Question
(a) Fig. 2.1 is a diagram of part of the human circulatory system.
The arrows show the direction of blood flow.
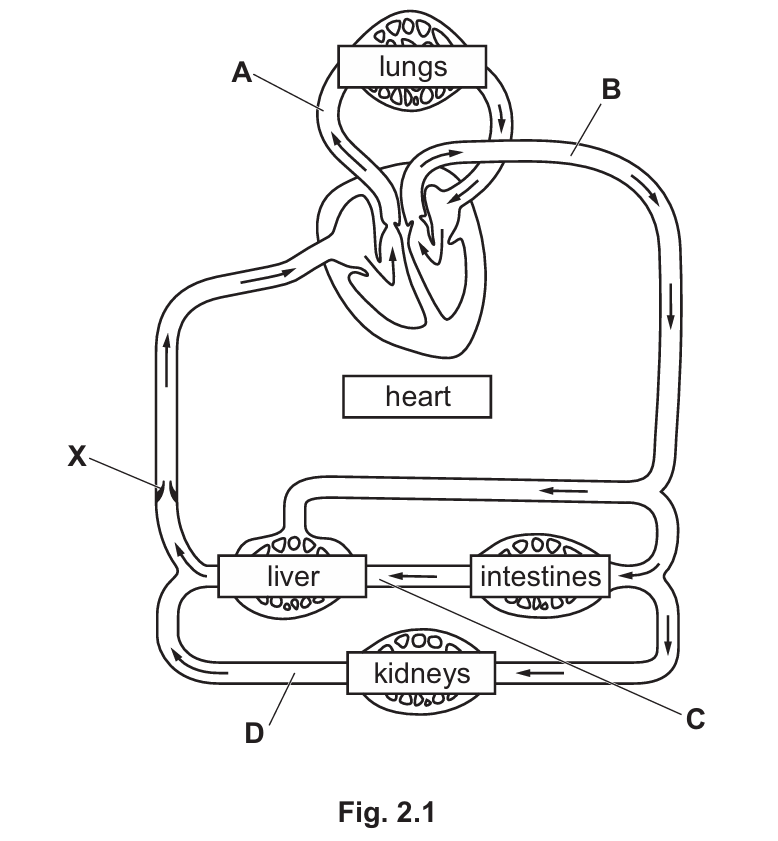
(i) Complete Table 2.1 by naming the blood vessels in Fig. 2.1 and stating whether the blood in each vessel is oxygenated.
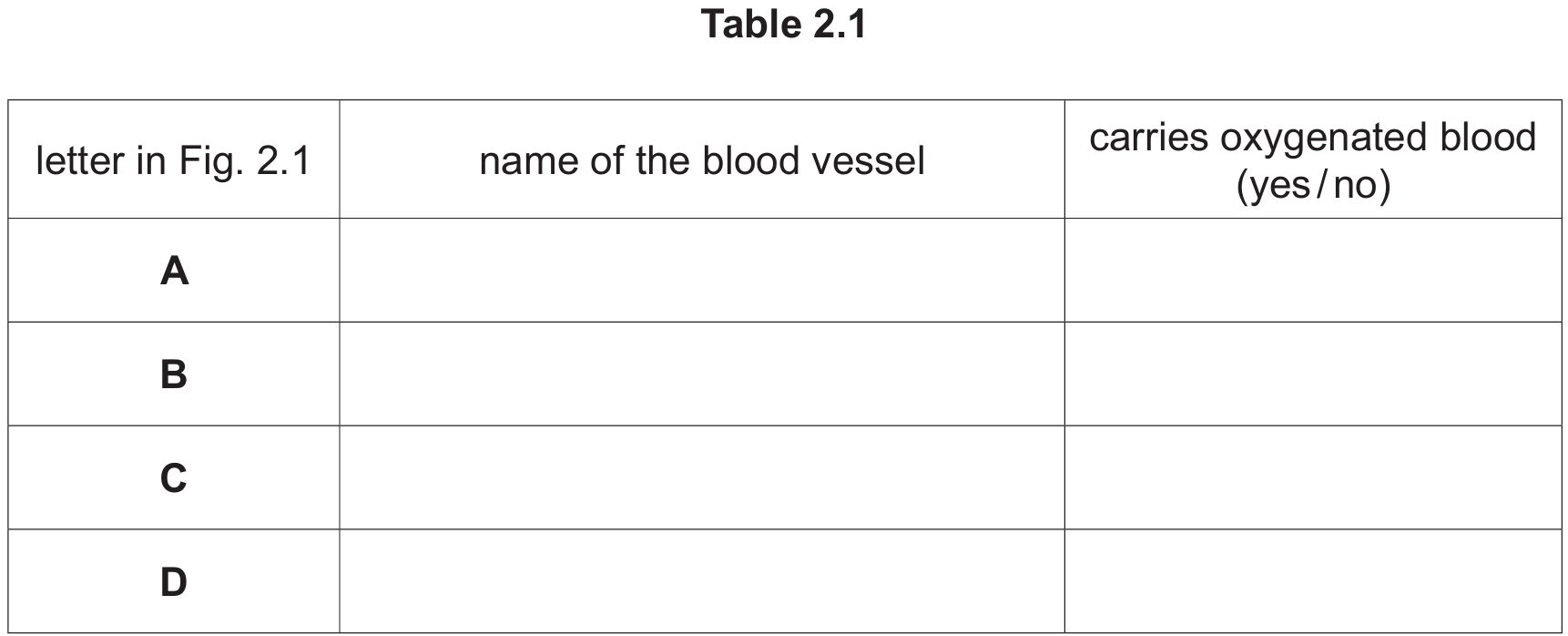
(ii) State the name of structure X in Fig. 2.1 and outline its function.
