Question
Students investigated the effect of mineral ion deficiencies on the growth of radish plants.
The seeds that were used in the experiment were from plants that had been self-pollinated for
many generations and were therefore all genetically identical.
(a) Explain the advantage of using genetically identical radishes in this investigation.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
The radish seedlings were divided into four groups. Each group was grown in a different mineral
ion solution as follows:
1 complete solution containing all the major mineral ions
2 solution with all the major mineral ions except nitrate ions
3 solution with all the major mineral ions except magnesium ions
4 solution with all the major mineral ions except phosphate ions
The apparatus used to investigate the growth of the plants is shown in Fig. 6.1.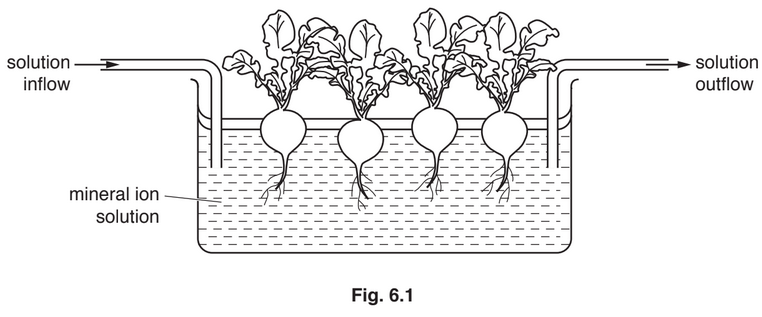
(b) State three other environmental factors that could affect the growth of the seedlings.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
3 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
The results of the investigation are shown in Table 6.1.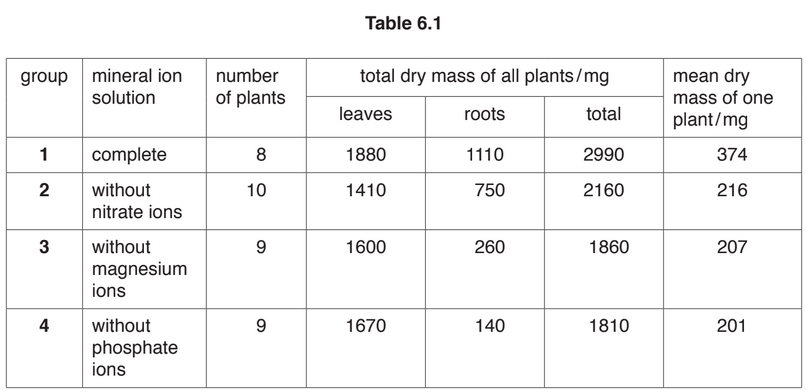
(c) Describe and explain the results for the radishes grown without nitrate ions (group 2).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(d) Describe the likely appearance of the radish plants grown in the solution without magnesium
ions (group 3) and explain your answer.
appearance ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
explanation …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(e) Phosphate ions are a component of DNA.
Suggest why the radish plants in group 4 grew less than the radish plants in the complete
solution (group 1).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: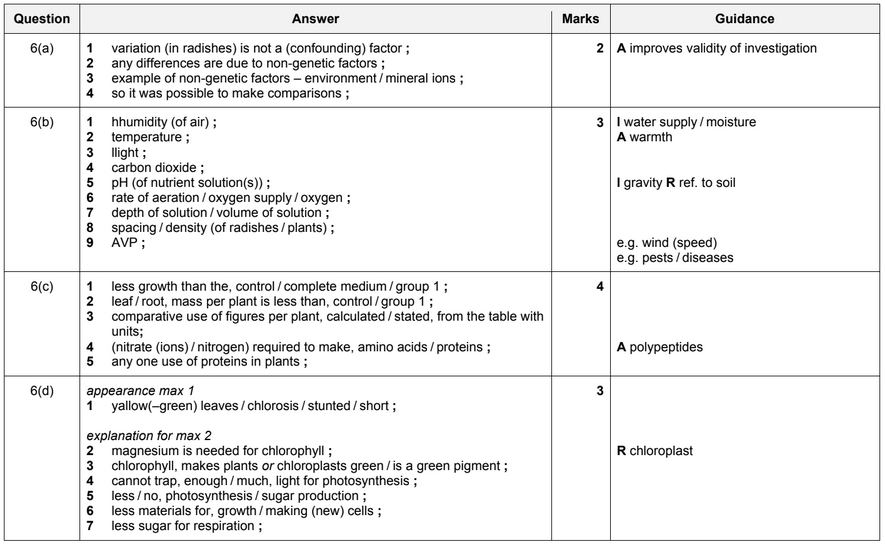

Question
(a) Fig. 9.1 shows a green plant.
