Which statements about monomers or polymers are correct?
- Monomers are always joined together by addition reactions.
- A polymer can be formed from a single type of monomer.
- A polymer can be formed by joining two different types of monomer.
- Water is always produced when monomer molecules join together.
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 3 and 4
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Let’s analyze each statement:
1. False – Monomers can join by addition (like in polyethene) or condensation reactions (like in nylon formation).
2. True – Many polymers like polyethene are made from a single monomer type (ethene).
3. True – Polymers like nylon are formed from two different monomers.
4. False – Water is only produced in condensation polymerization, not in addition polymerization.
Therefore, the correct statements are 2 and 3, making option C correct.
The structure of part of a polymer is shown.
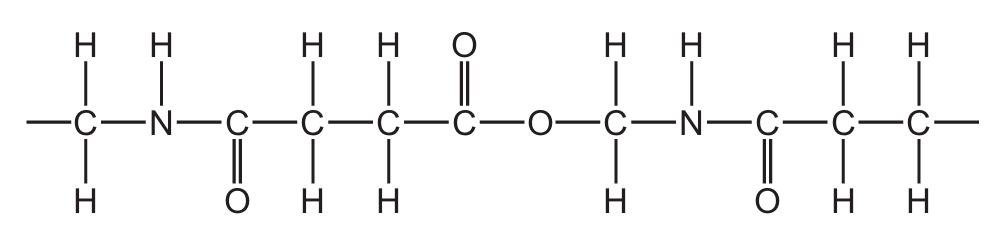
How many amide and ester linkages are included in the structure shown?
| amide linkages | ester linkages | |
|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 0 |
| B | 1 | 1 |
| C | 2 | 1 |
| D | 2 | 2 |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
To solve this, we need to identify the amide (-CONH-) and ester (-COO-) linkages in the polymer structure:
- Amide linkages are formed between the carbonyl carbon (C=O) and nitrogen (N-H) groups. In the given structure, there are two such connections visible in the repeating unit.
- Ester linkages are formed between the carbonyl carbon (C=O) and oxygen (O) groups. There is one clear ester linkage visible in the repeating unit.
The structure shows a repeating pattern with two amide bonds and one ester bond per unit, making option C (2 amide and 1 ester linkages) the correct choice.
Which structure represents part of a protein?
A) 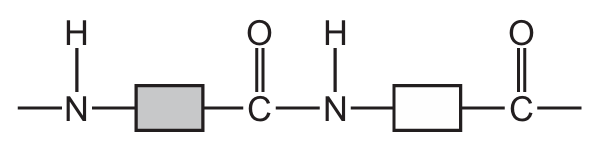
B) 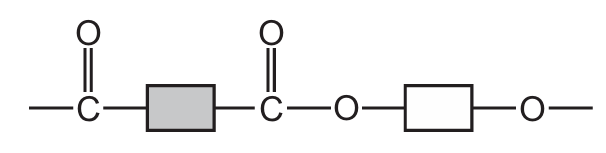
C) 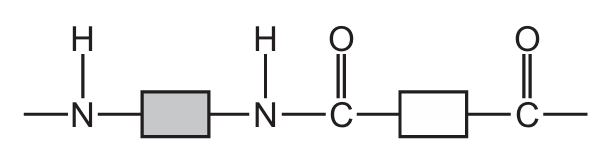
D) 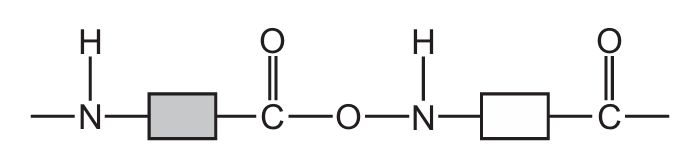
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Proteins are polymers made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (a type of amide bond). The key characteristics to look for are:
- The repeating -NH-CH-CO- backbone structure
- Peptide bonds between amino acids (shown as -CONH-)
- Presence of side chains (R groups) attached to the central carbon
Option A shows this characteristic protein structure with clear peptide bonds between amino acid residues. The other options show different types of polymers (B shows ester linkages typical of polyesters, C shows a mix of bonds, and D shows a more complex structure not typical of simple proteins).
Which diagram represents the structure of a protein?
