Nitrogen molecules are diatomic.
(a) (i) State the meaning of the term diatomic.
(ii) State the percentage of nitrogen in clean, dry air.
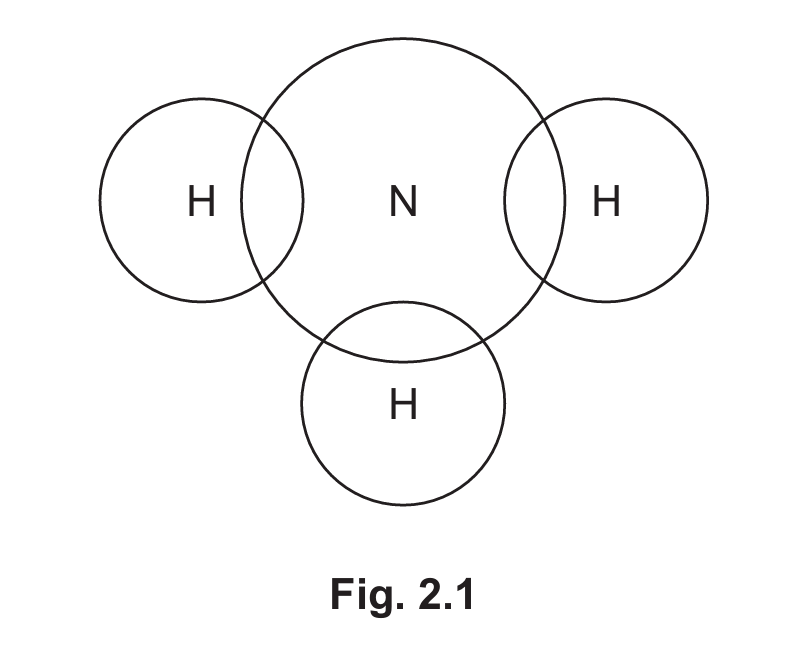
(b) Ammonia has a simple molecular structure. Complete Fig. 2.1 to show the dot-and-cross diagram for a molecule of ammonia. Show outer shell electrons only.
(c) Sodium chloride has a giant ionic structure of positive and negative ions.
(i) State the general name given to any positive ion.
(ii) State one physical property of an ionic compound.
(d) Graphite is used as an electrode.
(i) State one other use of graphite.
(ii) Choose the correct statement that describes the structure and bonding in graphite.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i) A diatomic molecule consists of two atoms chemically bonded together. Many elements like nitrogen (N₂), oxygen (O₂), and hydrogen (H₂) exist as diatomic molecules in their natural state.
(ii) Nitrogen makes up approximately 78% of clean, dry air by volume. The remaining 21% is mostly oxygen, with about 1% being other gases like argon and carbon dioxide.
(b) The dot-and-cross diagram for ammonia (NH₃) should show:
- Nitrogen (N) with 5 valence electrons (2 lone pairs and 3 bonding electrons)
- Each hydrogen (H) with 1 valence electron
- Three covalent bonds between nitrogen and each hydrogen (shared electron pairs)
- One lone pair remaining on the nitrogen atom
The final structure should show the nitrogen at the center with three hydrogen atoms bonded to it and one lone pair on nitrogen.
(c) (i) A positive ion is called a cation. Cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, resulting in a net positive charge.
(ii) Ionic compounds typically have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions. They also conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water because the ions become free to move.
(d) (i) Graphite is commonly used as a lubricant because its layered structure allows the sheets to slide over one another easily. It’s also used in pencils (as the “lead”) and as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
(ii) The correct description of graphite’s structure is giant covalent. Graphite consists of layers of carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal rings, with strong covalent bonds within each layer but weak van der Waals forces between layers.
(a) Hydrogen chloride has a simple molecular structure.
(i) State two physical properties of a compound with a simple molecular structure.
(ii) Hydrogen chloride is a molecule with a covalent bond. Complete this sentence about a covalent bond. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of …… .
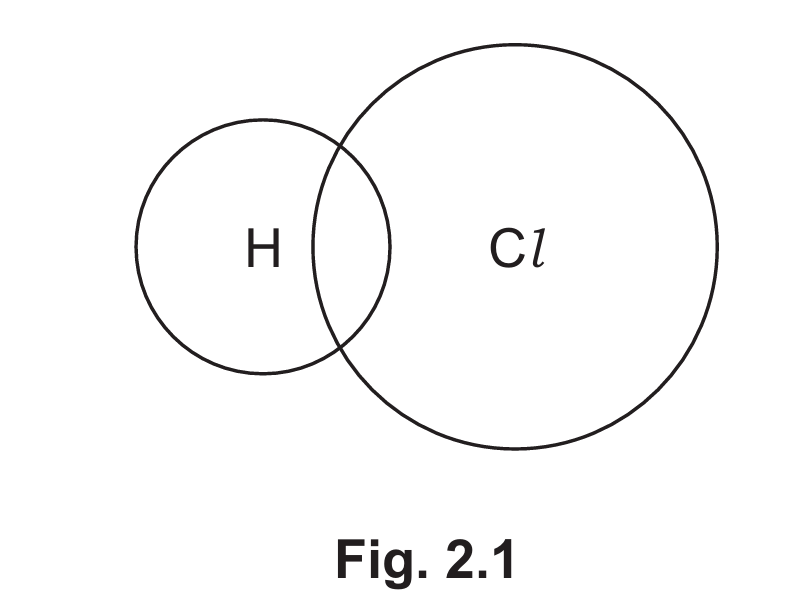
(iii) Complete Fig. 2.1 to show the dot-and-cross diagram for a molecule of hydrogen chloride. Show outer shell electrons only.
(b) Zinc chloride has a giant ionic structure of positive and negative ions. State the general name given to any negative ion.
(c) Diamond is used for jewellery.
(i) State one other use of diamond.
(ii) Choose the correct statement that describes the structure and bonding in diamond.
- simple covalent molecule
- giant covalent
- simple ionic
- giant ionic
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Two physical properties of simple molecular structures are:
- Low melting and boiling points (due to weak intermolecular forces)
- Poor electrical conductivity (as they don’t contain free electrons or ions)
(a)(ii) A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons.
(a)(iii) The dot-and-cross diagram for HCl should show:
- One bonding pair of electrons between H and Cl (shared pair)
- Three lone pairs (6 electrons) on the chlorine atom
- No electrons on the hydrogen atom beyond the shared pair
(b) The general name for any negative ion is anion.
(c)(i) Another use of diamond is in cutting tools (due to its extreme hardness).
(c)(ii) The correct description of diamond’s structure is giant covalent (tick the second box). Diamond consists of carbon atoms each covalently bonded to four others in a giant three-dimensional lattice structure.
