(a) Hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium.
Name the products of this reaction and give the observations
(b) The rate of reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid can be determined by measuring the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide.
A student measured the time taken to produce $20 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of carbon dioxide at three different temperatures.
In each experiment the student used:
- $1 \mathrm{~g}$ of large pieces of iron(II) carbonate
- dilute hydrochloric acid of the same concentration and volume.
The results are shown in the table.
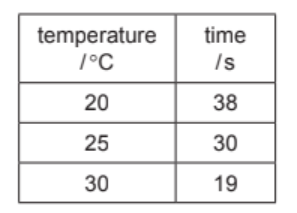
(i) Use the information in the table to describe how the rate of reaction changes with temperature.
(ii) Describe the effect of each of the following on the rate of this reaction at constant temperature.
● Smaller pieces of iron(II) carbonate are used.
All other conditions stay the same.
● The concentration of hydrochloric acid is decreased.
All other conditions stay the same.
(c) The reaction of iron(II) carbonate with hydrochloric acid is exothermic.
What is meant by the term exothermic?
(d) Rust contains compounds of iron.
State two conditions needed for iron to rust
(e) Iron and magnesium are both used in alloys.
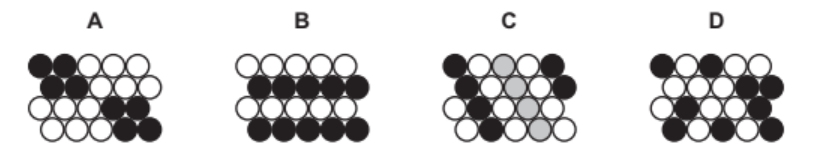
Which one of these diagrams, A, B, C or D, best represents an alloy?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: Magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed. Observations include effervescence (bubbles), the magnesium dissolving, and the reaction mixture warming up.
The reaction between hydrochloric acid (HCl) and magnesium (Mg) produces magnesium chloride (MgCl₂) and hydrogen gas (H₂). Observations include bubbles (H₂ gas), the solid Mg disappearing, and heat release (exothermic).
(b)(i) Ans: The rate of reaction increases as temperature increases.
Higher temperatures provide more kinetic energy to particles, increasing collision frequency and successful reactions, thus speeding up the rate.
(b)(ii) Ans: Smaller pieces increase the rate (greater surface area). Decreasing acid concentration decreases the rate (fewer reacting particles).
Smaller pieces increase surface area for collisions. Lower acid concentration reduces the number of reactive particles per unit volume.
(c) Ans: An exothermic reaction releases heat energy to the surroundings.
In exothermic reactions, the energy of products is lower than reactants, releasing heat (e.g., this reaction warms up).
(d) Ans: Water and oxygen (or air) are required for iron to rust.
Rusting is an oxidation process where iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of water to form hydrated iron(III) oxide.
(e) Ans: D
An alloy is a mixture of metals or a metal with another element. Diagram D shows a disordered arrangement of different-sized atoms, typical of alloys.
This question is about iron and its compounds.
(a) The table shows how easy it is to reduce four metal oxides by heating with carbon.
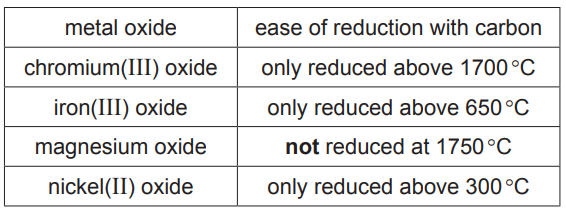
Use this information to put the metals in order of their reactivity. Put the least reactive metal first.[2]
(b) Iron is a transition element. Potassium is an element in Group I of the Periodic Table.
Describe three ways in which the properties of iron differ from those of potassium.
(c) Iron wire burns in oxygen.
Balance the chemical equation for this reaction.[2]
\(…Fe+O_{2}\rightarrow Fe_{3}O_{4}\)
(d) Pure iron can be made by reducing iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3, with hydrogen.
\(Fe_{2}O_{3}+3H_{2}\rightarrow 2Fe+3H_{2}O\)
How does this equation show that iron(III) oxide is reduced?
(e) When iron reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, iron(II) chloride is formed.
(i) Describe a test for iron(II) ions.
(ii) Another chloride of iron has the structure shown.
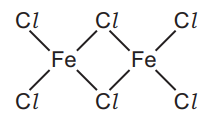
Deduce the molecular formula of this compound showing the number of iron and chlorine atoms.[1]
(f) Some iron nails were placed in bottles under different conditions.
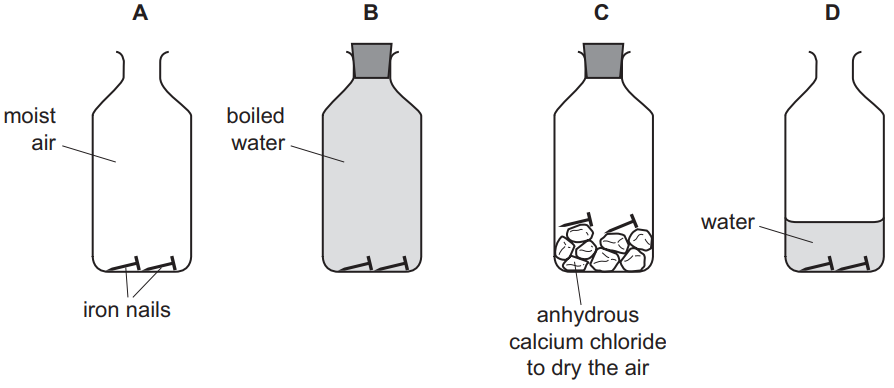
In which bottles will the iron nails not rust?
Give reasons for your answer.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Nickel < iron < chromium < magnesium. The order is determined by the ease of reduction – metals whose oxides are harder to reduce are less reactive.
(b) Three key differences: 1) Iron has higher melting point than potassium. 2) Iron forms colored compounds while potassium compounds are typically white. 3) Iron is magnetic whereas potassium is not.
(c) Balanced equation: \(3Fe + 2O_2 \rightarrow Fe_3O_4\). The coefficients balance the iron and oxygen atoms on both sides.
(d) The equation shows reduction as iron(III) oxide loses oxygen atoms, which are gained by hydrogen to form water.
(e)(i) Test: Add sodium hydroxide solution. Result: Green precipitate forms, indicating iron(II) ions.
(e)(ii) Molecular formula: Fe2Cl6. The diagram shows two iron atoms and six chlorine atoms.
(f) Bottles B (boiled water) and C (calcium chloride) prevent rusting. B lacks oxygen, C lacks water – both essential for rusting.