(b) Fig. 2.2 is a diagram of part of a fish circulatory system.
The arrows show the direction of blood flow.
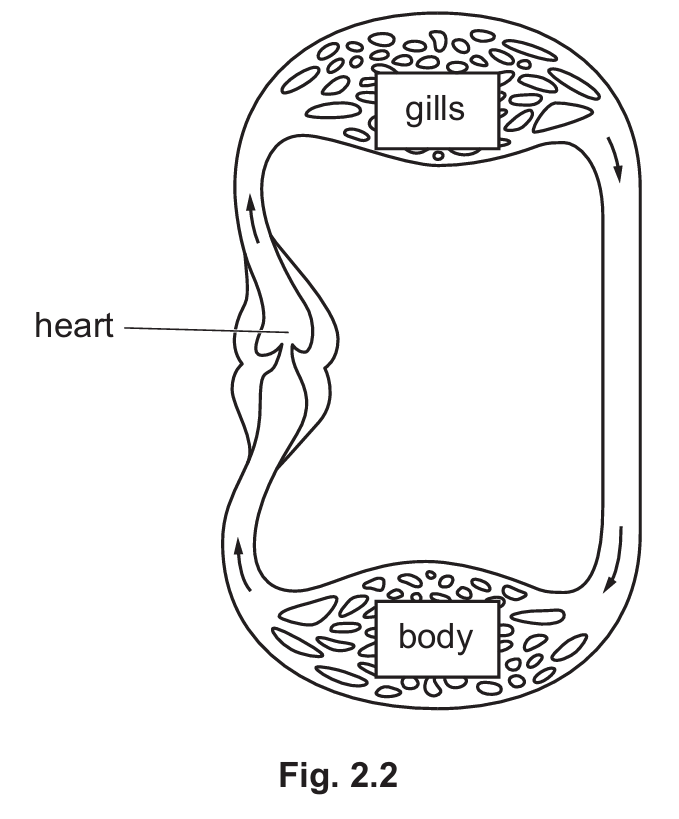
(i) Describe how the structure of the fish heart in Fig. 2.2 differs from a human heart.
(ii) Explain the advantages of the type of circulatory system found in humans, compared with the circulatory system shown in Fig. 2.2.
(c) Fig. 2.3 is a photomicrograph of an arteriole.
