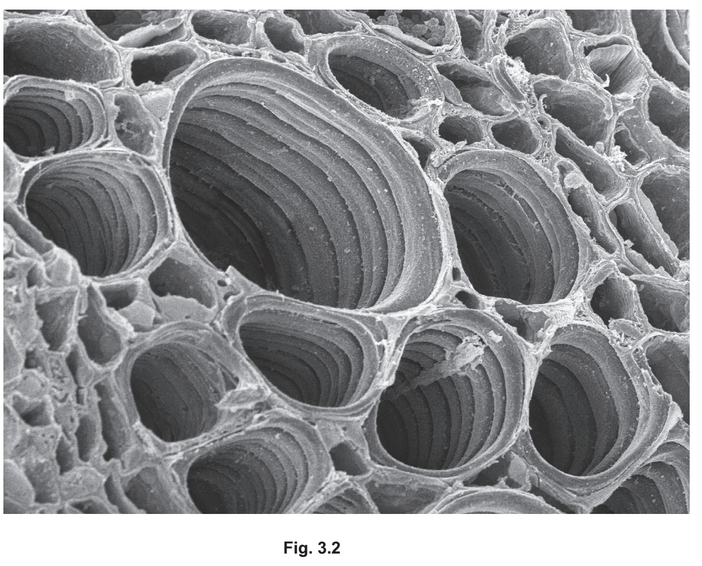
(i) State the name of the tissue shown in Fig. 3.2.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Describe how the tissue shown in Fig. 3.2 is adapted for its functions in the plant.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Explain how mineral ions enter a plant.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) any five from:
- as temperature increases the mass (of leaves) decreases / AW ;
- by (increased) transpiration ;
- evaporation increases ;
- from surface of the mesophyll cells ;
- due to increased (kinetic) energy of water molecules ;
- diffusion of water vapour increases ;
- through stomata ;
(ii) humidity /AVP ;
(b) (i) xylem ;
(ii) any three from :
- hollow/no cell contents, to reduce resistance / allow efficient flow ;
- no end walls, to reduce resistance / allow efficient flow ;
- large cross-sectional area / wide, to allow transport of large volume of water ;
- lignin to , prevent collapse / provide support/ provide strength ;
- waterproof to prevent water loss ;
- AVP ;
(c) any three form :
into the root hair (cell) ;
by active transport ;
against a concentration gradient/ AW ;
using energy;
using carrier proteins (in the cell membrane) ;
(also / initially) by diffusion;
