The apparatus used for electrolysis is shown.

Which statement is correct?
A) Copper forms at the anode in some electrolysis reactions.
B) Hydrogen forms at the cathode in some electrolysis reactions.
C) Oxygen forms at the cathode in some electrolysis reactions.
D) Sodium forms at the anode in some electrolysis reactions.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: B
During electrolysis, reduction occurs at the cathode where positively charged ions gain electrons. Hydrogen ions (H⁺) are commonly reduced to form hydrogen gas (H₂) at the cathode in many electrolysis reactions, especially in aqueous solutions. This makes option B correct.
Option A is incorrect because copper forms at the cathode, not the anode, in copper electrolysis. Option C is wrong because oxygen forms at the anode, not cathode, in water electrolysis. Option D is incorrect because sodium ions are reduced at the cathode, not oxidized at the anode.
Which statement about the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate is correct?
A) When copper electrodes are used, the solution turns from blue to colorless.
B) When graphite electrodes are used, bubbles of gas are formed at the cathode.
C) When copper electrodes are used, the anode gets smaller.
D) When graphite electrodes are used, the color of the solution does not change.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
In the electrolysis of copper(II) sulfate using copper electrodes, copper from the anode dissolves into the solution as Cu²⁺ ions, causing the anode to get smaller. This makes option C correct.
Option A is incorrect because the blue color (from Cu²⁺ ions) remains as copper is deposited at the cathode and dissolved from the anode in equal amounts. Option B is wrong because with graphite electrodes, hydrogen gas forms at the cathode (not oxygen). Option D is incorrect because with graphite electrodes, the blue color fades as copper is deposited and not replaced.
Aqueous copper(II) sulfate is electrolysed using graphite electrodes.
Which row identifies the product and observations at each electrode during the electrolysis?
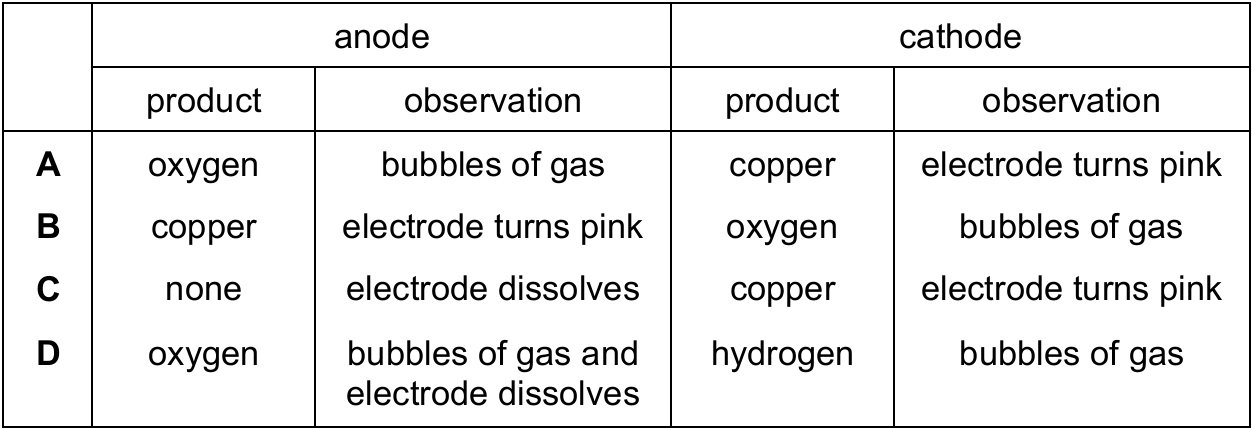
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
In the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate:
At the anode (positive electrode):
- OH– ions are discharged, producing oxygen gas (bubbles observed)
- 4OH– → O2 + 2H2O + 4e–
At the cathode (negative electrode):
- Cu2+ ions are reduced to copper metal, which deposits on the electrode (pink/brown color observed)
- Cu2+ + 2e– → Cu
Graphite electrodes are inert and don’t dissolve. This matches option A.
Molten sodium chloride is electrolysed using inert electrodes.
Which row shows the products formed at the cathode and anode?
| cathode | anode | |
|---|---|---|
| A | chlorine | hydrogen |
| B | chlorine | sodium |
| C | hydrogen | chlorine |
| D | sodium | chlorine |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
In the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride:
At the cathode (negative electrode):
- Na+ ions are reduced to sodium metal: Na+ + e– → Na
At the anode (positive electrode):
- Cl– ions are oxidized to chlorine gas: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
This matches option D. Note that in aqueous solution, hydrogen would form at the cathode instead, but in molten NaCl, sodium metal is produced.
