Question
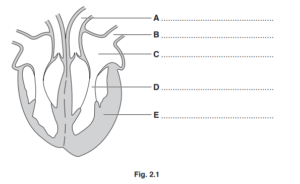
(i) Complete Fig. 2.1 by adding names to the label lines.
Choose names from this list:
aorta atrium muscular wall pulmonary artery
pulmonary vein septum vena cava ventricle
(ii) State the name of the heart chamber that pumps blood to the lungs.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) The volume of blood the heart pumps out per minute is called the cardiac output.
Fig. 2.2 shows how the cardiac output changes for students F and G as exercise increases.
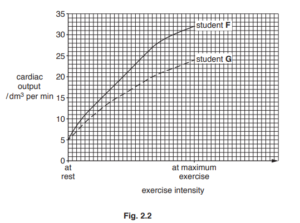
(i) Use Fig. 2.2 to state the cardiac output for student F when resting and when doing
maximum exercise.
when resting ………………………………………………………
when doing maximum exercise ………………………………………………………
(ii) Calculate the percentage increase in cardiac output of student G from rest to maximum
exercise.
Show your working.
…………………………………………………….%
(iii) Suggest two ways the activity of the heart changes to produce an increase in cardiac
output.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) During exercise, student F has a higher cardiac output than student G.
Suggest one reason for this difference.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A = aorta ;
B = pulmonary vein ;
C = atrium ;
D = ventricle ;
E = muscular wall ;
(ii) right ventricle
b (i) 5 and 32 ;
dm3 per min ;
(ii) 380
(iii) heart beats faster ;
heart pumps more blood out per beat / beats with more force per beat ;
(iv) F is fitter/AW/ has a stronger heart /is exercising more vigorously / has a larger body / larger heart /is male
Question
(a) Fig. 3.1 is a diagram of a section through a human heart.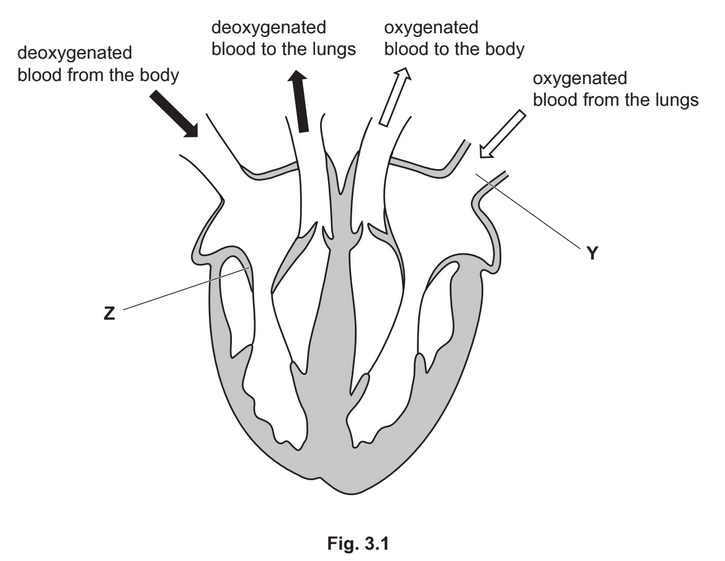
(i) Draw the letter X on Fig. 3.1 to show the position of the septum.
(ii) State the name of the blood vessel labelled Y in Fig. 3.1.
(iii) State the function of the part labelled Z in Fig. 3.1.
(iv) State how the part labelled Z in Fig. 3.1 can be used to monitor the activity of the heart.
(v) State the name of the main type of tissue that forms the wall of the heart.
(b) A scientist measured the average resting heart rate of seven different species of animal. They
also estimated the average life expectancy of each species.
Fig. 3.2 is a graph of the scientist’s data.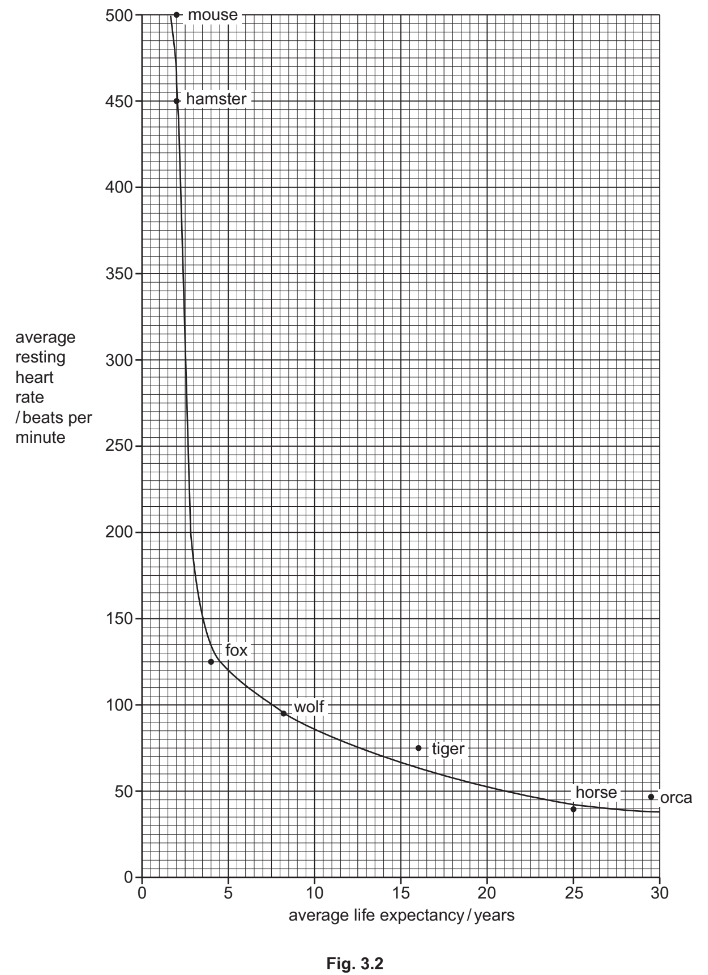
(i) Complete the sentences to describe the results in Fig. 3.2.
The animal with the highest average resting heart rate is the …………………………………. .
The animal with the longest average life expectancy is the …………………………………. .
The general trend is that as the average life expectancy increases, the average resting
heart rate …………………………………. .
(ii) Another animal species has an average life expectancy of 14 years.
Using the information in Fig. 3.2, predict the average resting heart rate of this animal
species.
………………………… beats per minute
(c) Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a blockage of one of the blood vessels of the heart.
(i) State the name of the blood vessel that becomes blocked in CHD.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) List two risk factors for coronary heart disease.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) List the names of two types of cell found in blood.
1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) (i) X drawn on the septum ;
(ii) pulmonary vein ;
(iii) stops backflow of blood (from right ventricle to right atrium) / AW ;
(iv) listen, (to the sound of) part Z/valve, closing ;
(v) muscle ;
(b) (i) mouse ;
orca ;
decreases / AW ;
(ii) 70 (beats per minute) ;
(c) (i) coronary artery ;
(ii) any two from :
- age/being older ;
- genetic predisposition / AW
- sex/being male ;
- (high levels of) stress ;
- smoking, tobacco/ cigarettes ;
- diet / diet high in, saturated fats / cholesterol ;
7,8 AVP ;;
(iii) red (blood cells) ;
white (blood cells) ;
