(a) Table 5.1 shows some properties of five halogens.

Use the information in Table 5.1 to predict:
(i) the melting point of iodine
(ii) the atomic radius of fluorine
(iii) the physical state of bromine at 0°C. Give a reason for your answer.
(b) Aqueous chlorine reacts with aqueous potassium iodide.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.
chlorine + potassium iodide → ………………………………………….. + …………………………………………..
(ii) Explain why aqueous iodine does not react with aqueous potassium bromide.
(c) Fluorine reacts with hot concentrated sodium hydroxide to produce sodium fluoride, water and oxygen.
(i) Complete the symbol equation for this reaction.
\( 2F_2 + 4NaOH \rightarrow ….NaF + 2H_2O + …… \)
(ii) Describe a test for oxygen.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Between −5°C and 180°C inclusive
Looking at the trend in melting points down the group (fluorine to astatine), we see they increase steadily. Iodine’s melting point should be between bromine’s (−7°C) and astatine’s (302°C). A reasonable prediction would be around 113°C (actual value is 113.7°C).
(a)(ii) Between 0.098 nm and 0.01 nm
Atomic radius increases down the group. Fluorine, being at the top, should have the smallest radius. From the given data, chlorine is 0.099 nm, so fluorine should be slightly smaller.
(a)(iii) liquid (1)
temperature between −7°C and +59°C / 0°C is between the melting and boiling point (1)
Bromine’s melting point is −7°C and boiling point is +59°C. At 0°C (between these two points), bromine would be in its liquid state.
(b)(i) iodine (1)
potassium chloride (1)
This is a displacement reaction where the more reactive chlorine displaces iodine from potassium iodide:
\( Cl_2 + 2KI \rightarrow I_2 + 2KCl \)
(b)(ii) iodine is less reactive than bromine / bromine is more reactive than iodine / bromine is higher in the electrochemical series than iodine
In halogen displacement reactions, a more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive one from its compound. Since iodine is less reactive than bromine, it cannot displace bromine from potassium bromide.
(c)(i) 4(NaF) (1)
\( O_2 \) (1)
The balanced equation is:
\( 2F_2 + 4NaOH \rightarrow 4NaF + 2H_2O + O_2 \)
(c)(ii) glowing splint (1)
relights (1)
Oxygen supports combustion. The standard test is to insert a glowing splint into the gas. If oxygen is present, the splint will relight.
(a) Table 5.1 shows some properties of five halogens.
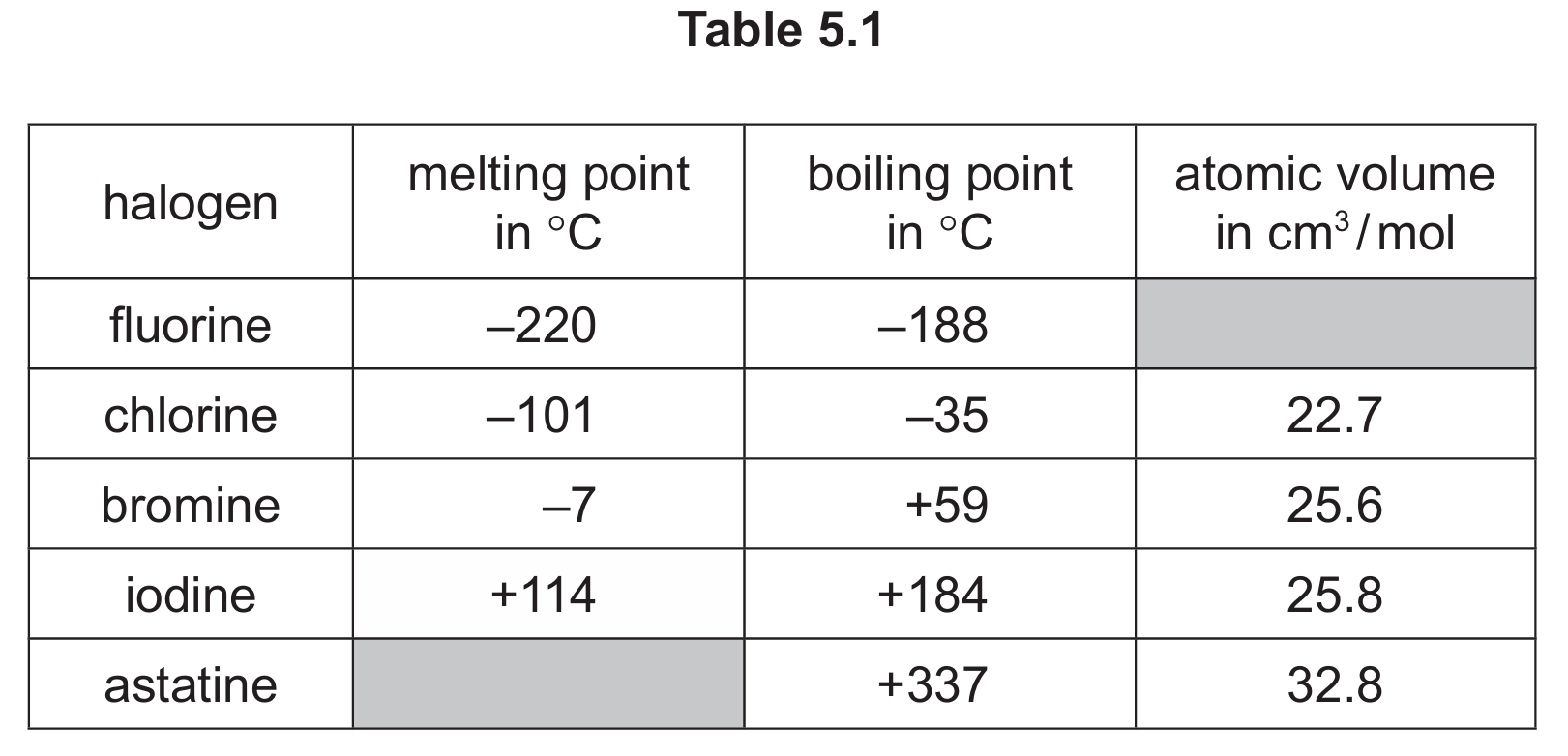
Use the information in Table 5.1 to predict:
(i) the melting point of astatine
(ii) the atomic volume of fluorine
(iii) the physical state of fluorine at −240°C. Give a reason for your answer.