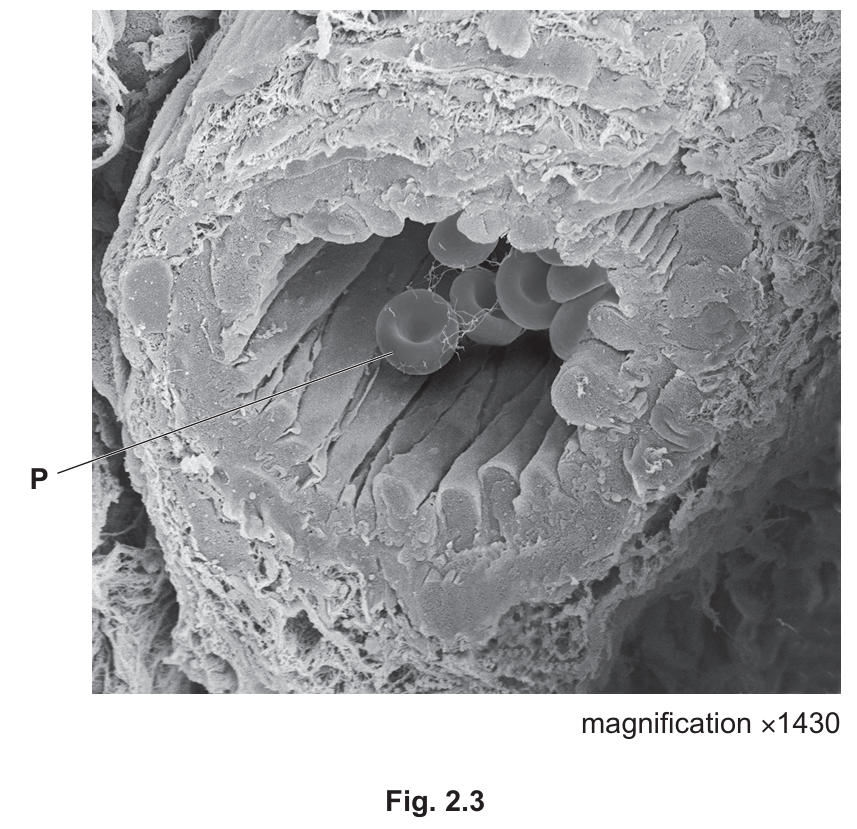
(i) Identify the structure labelled P in Fig. 2.3.
(ii) The magnification of the image is provided. Write the formula that would be used to calculate the actual diameter of the lumen of the arteriole in Fig. 2.3.
Convert $0.0315 \, \text{mm}$ to micrometres ($\mu \text{m}$).
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Table 2.1 Completion:
| Letter | Name of Blood Vessel | Carries Oxygenated Blood? |
| A | Pulmonary artery | No |
| B | Aorta | Yes |
| C | Hepatic portal vein | No |
| D | Renal vein | No |
Explanation:
• A (Pulmonary artery): Carries blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated. It is the only artery that carries deoxygenated blood.
• B (Aorta): The main artery carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
• C (Hepatic portal vein): Connects the intestines to the liver. It carries nutrient-rich but deoxygenated blood.
• D (Renal vein): Carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys back toward the vena cava.
(a)(ii)
Name: Valve
Function: Prevents the back flow of blood.
Explanation: Veins (where X is located) operate under low pressure. Valves are essential to ensure blood flows in only one direction (towards the heart) and does not pool due to gravity.
(b)(i) Differences in Heart Structure:
• The fish heart has only two chambers (one atrium and one ventricle), whereas the human heart has four.
• The fish heart lacks a septum separating left and right sides (since it is a single loop), while the human heart has a septum.
• The fish heart has fewer valves and fewer blood vessels attached compared to the human heart.
(b)(ii) Advantages of Human Circulatory System (Double Circulation):
• Separation of blood: Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are kept separate by the septum, maintaining a steep concentration gradient for efficient gas exchange.
• High Pressure to Body: Blood loses pressure in the capillaries of the lungs. By returning to the heart (left side), it can be pumped out to the body at a much higher pressure, ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues to support a high metabolic rate.
• Low Pressure to Lungs: The pulmonary circuit remains at lower pressure, preventing damage to the delicate capillaries in the lungs.
(c)(i)
Structure P: Red blood cell (Erythrocyte).
Note: These are recognizable by their biconcave disc shape and location inside the vessel lumen.
(c)(ii)
Formula: $$\text{Actual size} = \frac{\text{Image size}}{\text{Magnification}}$$
(c)(iii)
Answer: $31.5 \, \mu\text{m}$
Calculation: To convert millimeters (mm) to micrometers ($\mu\text{m}$), multiply by 1000.
$$0.0315 \, \text{mm} \times 1000 = 31.5 \, \mu\text{m}$$
