Give the name of the process that is used:
(a) to produce ammonia from nitrogen
(b) to separate nitrogen from liquid air
(c) to produce bromine from molten lead(II) bromide
(d) to separate an undissolved solid from an aqueous solution
(e) to produce amino acids from proteins
(f) to separate a mixture of amino acids.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) The process is the Haber process, where nitrogen and hydrogen react under high pressure and temperature to form ammonia (\( \text{N}_2 + 3\text{H}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{NH}_3 \)).
(b) Fractional distillation is used to separate nitrogen from liquid air, exploiting differences in boiling points of gases.
(c) Electrolysis decomposes molten lead(II) bromide (\( \text{PbBr}_2 \)) into lead and bromine (\( \text{Br}_2 \)) via redox reactions.
(d) Filtration separates an undissolved solid from a liquid by passing the mixture through a filter medium.
(e) Hydrolysis breaks peptide bonds in proteins using water, converting them into amino acids.
(f) Chromatography separates amino acids based on their differing solubilities and affinities to the stationary/mobile phases.
(a) Copper(II) nitrate decomposes when heated. Two gases, oxygen and nitrogen dioxide, and a solid are made in the reaction.
A sample of copper(II) nitrate was decomposed using the apparatus shown.
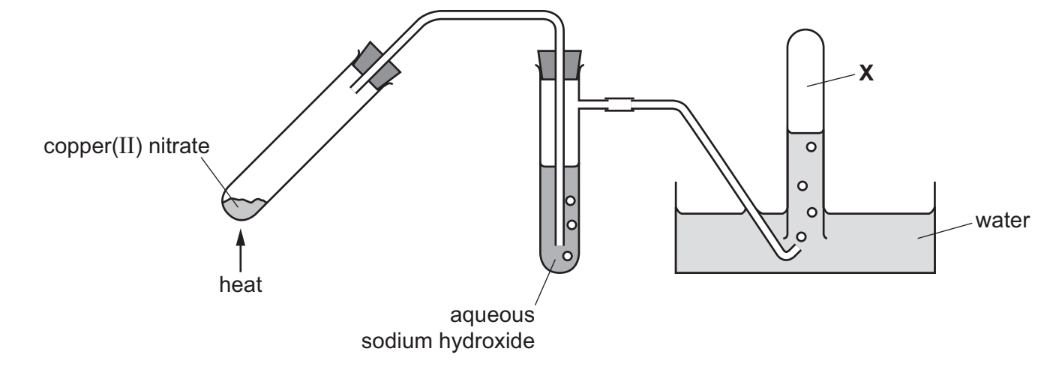
(i) Complete the chemical equation for the reaction.
\(2Cu(NO_3)_{2}\rightarrow O_{2}+……….NO_{2}+………………… \)
(ii) Only oxygen gas is collected at X. Explain why.
(b) Nitrogen dioxide and other oxides of nitrogen are formed in car engines. Explain how nitrogen dioxide is formed in car engines.
(c) A teacher heated 18.8g of copper(II) nitrate.
(i) Calculate the number of moles of copper(II) nitrate present in the 18.8g.
(ii) Calculate the maximum number of moles of oxygen that can be made by heating 18.8g of copper(II) nitrate.
(iii) Calculate the maximum volume of oxygen at room temperature and pressure, in \(cm^{3}\), that can be made by heating 18.8g of copper(II) nitrate.
(d) A sample of copper(II) nitrate was dissolved in water to form an aqueous solution. The aqueous solution was split into three portions. A separate test was done on each portion as shown.
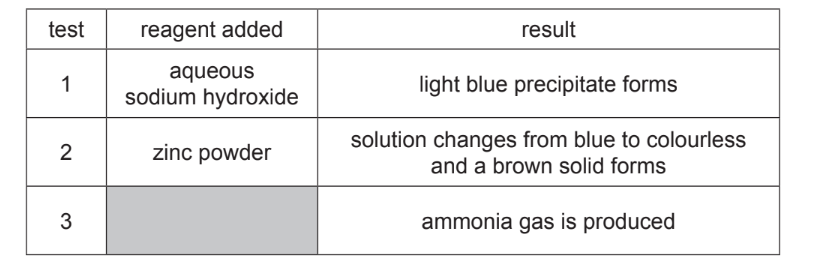
(i) Give the formula of the light blue precipitate formed in test 1.
(ii) Explain the changes seen in test 2.
(iii) Identify the two reagents that must be added to the aqueous copper(II) nitrate in test 3.
(e) Copper(II) nitrate can be made by reacting copper(II) carbonate with nitric acid. One of the products is carbon dioxide.
(i) Write a chemical equation for the reaction of copper(II) carbonate with nitric acid.
(ii) Carbon dioxide is added to the air by living things. Name the chemical process by which living things add carbon dioxide to the air.
(iii) Carbon dioxide is removed from the air by plants. Name the chemical process by which plants remove carbon dioxide from the air.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) The balanced equation is: \(2Cu(NO_3)_2 \rightarrow O_2 + 4NO_2 + 2CuO\).
Explanation: Copper(II) nitrate decomposes into oxygen (\(O_2\)), nitrogen dioxide (\(NO_2\)), and copper(II) oxide (\(CuO\)).
(a)(ii) Only oxygen is collected at X because nitrogen dioxide (\(NO_2\)) is acidic and reacts with sodium hydroxide, leaving oxygen as the only gas collected.
(b) Nitrogen dioxide forms in car engines when nitrogen (\(N_2\)) and oxygen (\(O_2\)) from the air react at high temperatures (due to combustion).
(c)(i) Moles of \(Cu(NO_3)_2 = \frac{18.8}{188} = 0.1 \text{ mol}\).
(c)(ii) Moles of \(O_2 = 0.05 \text{ mol}\) (from stoichiometry: 2 moles of \(Cu(NO_3)_2\) produce 1 mole of \(O_2\)).
(c)(iii) Volume of \(O_2 = 0.05 \times 24000 = 1200 \text{ cm}^3\) (using molar volume at RTP).
(d)(i) The light blue precipitate is \(Cu(OH)_2\).
(d)(ii) Zinc displaces copper from the solution (redox reaction), forming brown copper solid and colourless zinc nitrate.
(d)(iii) The two reagents are sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and aluminium (Al).
(e)(i) The reaction is: \(CuCO_3 + 2HNO_3 \rightarrow Cu(NO_3)_2 + CO_2 + H_2O\).
(e)(ii) Living things add \(CO_2\) to the air through respiration.
(e)(iii) Plants remove \(CO_2\) from the air through photosynthesis.
