The diagram shows part of an ionic lattice structure.
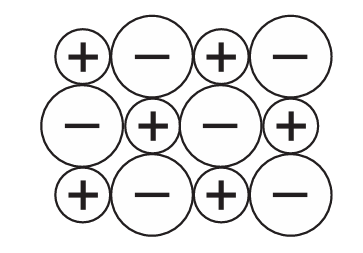
Which compound does the diagram represent?
A) potassium bromide
B) sodium oxide
C) magnesium chloride
D) carbon monoxide
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The question implies the diagram shows a simple 1:1 ionic lattice (one positive ion for each negative ion). Let’s analyze the options:
A) KBr – potassium forms 1+ ions, bromine forms 1- ions → 1:1 ratio
B) Na₂O – sodium forms 1+ ions, oxygen forms 2- ions → 2:1 ratio
C) MgCl₂ – magnesium forms 2+ ions, chlorine forms 1- ions → 1:2 ratio
D) CO – covalent molecular compound, not ionic
Only potassium bromide (KBr) forms a simple 1:1 ionic lattice among the options.
Which pair of elements react to form a compound with a strong attraction between oppositely charged ions?
A) carbon and bromine
B) carbon and nitrogen
C) sodium and oxygen
D) sodium and potassium
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
We need to identify which pair forms an ionic compound with strong electrostatic attraction.
Let’s evaluate each option:
A) C + Br: Forms covalent bonds (both non-metals)
B) C + N: Forms covalent bonds (both non-metals)
C) Na + O: Forms ionic compound Na₂O (metal + non-metal). Sodium donates electrons to oxygen, creating Na⁺ and O²⁻ ions with strong attraction.
D) Na + K: Both are metals and don’t form ionic compounds with each other.
Key points:
– Ionic compounds form between metals and non-metals
– Sodium (Group I) easily loses electrons
– Oxygen (Group VI) readily gains electrons
This makes sodium oxide (Na₂O) a classic ionic compound with strong ionic bonds.
What happens when sodium atoms combine with chlorine atoms to form sodium chloride?
A) Sodium atoms each gain one electron, and chlorine atoms each lose one electron.
B) Sodium atoms each lose one electron, and chlorine atoms each gain one electron.
C) Sodium atoms and chlorine atoms share one electron with each other.
D) Sodium atoms and chlorine atoms share two electrons with each other.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
Sodium (Na) is in Group I and has 1 valence electron, while chlorine (Cl) is in Group VII and needs 1 more electron to complete its outer shell. In ionic bonding:
– Sodium atoms lose their single valence electron to achieve a stable electron configuration (becoming Na⁺).
– Chlorine atoms gain one electron to complete their outer shell (becoming Cl⁻).
The options describing electron sharing (C and D) refer to covalent bonding, which doesn’t occur in NaCl formation.
The table shows some properties of four substances.
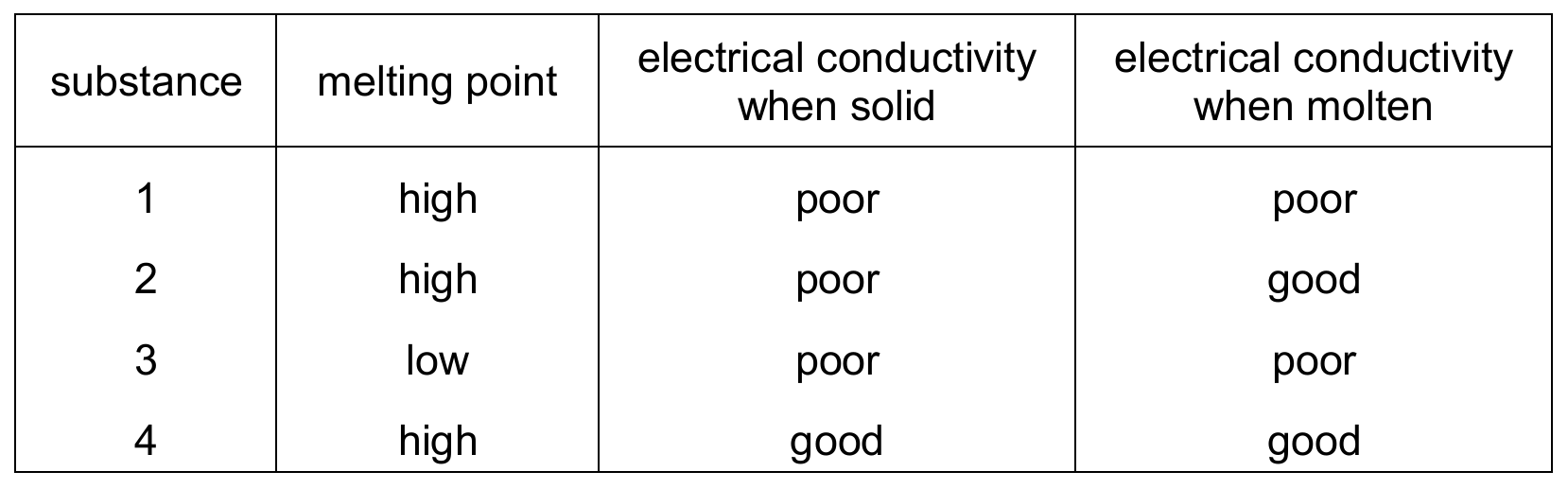
Which substances are ionic?
A) 1, 3 and 4
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Ionic compounds typically have:
1. High melting points (eliminates substance 3)
2. Poor conductivity when solid (ions can’t move)
3. Good conductivity when molten (ions are free to move)
Only substance 2 fits all these criteria. Substance 4 conducts in solid state, suggesting metallic bonding. Substance 1 is likely covalent (poor conductor in both states). Therefore, only substance 2 is ionic.
