Question
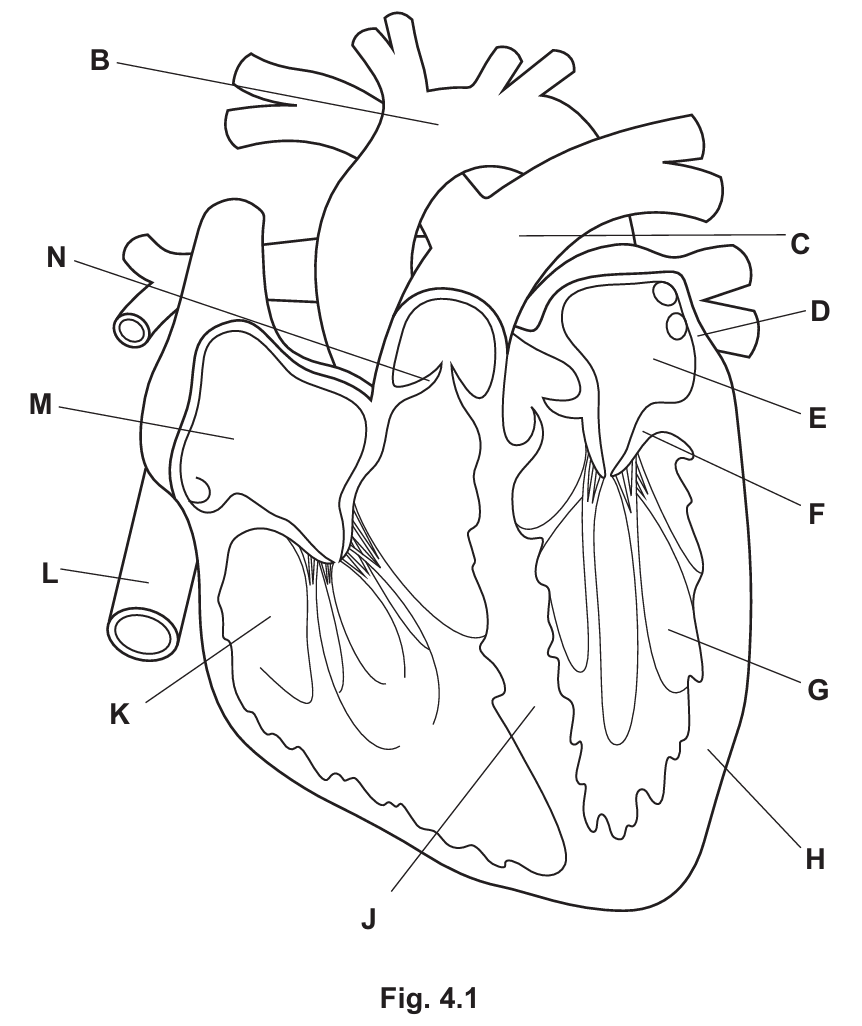
(a) (i) State the letter in Fig. 4.1 that identifies:
- the structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood ……………
- an atrioventricular valve ………….
(iii) Table 4.1 contains eight descriptions of parts of the pathway a red blood cell takes as it moves from the vena cava to the aorta.
Using Fig. 4.1, complete Table 4.1 by numbering the descriptions to show the correct sequence.
Two have been done for you.
State three other factors that can increase the risk of coronary heart disease.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i)
Structure separating oxygenated and deoxygenated blood: J (Septum)
An atrioventricular valve: F (Bicuspid/Mitral valve)
Explanation: The septum (J) divides the left and right sides of the heart to prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. The structure F is the valve situated between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
(a) (ii)
H (the left ventricle) has a much thicker muscular wall than D (the left atrium). This is because the ventricle needs to generate higher pressure to pump blood a longer distance (to the entire body/systemic circulation). The atrium only pumps blood a short distance into the ventricle.
(a) (iii)
The correct sequence is as follows:
| description | sequence |
|---|---|
| blood enters C (Pulmonary Artery) | 4 |
| blood enters E and then E contracts (Left Atrium) | 6 |
| blood enters M and then M contracts (Right Atrium) | 1 |
| blood travels to lungs | 5 |
| blood moves into G (Left Ventricle) | 7 |
| blood moves into B (Aorta) | 8 |
| N opens (Pulmonary Valve) | 3 |
| blood moves into K (Right Ventricle) | 2 |
(b) (i)
Exercise increases the heart rate. This occurs because:
• Muscles require more oxygen and glucose for increased aerobic respiration to release energy for contraction.
• Increased blood flow is needed to remove carbon dioxide (and lactic acid) produced by the muscles.
• Adrenaline may be released, stimulating the heart rate to rise.
(b) (ii)
Any three from:
• Diet (high in saturated fats, salt, or cholesterol)
• Smoking (tobacco)
• Stress (uncontrolled)
• Genetic predisposition (family history)
• Age (risk increases with age)
• Sex (males are generally at higher risk)