Plants need to move substances around between their leaves, stems and roots. One of the processes they use is translocation.
Describe the process of translocation.
(b) Fig. 9.2 shows the whole plant and sections through its root, stem and a leaf.
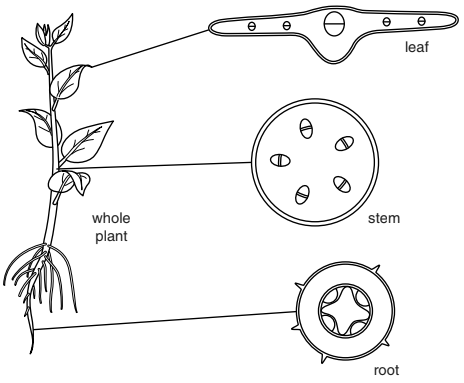
Fig. 9.2
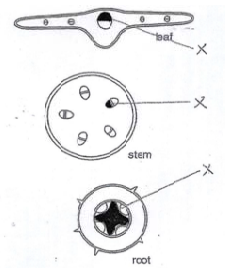
On Fig. 9.2 use label lines and the letter X to identify one region of xylem in each section (root, stem and leaf).
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) movement of sugars / named sugar/ amino acids ;
in phloem ;
from region of production/ leaves / source ;
to region of utilisation/ storage/ growth ;
energy required/AW ;
(b) correctly labelled:
xylem in leaf:;
xyelm in stem;
xylem in root;
Question
Fig. 2.1 shows an apparatus used to study the effect of minerals on plant growth.
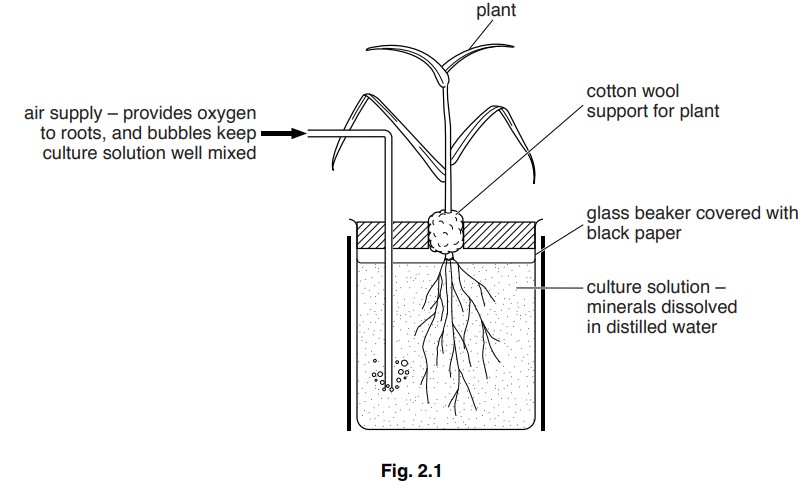
(a) The plant grows better if air is bubbled through the solution surrounding its roots. Name the process that uses oxygen from the air to release energy in the plant’s cells.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) An investigation was carried out into bean plants, using the apparatus shown in Fig. 2.1. Table 2.1 shows the mean dry mass of three groups of bean plants grown in different solutions for seven days
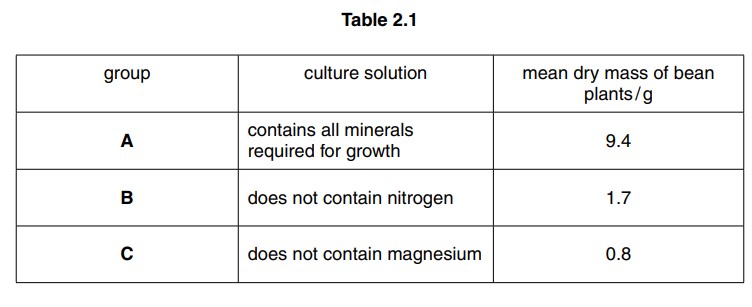
(i) Explain why, compared with group A, the dry mass was less in group B and group C.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Describe the expected appearance of plants in group C at the end of the investigation.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
2 (a) (aerobic) respiration;
(b) (i) link of lower dry mass with less growth;
B (no nitrogen) plant cannot produce proteins / amino acids /enzymes;
C (no magnesium) plant cannot make chlorophyll; cannot photosynthesise/ produce carbohydrate/ sugar/ glucose;
reference to growth (more cells / larger cells) requiring synthesis of chemicals /AW;
no carbohydrates / glucose/ sugar made means limited energy supplies (for growth);
(ii) (C plant’s) leaves pale green/ yellow/AW; growth stunted/AW;
