This question is about air.
(a) The pie chart shows the proportions of the main gases in clean, dry air.

(i) Name the gases G and H.[2]
gas G
gas H
(ii) The graph shows how the volume of a sample of gas G changes as temperature increases. The pressure is kept constant.

Describe how the volume of gas G changes as temperature increases.[1]
(iii) There is a small percentage of noble gases in the air.
The noble gases are unreactive.
Explain why the noble gases are unreactive in terms of their electronic structure.[1]
(iv) Describe the arrangement and separation of the particles in a gas.[2]
arrangement
separation
(b) Two of the pollutants in air are oxides of nitrogen and lead compounds.
(i) Give one effect of each of these pollutants on health.[2]
oxides of nitrogen
lead compounds
(ii) Name two other pollutants present in air.
State the source of each of these pollutants.[4]
pollutant 1
source of pollutant 1
pollutant 2
source of pollutant 2 [Total: 12]
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: G is oxygen, H is nitrogen
The pie chart shows that gas G is the second largest component (~21%), which is oxygen, and gas H is the largest (~78%), which is nitrogen.
(a)(ii) Ans: Volume increases as temperature increases
The graph shows a linear increase in volume with temperature, following Charles’s Law (\(V \propto T\) at constant pressure).
(a)(iii) Ans: They have a full outer shell of electrons
Noble gases have stable electronic configurations, making them chemically inert.
(a)(iv) Ans: Arrangement – random; Separation – far apart
Gas particles are randomly arranged and widely spaced due to weak intermolecular forces.
(b)(i) Ans: Oxides of nitrogen – breathing difficulties; Lead compounds – toxic to nervous system
NO₂ irritates lungs, while lead compounds accumulate in the body, causing neurological damage.
(b)(ii) Ans: Example – Sulfur dioxide (from burning fossil fuels); Carbon monoxide (from incomplete combustion)
Common pollutants include SO₂ (industrial emissions) and CO (vehicle exhausts).
The table shows the mass of air pollutants, in nanograms, in $1000 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ samples of air taken over a four-month period.
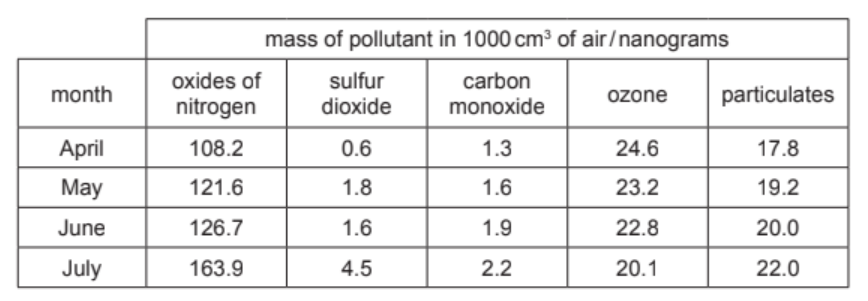
(a) Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) Name the pollutant that shows a decrease in concentration between April and July.[1]
(ii) Name the pollutant present in the lowest concentration in May.[1]
(iii) Calculate the mass of sulfur dioxide in $250 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of the sample of air taken in April.
nanograms [1]
(b) Oxides of nitrogen are produced when oxygen combines with nitrogen during thunderstorms.
(i) State one other source of oxides of nitrogen in the air.[1]
(ii) Give one adverse effect of oxides of nitrogen on health.[1]
(iii) Complete the chemical equation for the reaction of nitrogen with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide.
$+2 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow \ldots . . \mathrm{NO}_2$
(c) Particulates are tiny solid particles in the air.
The movement of these particles is shown by the arrows in the diagram.
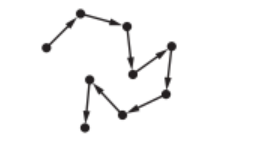
State the name given to this random motion of particles.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1] [Total: 8]
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: ozone
From the table, ozone decreases from 0.60 ng in April to 0.30 ng in July.
(a)(ii) Ans: carbon monoxide (CO)
In May, CO has the lowest concentration (0.50 ng) compared to other pollutants.
(a)(iii) Ans: 0.15 ng
Sulfur dioxide in April is 0.60 ng per 1000 cm³. For 250 cm³: $(0.60 \times 250)/1000 = 0.15$ ng.
(b)(i) Ans: car exhausts
Common sources include vehicle emissions or industrial combustion.
(b)(ii) Ans: irritation of lungs
Oxides of nitrogen can cause respiratory issues like asthma or throat irritation.
(b)(iii) Ans: $\mathrm{N}_2 + 2\mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\mathrm{NO}_2$
Balancing the equation: Nitrogen reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide.
(c) Ans: Brownian motion
The random movement of particles suspended in a fluid is called Brownian motion.
