(a) Fig. 4.1 shows the displayed formula of compound A.
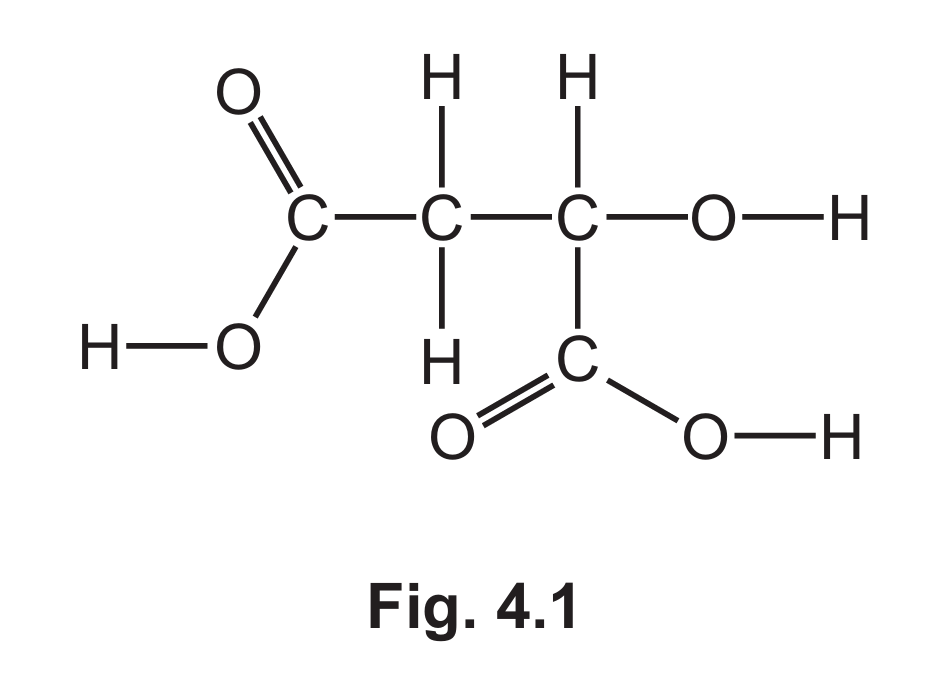
(i) On Fig 4.1 draw a circle around the alcohol functional group.
(ii) Deduce the molecular formula of compound A.
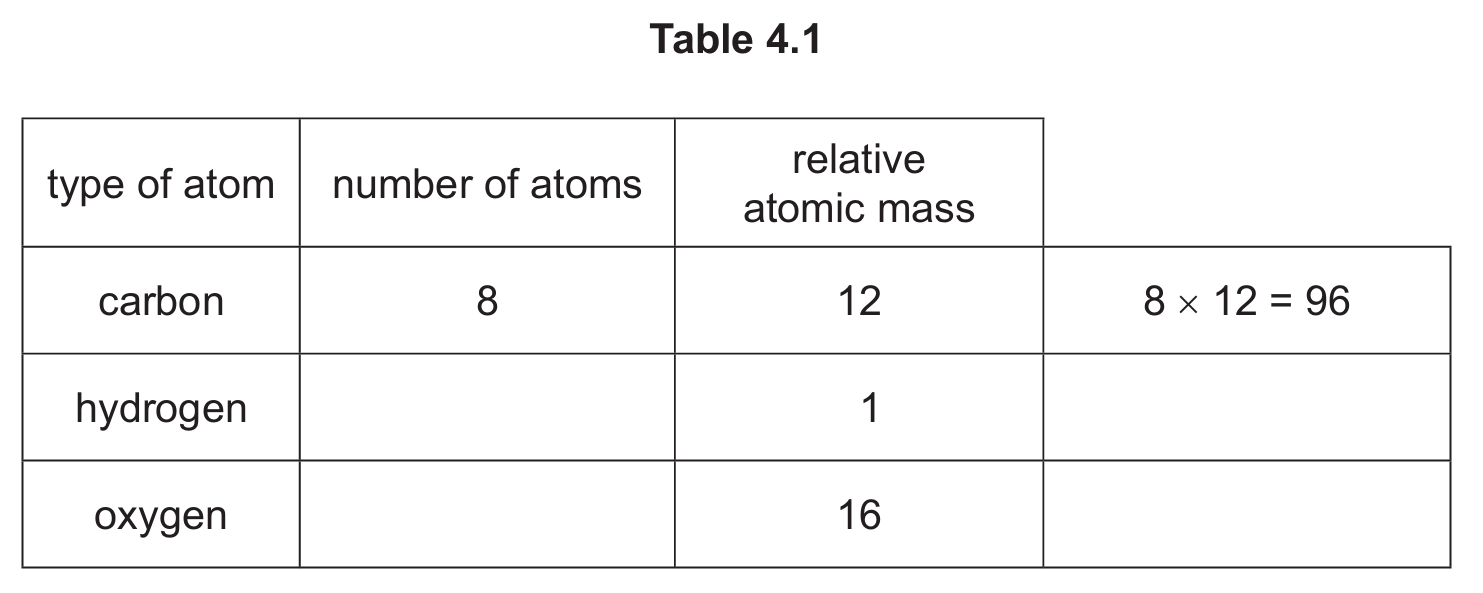
(b) Compound A reacts with ethanol to produce a compound with the molecular formula C8H14O5.