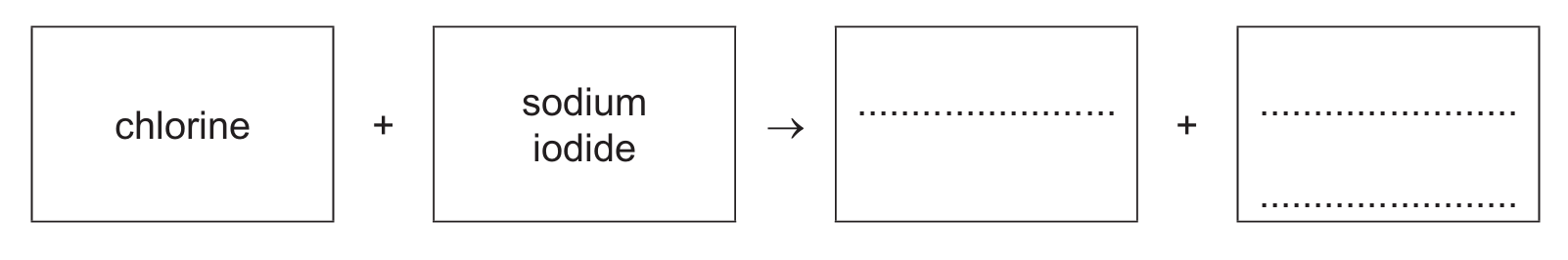
(b) Aqueous chlorine reacts with aqueous sodium iodide.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.
(ii) Explain why aqueous bromine does not react with aqueous sodium chloride.
(c) Fluorine reacts with water to produce hydrogen fluoride and oxygen.
Complete the symbol equation for this reaction.
\[ 2F_2 + \ldots H_2O \rightarrow 4HF + \ldots \]
(d) Name an anhydrous compound used to test for water. State the colour of the compound after water is added.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Between 116°C and 335°C (inclusive)
Looking at the trend in melting points down Group 17 (halogens), we see they increase: F (-220°C), Cl (-101°C), Br (-7°C), I (114°C). Astatine, being below iodine, would have a higher melting point than iodine but lower than its boiling point of 337°C.
(a)(ii) Less than 22.7 cm³/mol (but not below 1.0)
The atomic volume increases down the group: Cl (22.7), Br (25.6), I (25.8), At (32.8). Fluorine, being above chlorine, would have a smaller atomic volume.
(a)(iii) Solid (1), because −240°C is below fluorine’s melting point of −220°C (1)
At temperatures below its melting point, a substance exists as a solid. Since −240°C is 20 degrees below fluorine’s melting point, it would be solid.
(b)(i) iodine (1) + sodium chloride (1)
This is a displacement reaction where the more reactive chlorine displaces iodine from sodium iodide: Cl₂ + 2NaI → I₂ + 2NaCl
(b)(ii) Bromine is less reactive than chlorine / chlorine is more reactive than bromine (1)
In the reactivity series of halogens, chlorine is above bromine, meaning it can displace bromine but bromine cannot displace chlorine. Therefore, bromine cannot displace chlorine from sodium chloride.
(c) \[ 2F_2 + 2H_2O \rightarrow 4HF + O_2 \] (2 marks: 1 for each correct coefficient)
The reaction shows fluorine reacting with water to produce hydrogen fluoride and oxygen. Balancing the equation requires 2 water molecules to produce 1 oxygen molecule while maintaining the hydrogen and fluorine counts.
(d) Copper(II) sulfate (1) → blue (1) OR Cobalt(II) chloride (1) → red/pink (1)
Anhydrous copper(II) sulfate is white and turns blue when hydrated. Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride is blue and turns pink when hydrated. Both are common tests for water.
