(a) The table shows the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.
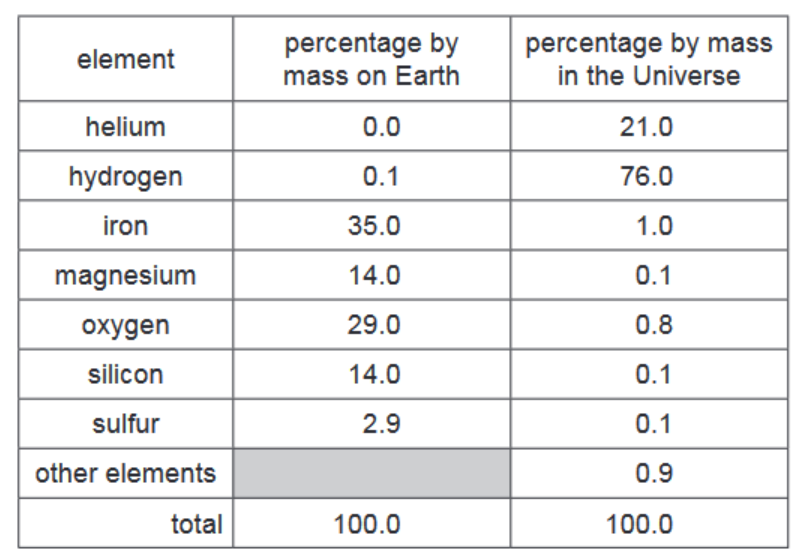
Answer these questions using only the information in the table.
(i) Deduce the percentage by mass of other elements present on Earth.$\%[1]$
(ii) Which non-metallic element is present on Earth in the greatest percentage by mass?[1]
(iii) Give two major differences in the percentage by mass of the elements on Earth and in the Universe.[2]
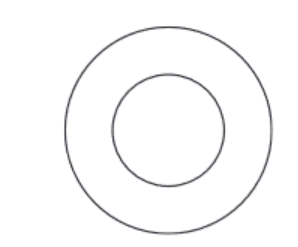
(b) Complete the diagram to show the electron arrangement in an oxygen atom.
(c) Helium, neon and argon are noble gases.
(i) Explain, in terms of the electronic structure, why neon is unreactive.[1]
(ii) State one use of argon.[1] [Total: 7]
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: 5.0%
Subtract the sum of given percentages (Fe + O + Si + Mg + S = 95%) from 100%.
(a)(ii) Ans: oxygen
Oxygen (47%) has the highest percentage among non-metals in the Earth’s composition.
(a)(iii) Ans: Any two differences
• The Universe has more hydrogen (75%) compared to Earth (not listed).
• Earth has more oxygen (47%) compared to the Universe (0.1%).
(b) Ans: 2,6 electron arrangement
Oxygen (atomic number 8) has 2 electrons in the first shell and 6 in the outer shell.
(c)(i) Ans: Neon has a complete outer electron shell
Neon’s outer shell is full (8 electrons), making it stable and unreactive.
(c)(ii) Ans: Used in lamps or as an inert atmosphere
Argon is chemically inert, making it useful in lighting and metalworking.
This question is about air.
(a) The pie chart shows the proportions of the main gases in clean, dry air.

(i) Name the gases G and H.[2]
gas G
gas H
(ii) The graph shows how the volume of a sample of gas G changes as temperature increases. The pressure is kept constant.

Describe how the volume of gas G changes as temperature increases.[1]
(iii) There is a small percentage of noble gases in the air.
The noble gases are unreactive.
Explain why the noble gases are unreactive in terms of their electronic structure.[1]
(iv) Describe the arrangement and separation of the particles in a gas.[2]
arrangement
separation
(b) Two of the pollutants in air are oxides of nitrogen and lead compounds.
(i) Give one effect of each of these pollutants on health.[2]
oxides of nitrogen
lead compounds
(ii) Name two other pollutants present in air.
State the source of each of these pollutants.[4]
pollutant 1
source of pollutant 1
pollutant 2
source of pollutant 2 [Total: 12]
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Ans: G is oxygen, H is nitrogen
The pie chart shows the composition of clean, dry air. The largest segment (78%) is nitrogen (H), and the second largest (21%) is oxygen (G).
(a)(ii) Ans: Volume increases with temperature
According to Charles’s Law, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant pressure, so the volume of gas G (oxygen) increases as temperature rises.
(a)(iii) Ans: Noble gases have a full outer shell
Noble gases are unreactive because their outermost electron shell is completely filled, making them stable and unlikely to gain or lose electrons.
(a)(iv) Ans: Arrangement – random; Separation – far apart
Gas particles are arranged randomly and are far apart due to weak intermolecular forces, allowing them to move freely.
(b)(i) Ans: Oxides of nitrogen – irritates lungs; Lead compounds – toxic to nervous system
Oxides of nitrogen can cause respiratory issues, while lead compounds are poisonous and can damage the nervous system.
(b)(ii) Ans: Example – Sulfur dioxide from burning fossil fuels; Carbon monoxide from incomplete combustion
Other pollutants include sulfur dioxide (from burning fossil fuels) and carbon monoxide (from incomplete combustion of carbon-based fuels).
