This question is about acids, bases and salts.
(a) Crystals of potassium chloride can be made by reacting an acid with an alkali.
(i) Name the acid and the alkali used.
(ii) Choose from the list the type of reaction that takes place when an acid reacts with an alkali.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
addition neutralisation redox substitution
(iii) Thymolphthalein is an acid-base indicator.
State the colour of thymolphthalein at pH2 and at pH12.
(iv) Describe how to make dry crystals of potassium chloride from an aqueous solution of potassium chloride.
(b) Crystals of potassium chloride dissolve in water. This process is endothermic.
(i) Define the term endothermic.
(ii) Fig. 7.1 shows the reaction pathway diagram for dissolving potassium chloride in water.
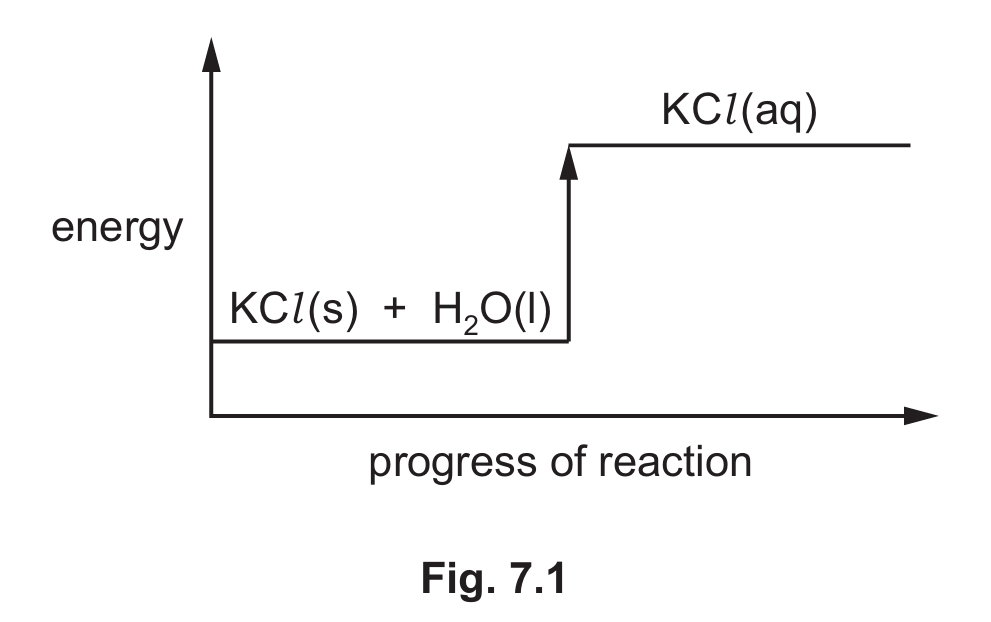
Answer the following questions using the information in Fig. 7.1.
– State the meaning of the state symbol (l).
– Explain how Fig. 7.1 shows that dissolving potassium chloride in water is endothermic.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) acid: hydrochloric acid (1)
alkali: potassium hydroxide (1)
Detailed solution: Potassium chloride can be made by neutralization reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and potassium hydroxide (KOH). The balanced equation is: \( \text{HCl} + \text{KOH} \rightarrow \text{KCl} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \).
(a)(ii) neutralisation
Detailed solution: The reaction between an acid and a base is called a neutralization reaction, where the acid and base react to form a salt and water.
(a)(iii) pH 2: colourless (1)
pH 12: blue (1)
Detailed solution: Thymolphthalein is a pH indicator that changes color around pH 9.3-10.5. In acidic conditions (pH 2), it remains colorless. In basic conditions (pH 12), it turns blue.
(a)(iv) One mark each for any two of:
• evaporate some of the water / heat to the point of crystallisation / heat until crystals seen
• filter off crystals / pick out crystals
• dry crystals with filter paper
Detailed solution: To obtain dry KCl crystals from solution: First, heat the solution to evaporate water until crystals begin to form (point of crystallization). Then, filter the solution to separate the crystals from remaining liquid. Finally, dry the crystals between filter papers to remove any residual moisture.
(b)(i) absorption of thermal energy
Detailed solution: An endothermic process is one that absorbs heat energy from the surroundings. When KCl dissolves in water, it takes in heat, causing the temperature of the solution to decrease.
(b)(ii) state symbol: liquid (1)
explanation: the energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants / the energy of KCl + H₂O is greater than the energy of KCl (aq) (1)
Detailed solution: The (l) symbol indicates the substance is in liquid state. The diagram shows an endothermic process because the products (KCl in solution) have higher energy than the reactants (solid KCl and liquid water). This upward energy change means energy is absorbed during dissolution.
This question is about acids, bases and salts.
