Question
Fig. 2.1 is a photomicrograph of human blood.
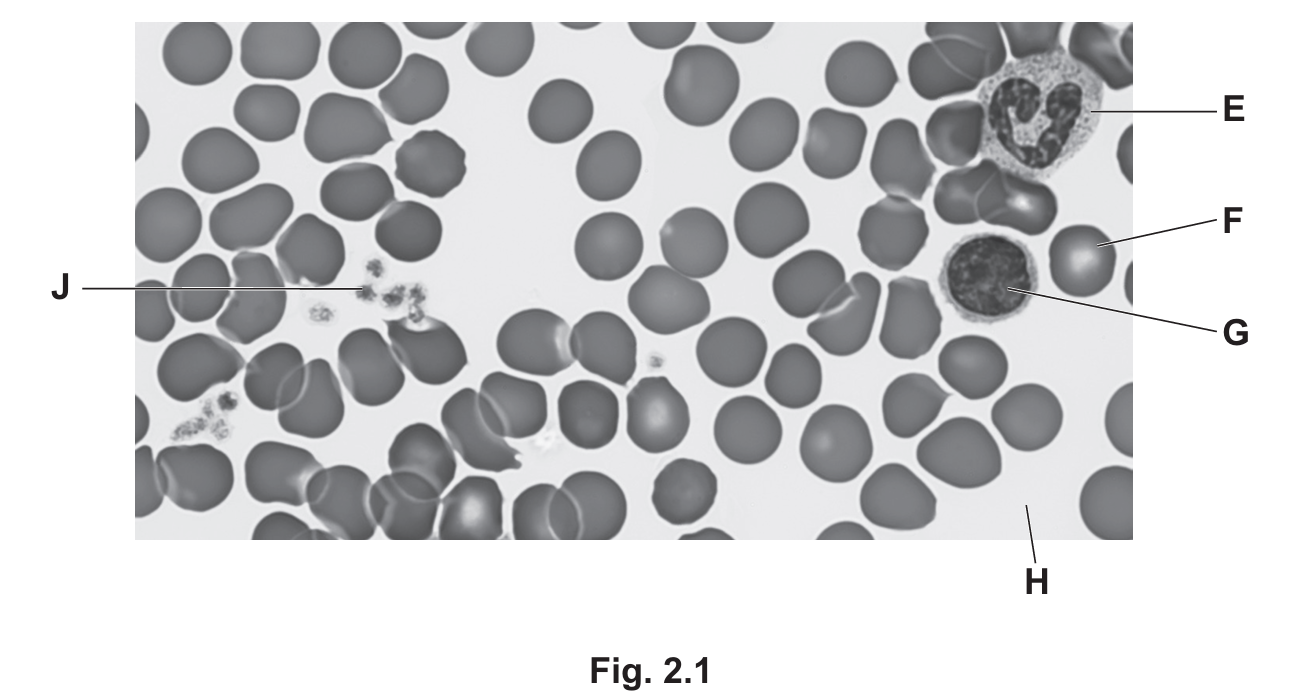
(a) Use the information in Fig. 2.1 to complete Table 2.1
(b) Some diseases are transmissible.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
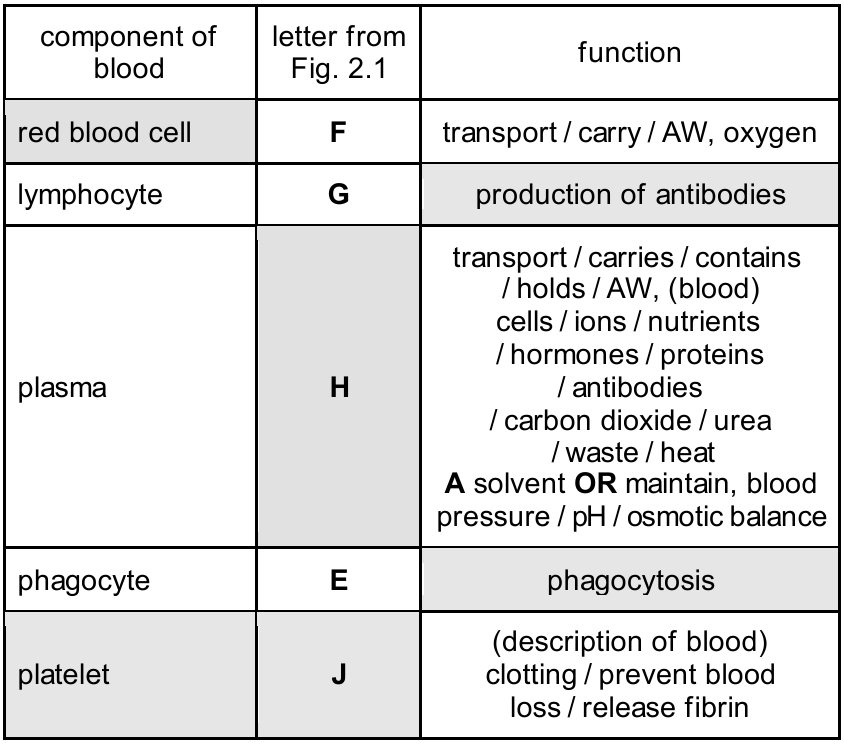
The completed table is as follows:
- Red blood cell:
- Letter: F (These are the numerous small, biconcave cells lacking a nucleus).
- Function: Transport of oxygen (mediated by haemoglobin).
- Lymphocyte:
- Component: lymphocyte (Identified by the large, round nucleus that fills most of the cell, labeled G).
- Letter: G.
- Function: Production of antibodies.
- Plasma:
- Component: plasma (The liquid medium surrounding the cells).
- Letter: H.
- Function: Transport of blood cells, ions, nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids), hormones, carbon dioxide, urea, and heat. It also acts as a solvent.
- Phagocyte:
- Component: phagocyte (Identified by the lobed or irregular-shaped nucleus, labeled E).
- Letter: E.
- Function: Phagocytosis (engulfing and digesting pathogens).
- Platelet:
- Letter: J (Small cell fragments).
- Function: Blood clotting (prevents blood loss and entry of pathogens) / release of fibrin.
(b)(i)
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
(b)(ii)
Any two of the following:
• Contaminated surfaces / objects (fomites)
• Contaminated food or water
• Air (droplets / airborne)
• Vectors (animals that carry the pathogen, e.g., mosquitoes)
• Faeces / sewage
(c)
Antibodies are proteins produced by lymphocytes. Their role includes:
• Specificity: They have a shape complementary to specific antigens on the surface of pathogens.
• Binding: They bind/attach to these specific antigens.
• Destruction: This binding can mark the pathogen for destruction by phagocytes, cause the pathogens to clump together (agglutination), or neutralize toxins produced by the pathogen.
(d)
The key differences are:
• Source: Active immunity is produced by the body’s own immune system (production of antibodies by lymphocytes) after infection or vaccination. Passive immunity is the acquisition of ready-made antibodies from another individual (e.g., via placenta, breast milk, or injection).
• Memory: Active immunity produces memory cells, providing long-term protection. Passive immunity does not produce memory cells.
• Duration: Active immunity is long-term (or permanent). Passive immunity is short-term (antibodies are eventually broken down).
• Speed: Active immunity takes time to develop (slower response initially). Passive immunity provides immediate protection.