Complete Table 4.1 to calculate the relative molecular mass of C8H14O5.
(c) Complete the word equation for the complete combustion of ethanol.
ethanol + oxygen → …………………… + ……………………
(d) Table 4.2 shows the names, formulae and boiling points of ethene, propene, butene and pentene.
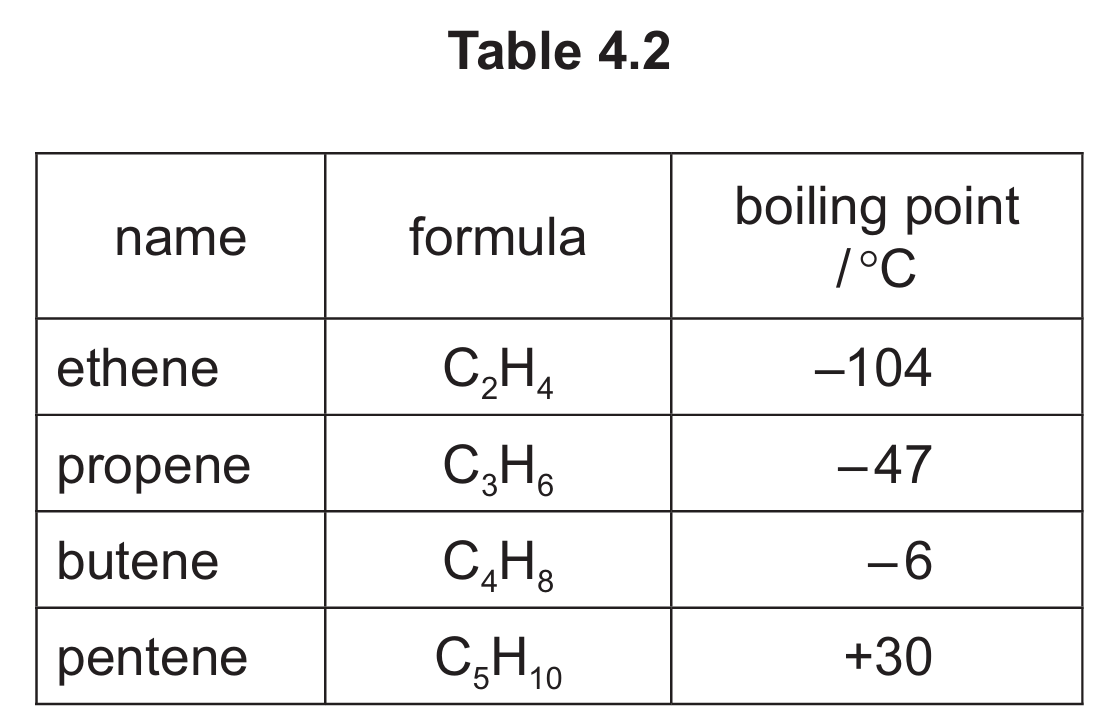
Use the information in Table 4.2 to answer these questions.