(a) Crystals of zinc chloride can be made by warming excess solid zinc oxide with dilute hydrochloric acid.
\[ \text{ZnO(s)} + 2\text{HCl(aq)} \rightarrow \text{ZnCl}_2\text{(aq)} + \text{H}_2\text{O(…….)} \]
(i) Complete the symbol equation by adding the state symbol for water at room temperature.
(ii) State the method used to separate the excess solid zinc oxide from the reaction mixture.
(iii) Describe how to make dry crystals of zinc chloride from an aqueous solution of zinc chloride.
(b) Choose from the list the ion that is present in all acids.
Draw a circle around your chosen answer.
Cl– H+ O2- OH–
(c) The reaction of zinc oxide with hydrochloric acid is exothermic.
(i) Define the term exothermic.
(ii) Fig. 7.1 shows the incomplete reaction pathway diagram for the reaction of zinc oxide with hydrochloric acid.
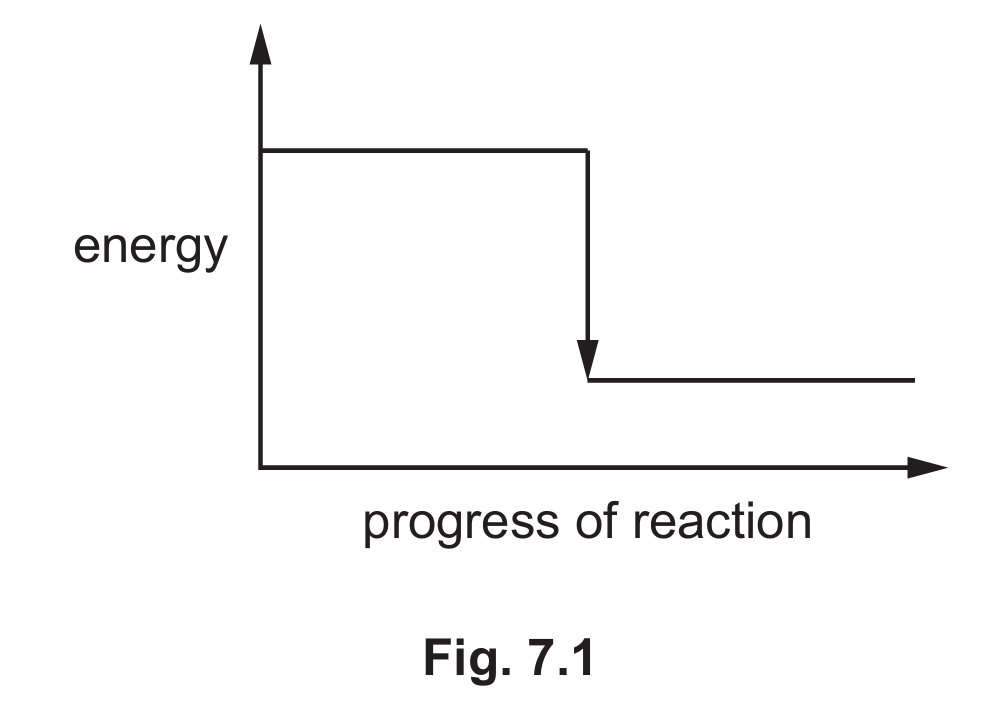
Complete Fig. 7.1 by writing these formulae on the diagram:
• ZnO + 2HCl
• ZnCl2 + H2O.
(iii) Explain how Fig. 7.1 shows that the reaction is exothermic.
(d) Litmus is an acid-base indicator.
State the colour of litmus at pH 2 and at pH 12.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) (l)
Water at room temperature is in liquid state, so the state symbol is (l).
(a)(ii) filtration
Filtration is used to separate an insoluble solid (zinc oxide) from a liquid (zinc chloride solution).
(a)(iii) Heat the solution to evaporate some water until saturation point is reached (1), then allow it to cool for crystals to form (1). Filter off the crystals (1) and dry them between filter papers (1).
The process involves concentrating the solution by evaporation, then allowing crystals to form through cooling. The crystals are then separated and dried.
(b) H+
All acids contain hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution, which is what gives them their acidic properties.
(c)(i) A reaction that releases thermal energy/heat to the surroundings.
Exothermic reactions are characterized by energy being given out, usually in the form of heat.
(c)(ii) ZnO + 2HCl should be written on the higher energy line (left side), and ZnCl2 + H2O on the lower energy line (right side).
The reactants should be placed at a higher energy level than the products to show energy is released.
(c)(iii) The energy level of the reactants is higher than the energy level of the products, showing energy is released.
In an exothermic reaction, the products are at a lower energy level than the reactants, with the difference being released as heat.
(d) pH 2: red/pink (1), pH 12: blue (1)
Litmus is red in acidic solutions (pH < 7) and blue in alkaline solutions (pH > 7). At pH 2 (strongly acidic) it’s red, and at pH 12 (strongly alkaline) it’s blue.
