Which row describes the structure and a use of diamond?
| structure | use | |
|---|---|---|
| A | ionic | in cutting tools |
| B | ionic | as a lubricant |
| C | giant covalent | in cutting tools |
| D | giant covalent | as a lubricant |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Diamond has a giant covalent structure where each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
Key properties and uses:
- Extremely hard due to strong covalent bonds – used in cutting tools
- High melting point
- Doesn’t conduct electricity (no free electrons)
Graphite is the form of carbon used as a lubricant, not diamond. Diamond is never ionic (options A and B are incorrect).
Which statements about the structure and bonding in diamond are correct?
- Each carbon atom in diamond is bonded to three other carbon atoms only.
- Diamond contains many strong covalent bonds.
- Diamond contains layers of carbon atoms, which can slide over each other.
- Diamond has a giant structure.
A) 1, 2 and 3
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4
D) 4 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each statement:
1. Incorrect – Each carbon atom in diamond is actually bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement.
2. Correct – Diamond does contain many strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms, which is why it’s so hard.
3. Incorrect – This describes graphite, not diamond. Diamond has a 3D network structure, not layers.
4. Correct – Diamond does have a giant covalent structure where all atoms are connected by covalent bonds.
Therefore, only statements 2 and 4 are correct.
Question
Which pair of statements about diamond and graphite is correct?
A. Diamond and graphite are both pure carbon. They are both macromolecules.
B. Diamond and graphite can both be used as electrodes. Graphite is also used as a lubricant.
C. Diamond has covalent bonds. Graphite has ionic bonds.
D. Diamond is hard with a high melting point. Graphite is soft with a low melting point.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
A
Diamond and graphite are both pure carbon. They are both macromolecules.
Graphite is soft and slippery due to the weak forces between the layers. The layers can easily slide past each other, giving graphite its lubricating properties.
Diamond is an excellent insulator and does not conduct electricity.
Both have covalent bonds.
Only Graphite is used as electrodes.
Graphite has a high melting point.
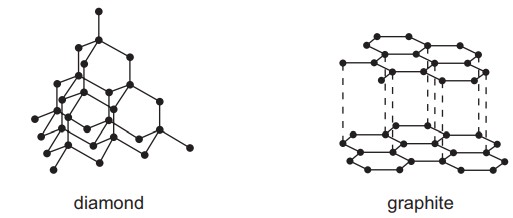
Question
The structures of diamond and graphite are shown.

Which statement about diamond and graphite is correct?
A Diamond and graphite have low melting points.
B Diamond and graphite have mobile electrons.
C Diamond and graphite have layered structures.
D Diamond and graphite contain strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:D
Diamond and graphite have high melting points.
Diamond does not have mobile electrons.
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity. Within each graphene layer, carbon atoms are covalently bonded, but one electron from each carbon atom remains delocalized and is free to move throughout the layers, allowing for electrical conductivity.
Diamond and graphite contain strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
Only Graphite has layered structure.