(i) Name the homologous series that includes ethene, propene, butene and pentene.
(ii) Deduce the general formula of this homologous series.
(iii) State the trend in the boiling point of this homologous series as the number of carbon atoms increases.
(e) Ethene is manufactured by cracking.
(i) Describe the manufacture of ethene by cracking.
(ii) Give a reason for cracking hydrocarbons.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) O-H group circled
The alcohol functional group is the hydroxyl group (-OH). In the displayed formula, this would be one of the O-H groups shown in the structure.
(a)(ii) C4H6O5
Counting all atoms in the displayed formula: 4 carbon atoms, 6 hydrogen atoms, and 5 oxygen atoms.
(b) 190
Calculation: (8 × 12) + (14 × 1) + (5 × 16) = 96 + 14 + 80 = 190
For hydrogen: 14 atoms × 1 = 14
For oxygen: 5 atoms × 16 = 80
(c) water + carbon dioxide
The complete combustion of ethanol follows the general pattern of hydrocarbon combustion: ethanol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water.
(d)(i) alkenes
All these compounds contain a carbon-carbon double bond, which is the defining feature of the alkene homologous series.
(d)(ii) CnH2n
This is the general formula for alkenes, where n is the number of carbon atoms. Each compound in the series follows this pattern.
(d)(iii) increases
As the number of carbon atoms increases (from ethene to pentene), the boiling point increases (-104°C to +30°C). This is because larger molecules have stronger intermolecular forces.
(e)(i) Cracking involves breaking down larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones (like ethene) using high temperatures and often a catalyst. The process typically uses long-chain alkanes from petroleum fractions.
Key points:
- Large alkane molecules are heated to high temperatures (400-900°C)
- Sometimes a catalyst (like aluminum oxide) is used
- Breaks C-C bonds to form smaller molecules including alkenes like ethene
- May also produce other useful products like hydrogen
(e)(ii) To produce more useful hydrocarbons that are in demand, particularly shorter chain alkenes like ethene which are important for making plastics and other chemicals.
Cracking converts less useful long-chain hydrocarbons into more valuable shorter-chain hydrocarbons that are in higher demand for industrial processes.
The table shows the structures of some organic compounds.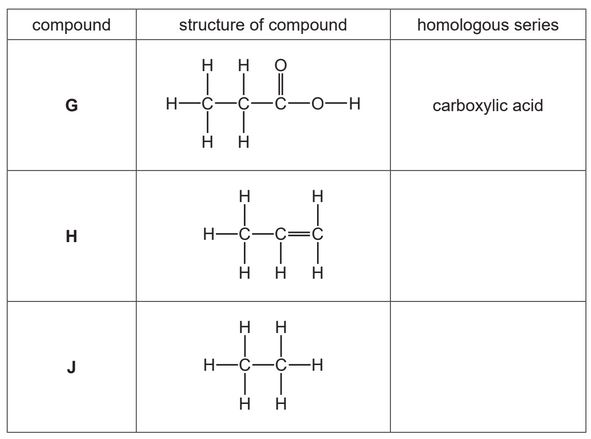
(a) Complete the table by naming the homologous series.
The first one has been done for you.
(b) Draw the structure of a compound containing two carbon atoms which belongs to the same homologous series as compound H.
Show all of the atoms and all of the bonds.
(c) State which compound in the table is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Explain your answer.
(d) State which compound in the table reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
Explain your answer.
(e) State the names of the two compounds formed during the complete combustion of compound J.
(f) Compound H can be polymerised.
(i) State the general name given to the small units which join together to form a polymer.
(ii) Terylene is also a polymer.
Give one use of Terylene.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans:
H: Alkene (1)
J: Alkane (1)
(b) Ans:
![]()
(c) Ans: H is unsaturated because it contains a C=C double bond, which is characteristic of alkenes.
(d) Ans: G (carboxylic acid) reacts with NaOH because acids react with bases to form salt and water.
(e) Ans: Carbon dioxide and water are formed during the complete combustion of J (an alkane).
(f)(i) Ans: Monomers are the small units that join to form polymers.
(f)(ii) Ans: Terylene is used in clothing due to its durability and resistance to wrinkles.
