Question
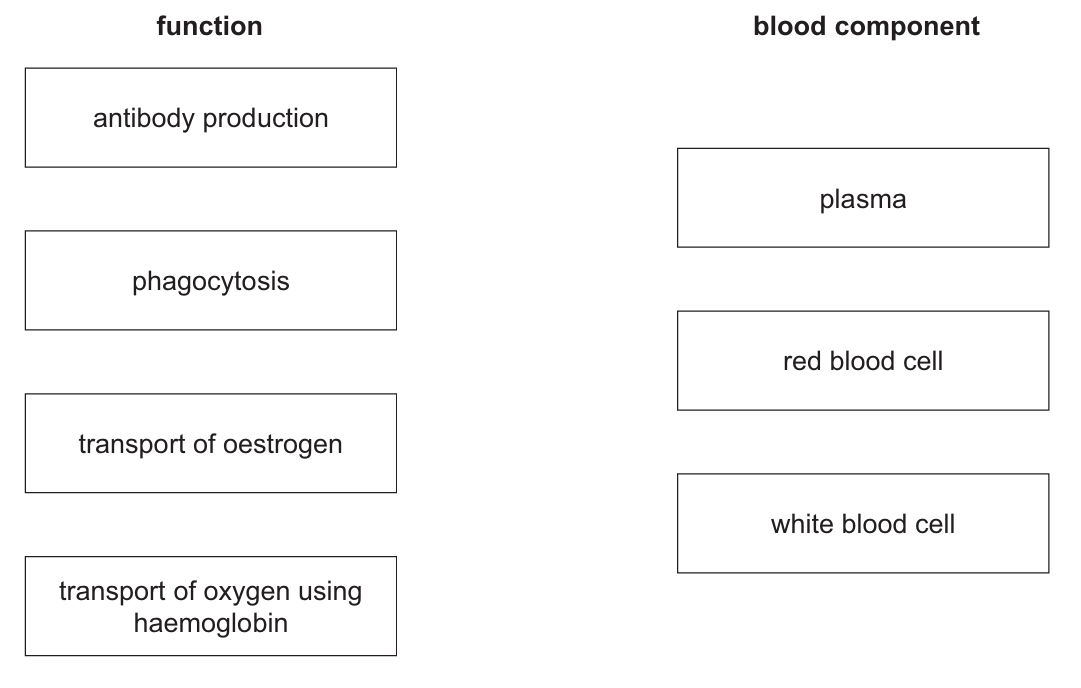
The boxes on the right contain the names of some blood components.
Draw four straight lines from each function to the blood component that carries out that function.
(b) Platelets are a blood component.
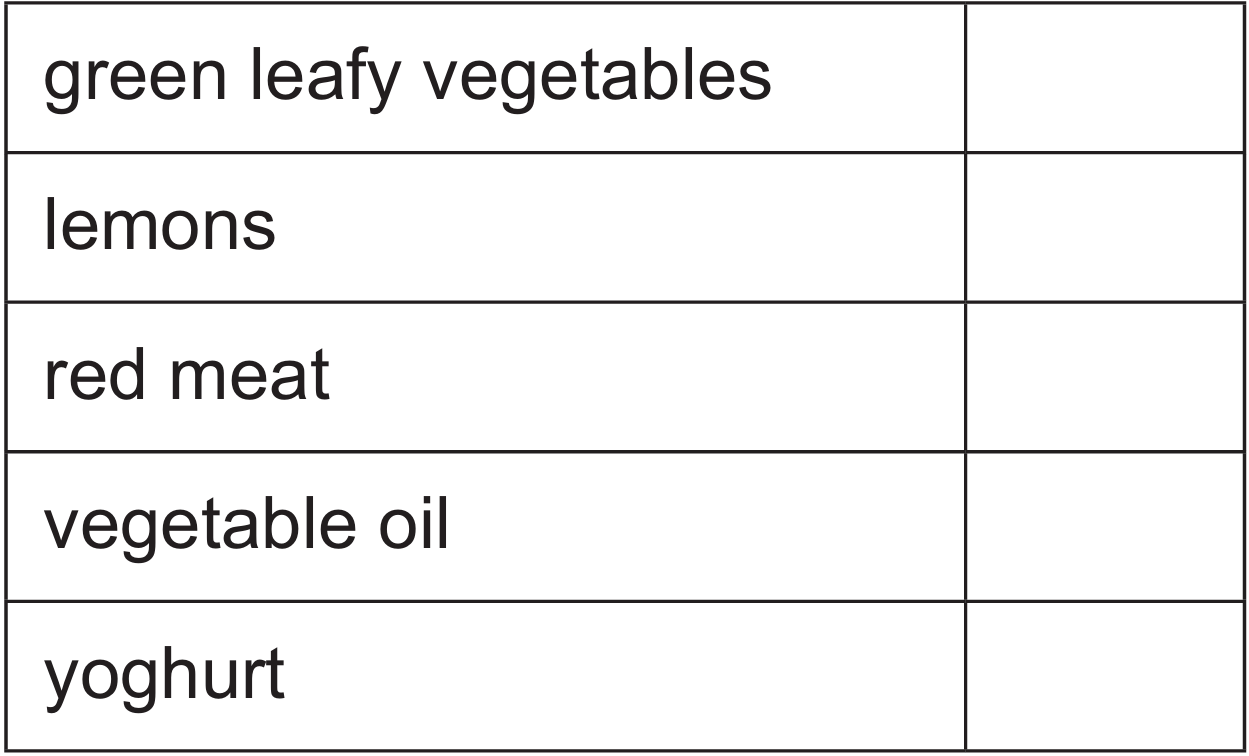
(i) A high number of platelets can be caused by a lack of iron in the diet. Tick (\(\checkmark\)) two boxes that show food that is high in iron.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Matching Functions:
• antibody production \(\rightarrow\) white blood cells
• transport of oxygen \(\rightarrow\) red blood cells
• transport of oestrogen \(\rightarrow\) plasma
• phagocytosis \(\rightarrow\) white blood cells
(b) (i) High Iron Foods:
The two correct boxes are:
• green leafy vegetables (\(\checkmark\))
• red meat (\(\checkmark\))
(b) (ii) Roles of Blood Clotting:
1. To prevent blood loss (stop bleeding).
2. To prevent the entry of pathogens (such as bacteria and viruses) into the body.
(c) Main Vessel:
The aorta.
Expert Explanation:
Blood Composition:
• Red blood cells: Contain haemoglobin to bind and transport oxygen from the lungs to respiring tissues.
• White blood cells: Part of the immune system. Phagocytes engulf pathogens (phagocytosis), and lymphocytes produce antibodies to neutralize them.
• Plasma: The liquid component that transports dissolved substances, including hormones (like oestrogen), nutrients (glucose, amino acids), carbon dioxide, and urea.
Clotting: When platelets encounter a damaged vessel, they trigger the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. This forms a mesh that traps blood cells, creating a clot to seal the wound and block infection.
Circulation: The aorta is the largest artery, carrying high-pressure, oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the systemic circulation (the rest of the body).
