This question is about iron and iron compounds.
(a) Name the main ore of iron.
(b) In a blast furnace used for the extraction of iron, carbon reacts with oxygen from the air to form carbon monoxide. Complete the chemical equation for this reaction. $$….. \rm{C}+\ldots \rightarrow2 \mathrm{CO}$$
(c) In the hotter parts of the furnace, carbon reacts with the iron(III) oxide present in the iron ore. $$3 \mathrm{C}+\mathrm{Fe}_2 \mathrm{O}_3 \rightarrow 3 \mathrm{CO}+2 \mathrm{Fe}$$ How does this equation show that carbon is oxidised?
(d) Limestone is added to the blast furnace. The limestone is converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The reaction is endothermic. $$\mathrm{CaCO}_3 \stackrel{\text { heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CaO}+\mathrm{CO}_2$$
(i) What type of chemical reaction is this?
(ii) What type of oxide is calcium oxide? Give a reason for your answer.
(e) Iron is a metal. Give three physical properties that are characteristic of metals.
(f) The structure of a compound of iron is shown.

Deduce the molecular formula of this compound to show the number of iron, carbon and oxygen atoms.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: hematite
Hematite (Fe2O3) is the primary ore of iron, containing about 70% iron by mass.
(b) Ans: 2C + O2 → 2CO
The equation balances with 2 carbon atoms reacting with 1 oxygen molecule (O2) to produce 2 carbon monoxide molecules.
(c) Ans: Carbon gains oxygen (from Fe2O3)
Oxidation is defined as gain of oxygen. Here carbon combines with oxygen from iron oxide to form CO.
(d)(i) Ans: thermal decomposition
The reaction involves breaking down calcium carbonate into simpler substances (CaO and CO2) using heat.
(d)(ii) Ans: basic oxide
Calcium oxide is a basic oxide because it reacts with acids to form salts and water, typical behavior of metal oxides.
(e) Ans: Any three from:
• Good electrical conductor
• Good thermal conductor
• Malleable
• Ductile
• Lustrous/shiny
These are characteristic metallic properties due to the ‘sea of delocalized electrons’ in metallic bonding.
(f) Ans: Fe2C9O9
The structure shows 2 iron atoms, 9 carbon atoms, and 9 oxygen atoms in the molecular unit.
The diagram shows a blast furnace used in the extraction of iron.
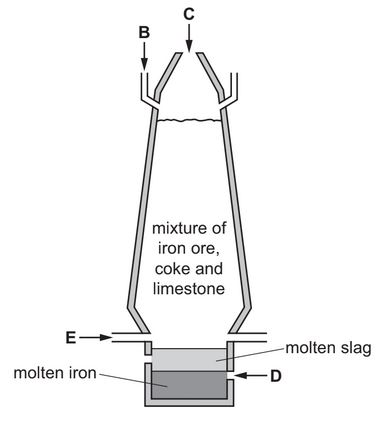
(a) Air is blown into the furnace.
State which letter on the diagram, B, C, D or E, shows where air is blown into the furnace.
(b) (i) Complete the chemical equation for the reduction of iron(III) oxide in the blast furnace.
\(Fe_2O_3 + 3C → ……Fe + ……CO\)
(ii) Explain how this equation shows that iron(III) oxide is reduced.
(c) Calcium carbonate (limestone) is added to the blast furnace.
The calcium carbonate undergoes thermal decomposition.
(i) Complete the word equation for this reaction.
(ii) One of the products of this reaction reacts with impurities in the iron to form slag.
Use the information in the diagram to suggest how you know that molten slag is less dense than molten iron.
(d) (i) Use words from the list to complete these sentences about how steel is made from iron.
acidic basic chlorides methane neutral
nitrogen oxides oxygen sulfates
A gas is blown through the molten iron. The name of this gas is …………………… .
Acidic gases are formed. These acidic gases react with …………………… ……………………
(ii) State one use of mild steel.
(iii) Metals such as chromium are added to iron to make stainless steel.
The symbol for an isotope of chromium is shown.
\(_{24}^{53}Cr\)
Deduce the number of electrons, neutrons and protons in one atom of this isotope of chromium.
(e) Chromium conducts electricity and is shiny.
Give two other physical properties of chromium that are characteristic of all metals.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Ans: E
Air is blown into the furnace at the tuyeres (E), which are located near the bottom to ensure efficient combustion.
(b)(i) Ans: \(Fe_2O_3 + 3C → 2Fe + 3CO\)
The balanced equation shows 2 iron atoms and 3 carbon monoxide molecules are produced per mole of iron(III) oxide.
(b)(ii) Ans: Iron(III) oxide loses oxygen
Reduction involves the loss of oxygen. Here, \(Fe_2O_3\) loses oxygen atoms to form iron (Fe).
(c)(i) Ans: calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate (\(CaCO_3\)) yields calcium oxide (\(CaO\)) and carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)).
(c)(ii) Ans: Slag floats above the iron
In the diagram, slag is seen above molten iron, indicating it is less dense.
(d)(i) Ans: oxygen; basic oxides
Oxygen is blown through molten iron to oxidize impurities, which react with basic oxides (e.g., calcium oxide) to form slag.
(d)(ii) Ans: Car bodies or machinery
Mild steel is ductile and strong, making it ideal for structural applications.
(d)(iii) Ans: Electrons: 24, Neutrons: 29, Protons: 24
For \(_{24}^{53}Cr\): Protons = atomic number (24), neutrons = mass number (53) – protons (24) = 29, and electrons = protons (24).
(e) Ans: Any two metallic properties
• Malleable (can be hammered into sheets)
• Ductile (can be drawn into wires)
• Good conductor of heat