A 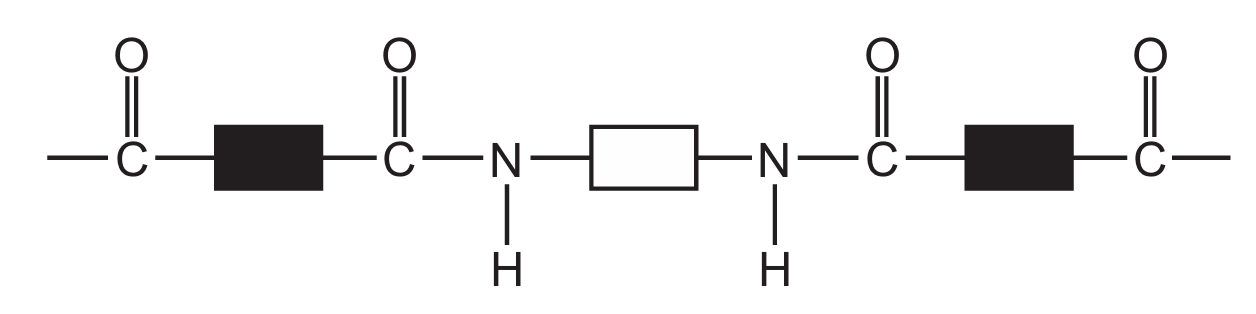
B 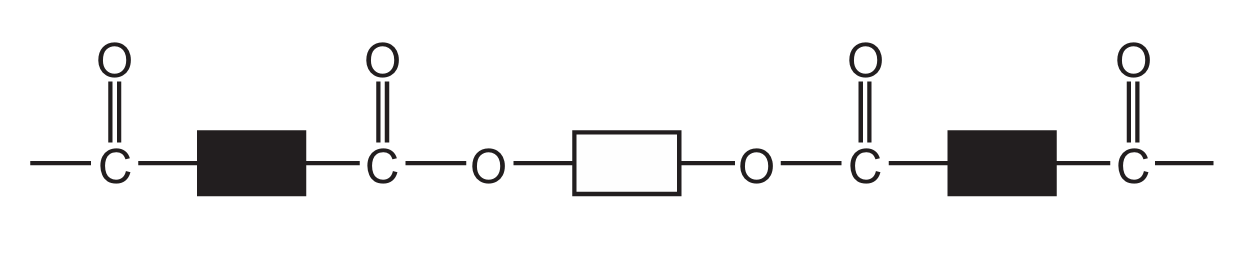
C 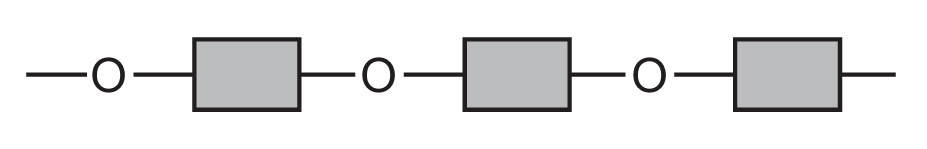
D 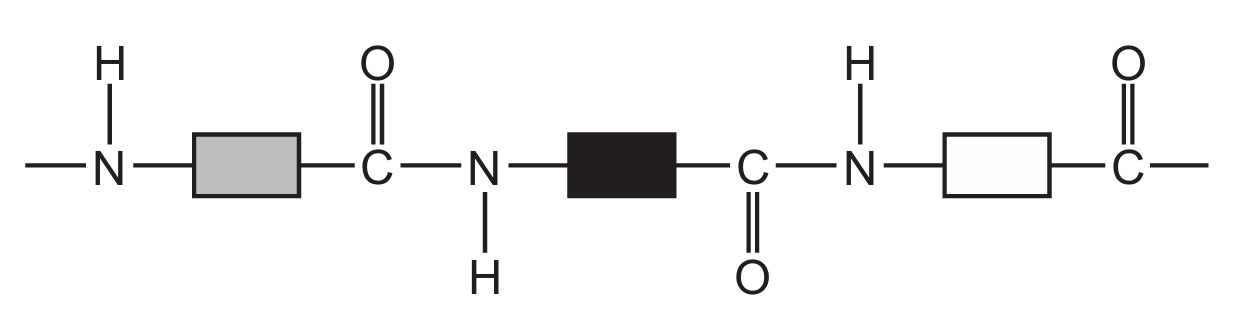
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Proteins have a complex structure with peptide bonds (formed between amino acids) creating long chains that fold into specific 3D shapes. The correct diagram should show:
1. Multiple amino acid units linked together
2. Peptide bonds (C-N bonds between amino acids)
3. A complex three-dimensional structure
Diagram D correctly represents this protein structure, showing the characteristic peptide bonds and complex folding pattern that distinguishes proteins from simpler organic molecules.
